Muscular evolution in humans is an overview of the muscular adaptations made by humans from their early ancestors to the modern man. Humans are believed...
12 KB (1,694 words) - 00:26, 16 October 2024
hominid subfamily), indicating that human evolution was not linear but weblike. The study of the origins of humans involves several scientific disciplines...
264 KB (26,349 words) - 18:32, 5 May 2025
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy predominantly affecting boys. The onset of muscle weakness typically begins around...
68 KB (6,827 words) - 20:02, 9 April 2025
In the context of human evolution, vestigiality involves those traits occurring in humans that have lost all or most of their original function through...
49 KB (6,029 words) - 16:34, 31 March 2025
The evolution of human bipedalism, which began in primates approximately four million years ago, or as early as seven million years ago with Sahelanthropus...
21 KB (2,658 words) - 21:55, 22 November 2024
human evolution for many years, but reasons why humans choose their mates are not fully understood. Sexual selection is quite different in non-human animals...
79 KB (9,028 words) - 21:34, 1 May 2025
leg-to-body ratio (long legs) of adult humans as opposed to human infants shows that there is not a holistic trend in humans towards neoteny when compared to...
54 KB (6,751 words) - 10:41, 26 April 2025
Neanderthal (category Fossil taxa described in 1864)
metabolism, brain function, and skeletal and muscular development. Some genes may have helped immigrating modern humans populations acclimatise faster, such as...
134 KB (13,579 words) - 03:48, 15 May 2025
Physiological prematurity (category Human pregnancy)
humans are born in a premature biological state. Although sensory organs and skeletal and muscular systems are largely developed prenatally, human babies...
2 KB (224 words) - 17:03, 26 December 2023
Skeletal muscle (redirect from Muscular branches)
voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types...
119 KB (13,832 words) - 20:30, 15 May 2025
Myostatin (redirect from Bovine muscular hypertrophy)
growth differentiation factor 8, abbreviated GDF8) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSTN gene. Myostatin is a myokine that is produced and...
47 KB (5,232 words) - 20:08, 13 May 2025
researched human penis adaptations are penis size and semen displacement. Evolution has caused sexually selected adaptations to occur in penis size in order...
65 KB (7,445 words) - 01:50, 13 May 2025
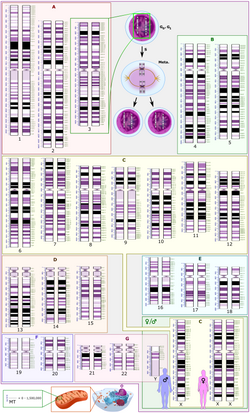
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus...
99 KB (10,102 words) - 13:33, 2 May 2025
Origin of language (redirect from Evolution of language in humans)
compared to anything found among non-humans, must have appeared fairly suddenly during the course of human evolution. Some theories consider language mostly...
172 KB (21,220 words) - 20:10, 15 May 2025
Cro-Magnon (redirect from Early European humans)
Cro-Magnons or European early modern humans (EEMH) were the first early modern humans (Homo sapiens) to settle in Europe, migrating from western Asia,...
159 KB (19,642 words) - 04:52, 4 May 2025
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of heritable diseases that cause degeneration of muscle and progressive...
176 KB (16,445 words) - 19:01, 20 February 2025
very little muscular tissue, and this exists in its root. The shaft and glans have no muscle fibers. Unlike most other primates, male humans lack a penile...
153 KB (16,454 words) - 02:44, 14 May 2025
flying–all the different ways of defying gravity–in imagination and in technology, in humans and in animals. It ranges over many instances of flight including...
3 KB (212 words) - 03:50, 3 April 2025
Gluteus maximus (section In art)
characteristic features of the muscular system in humans, connected as it is with the power of maintaining the trunk in the erect posture. Other primates...
16 KB (1,823 words) - 19:01, 11 January 2025
Hyoid bone (category Human head and neck)
greater horns are rough and close to its lateral border, and facilitates muscular attachment. The largest of muscles that attach to the upper surface of...
18 KB (2,258 words) - 11:44, 25 October 2024
thus human biology was created. The key aspects of human biology are those ways in which humans are substantially different from other mammals. Humans have...
11 KB (1,289 words) - 07:03, 23 November 2024
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (redirect from Peroneal Muscular Atrophy)
Howard Henry Tooth (1856–1925). In their original publication, titled “Concerning a Special Form of Progressive Muscular Atrophy,” Charcot and Marie acknowledged...
40 KB (4,299 words) - 10:12, 23 April 2025
Sex differences in human physiology are distinctions of physiological characteristics associated with either male or female humans. These differences are...
93 KB (10,414 words) - 15:36, 1 May 2025
Stomach (redirect from Anatomy of the human stomach)
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient...
49 KB (5,248 words) - 10:29, 13 May 2025
Gallbladder (category All Wikipedia articles written in American English)
stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure...
35 KB (3,981 words) - 13:20, 8 May 2025
Shoulder girdle (section In humans)
attachment being muscular. The shoulder girdle is the anatomical mechanism that allows for all upper arm and shoulder movement in humans. The shoulder girdle...
15 KB (1,853 words) - 02:09, 11 May 2025
Organ (biology) (section Origin and evolution)
intestines, gallbladder, bladder, and rectum. In the thoracic cavity, the heart is a hollow, muscular organ. Splanchnology is the study of the viscera...
22 KB (2,213 words) - 04:24, 10 May 2025
Vertebrate (redirect from Evolution of vertebrates)
skull of bone or cartilage, large brain divided into 3 or more sections, a muscular heart with multiple chambers; an inner ear with semicircular canals; sense...
48 KB (4,039 words) - 12:55, 14 May 2025
the modeling of virtual 3D human models, with a simple and complete pose system that includes the simulation of muscular movement. The interface is easy...
18 KB (2,174 words) - 16:18, 21 March 2025
Male reproductive system (redirect from Embryonic and prenatal development of the male reproductive system in humans)
seminar Chris tubules in the rete testis from the primary sex cord. Developing on the outside surface of each testis is a Phibro muscular cord called the gubernaculum...
26 KB (2,952 words) - 13:30, 17 April 2025