inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a kind of synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential...
22 KB (2,705 words) - 04:12, 7 February 2025
Postsynaptic potentials are changes in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse. Postsynaptic potentials are graded potentials...
16 KB (1,656 words) - 11:04, 12 July 2025
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary...
9 KB (1,100 words) - 05:46, 19 July 2025
EPSP, or an excitatory postsynaptic potential, and the hyperpolarization is called an IPSP, or an inhibitory postsynaptic potential. The only influences...
19 KB (2,354 words) - 19:18, 21 May 2025
excitatory or inhibitory. Graded potentials that make the membrane potential less negative or more positive, thus making the postsynaptic cell more likely...
6 KB (736 words) - 04:21, 26 July 2025
Chemical synapse (redirect from Postsynaptic)
neuron releasing an inhibitory neurotransmitter, such as GABA, can cause an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in the postsynaptic neuron, bringing...
36 KB (4,277 words) - 17:00, 25 May 2025
occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting...
56 KB (5,974 words) - 00:10, 31 July 2025
circuitry. Its inputs are analogous to excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials at neural dendrites, or activation. Its weights...
31 KB (3,602 words) - 10:03, 29 July 2025
synapse is to produce either an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) or an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP), which generate or repress the expression...
17 KB (2,047 words) - 14:28, 18 July 2025
are two forms of synaptic potential: excitatory and inhibitory. The type of potential produced depends on both the postsynaptic receptor, more specifically...
11 KB (1,541 words) - 09:24, 18 September 2023
reversal potential of the receptor to which the neurotransmitter binds is lower than the threshold potential, an inhibitory postsynaptic potential will occur...
23 KB (2,563 words) - 05:46, 19 July 2025
provoke a new action potential. Their joint efforts can be thwarted, however, by the counteracting inhibitory postsynaptic potentials.[citation needed] Neurotransmission...
149 KB (16,456 words) - 17:05, 9 August 2025
between active and (neighbouring) inactive neurons Inhibitory postsynaptic potential, a synaptic potential that decreases the firing of a neuron Corrosion...
2 KB (271 words) - 19:42, 25 May 2023
the neuron which occurs when an excitatory postsynaptic potential and an inhibitory postsynaptic potential are occurring close to each other on a dendrite...
999 bytes (128 words) - 01:28, 18 September 2022
postsynaptic potentials, or EPSPs, whereas neurotransmitters that act to open K+ or Cl− channels typically produce inhibitory postsynaptic potentials...
66 KB (8,312 words) - 00:08, 28 June 2025
is inhibitory, inhibitory neurotransmitters, normally GABA will be released into the synapse. This neurotransmitter causes an inhibitory postsynaptic potential...
30 KB (3,965 words) - 22:08, 22 April 2025
called inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). They hyperpolarize the membrane and make it harder for a cell to have an action potential. IPSPs are...
11 KB (1,299 words) - 12:29, 2 March 2024
Gelsemine (section Potential medical applications)
mammalian glycine receptor, the activation of which leads to an inhibitory postsynaptic potential in neurons following chloride ion influx, and systemically...
38 KB (3,851 words) - 21:29, 23 July 2025
Neurotransmitter (redirect from Inhibitory neurotransmitter)
McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark (2001), "Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials", Neuroscience. 2nd edition, Sinauer Associates, retrieved...
99 KB (8,910 words) - 17:36, 17 July 2025
potentials. This slow release is detectable and produces micro-inhibitory or micro-excitatory effects on the postsynaptic neuron. An action potential...
23 KB (2,721 words) - 22:21, 10 July 2025
theory Electrical synapse Excitatory postsynaptic potential Homeostatic plasticity Inhibitory postsynaptic potential Long-term potentiation (LTP) Short-term...
53 KB (6,455 words) - 15:04, 9 July 2025
Synaptic plasticity in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. In 1973, Terje Lømo and...
30 KB (3,613 words) - 22:21, 15 July 2025
action potential. Cells can also become hyperpolarized depending on channels and receptors present on the membrane, which can have an inhibitory effect...
11 KB (1,231 words) - 17:35, 16 July 2025
membrane potentials propagated from synaptic inputs to the dendrites or cell body are summed.[citation needed] Both inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs)...
9 KB (1,101 words) - 15:28, 26 May 2025
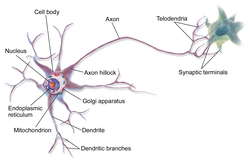
Cellular neuroscience (section Action potential)
are referred to as excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). Alternatively, inhibitory vesicles stimulate postsynaptic receptors such as to allow Cl−...
12 KB (1,398 words) - 19:18, 27 May 2025
transmission is realized mostly by excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs), and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). On the electrophysiological level...
23 KB (2,711 words) - 04:55, 28 April 2025
describe the amplitude and time course of an excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potential (PSP) caused by the spike t j f ′ {\displaystyle t_{j}^{f'}}...
115 KB (14,910 words) - 23:02, 16 July 2025
the postsynaptic neuron. In principle, a single neuron, releasing a single neurotransmitter, can have excitatory effects on some targets, inhibitory effects...
79 KB (9,222 words) - 01:14, 21 July 2025
demonstrated that there was a graded decrease of both EPSP and inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) amplitudes from small to large motoneurons. This seemed...
12 KB (1,575 words) - 15:46, 5 December 2024
Clobazam (section Abuse potential and addiction)
chloride influx at GABAA receptors, creating a hyperpolarizing, inhibitory postsynaptic potential. It was also reported that these effects were inhibited by...
27 KB (2,498 words) - 20:23, 29 May 2025