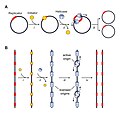
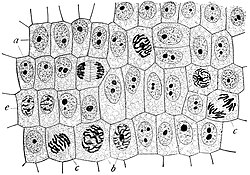
Eukaryotic chromosome structure refers to the levels of packaging from raw DNA molecules to the chromosomal structures seen during metaphase in mitosis...
7 KB (857 words) - 10:18, 3 January 2023
In genetics, eukaryotic chromosome fine structure refers to the structure of sequences for the chromosomes of eukaryotic organisms. Some fine sequences...
8 KB (989 words) - 07:10, 21 February 2025
(June 2015). "Origin, structure and function of millions of chromosomes present in the macronucleus of unicellular eukaryotic ciliate, Oxytricha trifallax:...
101 KB (5,168 words) - 06:20, 2 June 2025
Unicellular organism (redirect from Eukaryotic microorganism)
doi:10.1016/j.mib.2014.10.001. PMC 4359759. PMID 25460806. "Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure | Science Primer". scienceprimer.com. Retrieved 2015-11-22...
34 KB (3,415 words) - 05:54, 2 June 2025
Eukaryotic DNA replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts DNA replication to once per cell cycle. Eukaryotic DNA replication of chromosomal DNA...
121 KB (14,916 words) - 04:06, 3 January 2025
eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes...
64 KB (6,606 words) - 06:59, 2 June 2025
Chromosome condensation refers to the process by which dispersed interphase chromatin is transformed into a set of compact, rod-shaped structures during...
40 KB (4,969 words) - 17:38, 26 May 2025
of non-histone proteins that are essential in the structure and maintenance of eukaryotic chromosomes throughout the cell cycle. These scaffold proteins...
6 KB (708 words) - 19:40, 21 December 2024
Eukaryote (redirect from Eukaryotic cell)
called chromosomes; these are separated into two matching sets by a microtubular spindle during nuclear division, in the distinctively eukaryotic process...
63 KB (6,253 words) - 08:11, 31 May 2025
chromatin structures. The complexity of the eukaryotic genome necessitates a great variety and complexity of gene expression control. Eukaryotic transcription...
49 KB (5,867 words) - 10:43, 1 February 2025
both mitosis and meiosis. Chromosome segregation also occurs in prokaryotes. However, in contrast to eukaryotic chromosome segregation, replication and...
15 KB (1,706 words) - 11:18, 21 May 2024
A circular chromosome is a chromosome in bacteria, archaea, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, in the form of a molecule of circular DNA, unlike the linear...
21 KB (2,745 words) - 08:39, 17 November 2024
Origin of replication (section Eukaryotic)
sequence elements and that controls replication of the entire chromosome, most eukaryotic replicators – with the exception of budding yeast – are not defined...
113 KB (12,563 words) - 03:12, 16 December 2024
Cell division (redirect from Daughter chromosome)
prokaryotes. If the chromosomal number is reduced, eukaryotic cell division is classified as meiosis (reductional division). If the chromosomal number is not...
41 KB (4,763 words) - 18:41, 25 May 2025
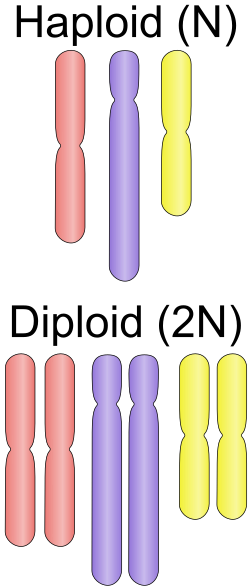
Ploidy (redirect from Chromosome number)
having a single copy of each chromosome – that is, one and only one set of chromosomes. In this case, the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is said to be haploid...
55 KB (6,183 words) - 09:56, 25 May 2025
common pattern. This finding suggested that chromosomal crossing over is a general characteristic of eukaryotic meiosis. There are two popular and overlapping...
36 KB (4,117 words) - 16:15, 23 May 2025
DNA replication (section DNA structure)
Essential and Cell-Cycle-Dependent ORC Dimerization Cycle Regulates Eukaryotic Chromosomal DNA Replication". Cell Reports. 30 (10): 3323–3338.e6. doi:10.1016/j...
60 KB (7,447 words) - 05:04, 1 June 2025
DNA (redirect from Structure of DNA)
translation. Within eukaryotic cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. Before typical cell division, these chromosomes are duplicated...
167 KB (17,915 words) - 22:22, 29 May 2025
Prokaryote (section Structure)
mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colonies...
45 KB (4,312 words) - 22:13, 25 May 2025
Cell nucleus (section Chromosomes)
seed'; pl.: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such...
88 KB (10,011 words) - 10:50, 11 May 2025
Cell biology (section Structure of eukaryotic cells)
chromosomes during cell division. Eukaryotic cells may also be composed of the following molecular components: Chromatin: This makes up chromosomes and...
42 KB (5,255 words) - 08:55, 25 May 2025
Chromomere (category Chromosomes)
idiomere, is one of the serially aligned beads or granules of a eukaryotic chromosome, resulting from local coiling of a continuous DNA thread. Chromomeres...
8 KB (953 words) - 21:45, 10 December 2024
as similar to eukaryotic sex: bacterial transformation, which involves the incorporation of foreign DNA into the bacterial chromosome; bacterial conjugation...
42 KB (5,181 words) - 19:44, 22 May 2025
Tubulin (section Eukaryotic)
and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. It was discovered and named by Hideo Mōri in 1968. Microtubules...
32 KB (3,392 words) - 07:17, 15 April 2025
Nuclear DNA (section Structure)
found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Its structure is a double helix, with two strands wound around each other, a structure first described by Francis...
16 KB (1,699 words) - 23:12, 22 April 2025
Cell (biology) (section Eukaryotic cells)
The eukaryotic DNA is organized in one or more linear molecules, called chromosomes, which are associated with histone proteins. All chromosomal DNA is...
59 KB (6,143 words) - 20:34, 23 May 2025
A protist (/ˈproʊtɪst/ PROH-tist) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural...
216 KB (23,075 words) - 08:14, 31 May 2025
Gene (section Chromosomes)
genomes on a single, large, circular chromosome. Similarly, some eukaryotic organelles contain a remnant circular chromosome with a small number of genes.: 14...
100 KB (11,208 words) - 22:21, 21 April 2025
Meiosis (redirect from Tetrad (chromosomal formation))
of chromosomes. Meiosis is now complete and ends up with four new daughter cells. Meiosis appears to be a fundamental characteristic of eukaryotic organisms...
76 KB (8,981 words) - 04:09, 29 May 2025
along the length of a chromosome are duplicated. In eukaryotic cells (cells that package their DNA within a nucleus), chromosomes consist of very long...
13 KB (1,612 words) - 19:13, 21 May 2025