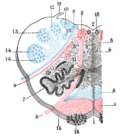
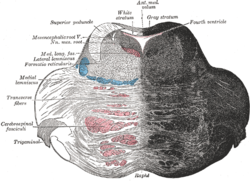
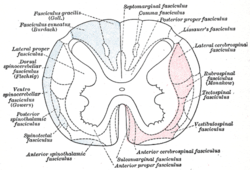
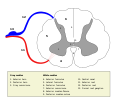
In neuroanatomy, the medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal...
6 KB (639 words) - 05:34, 2 January 2024
on each side are the medullary pyramids. The pyramids contain the fibers of the corticospinal tract (also called the pyramidal tract), or the upper motor...
24 KB (2,813 words) - 20:17, 23 May 2025
and/or the vertebral arteries) leads to death of the ipsilateral medullary pyramid, the medial lemniscus, and the hypoglossal nerve fibers that pass...
5 KB (373 words) - 21:34, 28 July 2024
Olivary body (redirect from Brainstem olive)
prominent oval structures on either side of the medullary pyramids in the medulla, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei. Each olivary...
3 KB (376 words) - 18:36, 9 March 2025
peduncle and into the brainstem and anterior medulla oblongata. Here they form two prominences called the medulla oblongatary pyramids. Below the prominences...
16 KB (1,679 words) - 05:45, 8 December 2024
side of this fissure are raised areas termed the medullary pyramids. The pyramids house the pyramidal tracts–the corticospinal tract, and the corticobulbar...
14 KB (1,626 words) - 20:05, 23 May 2025
the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata (also called "bulbar") region...
5 KB (531 words) - 23:11, 22 February 2025
Reticular formation (redirect from Brainstem reticular formation)
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei in the brainstem that spans from the lower end of the medulla oblongata to the upper end of...
60 KB (5,931 words) - 15:14, 29 January 2025
pons, and to the medullary pyramids, where about 90% of the axons cross to the contralateral side at the decussation of the pyramids. They then descend...
44 KB (5,278 words) - 20:52, 24 May 2025
Human brain (section Brainstem)
along the front of the medulla and cross over (decussate) at the medullary pyramids. These then travel down the spinal cord, with most connecting to interneurons...
170 KB (18,988 words) - 06:42, 25 May 2025
capsule, through the cerebral peduncle, and into the medulla. In the medullary pyramid, the corticospinal tract decussates and becomes the lateral corticospinal...
8 KB (889 words) - 15:27, 25 April 2025
the brainstem. The cranial nerves and cranial nerve nuclei are also located in the brainstem making them susceptible to damage from a brainstem lesion...
13 KB (1,394 words) - 21:29, 17 July 2024
brainstem at the junction of the pons and the medulla, superior to the medullary pyramid, and medial to the facial nerve. It runs upwards and forwards from...
15 KB (1,751 words) - 11:00, 25 May 2025
fourth ventricle, where they enter the brainstem below the inferior colliculi. They are bridged by the superior medullary velum. The superior cerebellar peduncles...
4 KB (463 words) - 14:23, 23 November 2024
the most medial efferent cerebellar nucleus, targeting the pontine and medullary reticular formation as well as the vestibular nuclei. This region deals...
23 KB (2,598 words) - 11:31, 21 February 2025
Cannabinoid receptor 1 (section Brainstem)
found in brainstem medullary nuclei, including the nucleus of the solitary tract and area postrema. CB1 receptor is relatively low in medullary respiratory...
42 KB (4,352 words) - 07:40, 17 May 2025
the medulla, the bottom part of the brainstem, in the anterolateral sulcus which separates the olive and the pyramid. The nerve passes through the subarachnoid...
25 KB (2,618 words) - 17:33, 21 March 2025
superior colliculus brachium pontis brachium restiformis brain brain stem brainstem branchia branchiomeric musculature breast bregma bridging veins broad...
55 KB (4,485 words) - 13:36, 13 February 2025
the spinal cord. Other brainstem sites, such as the parabrachial nucleus, the dorsal raphe, locus coeruleus, and the medullary reticular formation also...
28 KB (3,355 words) - 19:24, 25 May 2025
Lu J, Fuller PM (September 2014). "The GABAergic parafacial zone is a medullary slow wave sleep-promoting center" (PDF). Nat. Neurosci. 17 (9): 1217–1224...
52 KB (6,165 words) - 05:23, 20 May 2025
two major pathways: pyramidal tracts, which originate in the motor cortex, and extrapyramidal tracts, which originate in the brainstem (see schematic). An...
16 KB (1,659 words) - 17:50, 23 May 2025
cortex that reach their targets by traveling through the "pyramids" of the medulla. The pyramidal pathways, such as corticospinal and some corticobulbar...
18 KB (2,107 words) - 13:31, 28 May 2025
PMID 21068766. Lima D, Albino-Teixeira A, Tavares I (Mar 2002). "The caudal medullary ventrolateral reticular formation in nociceptive-cardiovascular integration...
22 KB (2,764 words) - 14:19, 21 October 2024
Tubercle Tuberosity Eminence (anatomy) Process Condyle Epicondyle Fossa Medullary cavity Endosteum Yellow bone marrow Red bone marrow Nutrient foramen Nutrient...
50 KB (4,111 words) - 20:02, 4 April 2025
Spreckelsen, C; Ewert, JP (1993). "Temporal discharge patterns of tectal and medullary neurons chronically recorded during snapping toward prey in toads Bufo...
28 KB (3,706 words) - 21:22, 24 May 2025