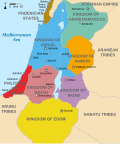
Tell Halaf (Arabic: تل حلف) is an archaeological site in Al-Hasakah in northeastern Syria, a few kilometers from the city of Ras al-Ayn near the Syria–Turkey...
21 KB (2,514 words) - 23:04, 27 March 2025
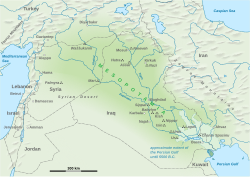
Tell Halaf Tell Brak Tell Sabi Abyad Tell Arpachiyah Tepe Gawra Chagar Bazar The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100...
11 KB (1,056 words) - 04:34, 17 June 2024
Max von Oppenheim (section Excavations at Tell-Halaf)
dynasty. Abandoning his career in diplomacy, he discovered the site of Tell Halaf in 1899 and conducted excavations there in 1911–13 and again in 1927–29...
27 KB (3,262 words) - 06:05, 5 February 2025
settlements began forming in the north, such as Hassuna, Jarmo, Samarra, and Tell Halaf, the north became the important region. The architecture at Hassuna was...
7 KB (738 words) - 12:47, 15 February 2024
Gozan Pedestal inscription (redirect from Tell Halaf inscription)
Pedestal inscription, also known as the Tell Halaf inscription, was an ancient Aramaic description discovered in Tell Halaf in 1933, and published in 1940. The...
2 KB (231 words) - 22:49, 14 September 2024
Bit Bahiani, one of the Post-Hittite states, centered in Guzana (modern Tell Halaf, in northeastern Syria). He ruled sometime in the 10th or 9th century...
5 KB (321 words) - 11:14, 24 May 2024
knowledge, more certainty is emerging. Tell Arpachiyah and Tepe Gawra are the sites where the transition from Halaf to Ubaid were quite abrupt. No transitional...
8 KB (859 words) - 17:28, 27 April 2024
neutron activation analysis of Halaf and Ubaid pottery from Tell Arpachiyah and Tepe Gawra, Iraq, vol. 42, pp. 155–67, 1980 Halaf Bowl from Arpachiyah - British...
6 KB (567 words) - 20:48, 23 January 2025
earliest semi-independent kingdoms in northern Mesopotamia was Bît-Bahiâni (Tell Halaf). Some Georgian linguists see a connection between the Kartvelian languages...
82 KB (9,199 words) - 12:25, 4 June 2025
several mounds, called tells, can be found in close proximity: Tell Fekheriye, Ras al-Ayn, and 2.5 kilometers east of Tell Halaf, site of the Aramean and...
15 KB (1,535 words) - 11:43, 16 May 2025
Prehistory of Mesopotamia (section The Halaf culture)
Museum. Halaf-type pottery seems to have been produced at specialized centers such as Tell Arpachiyah, Tell Brak, Chagar Bazar and Tell Halaf. At Tell Arpachiyah...
121 KB (16,422 words) - 22:45, 3 May 2025
Hall of Hama Region The Hall of Ugarit The Hall of Tell Halaf The Hall of Arslan Tash The Hall of Tell Ahmar The Hall of Ancient Statues and Cuneiform Scripts...
8 KB (796 words) - 09:03, 15 January 2025
(1860-1946) and the French semitologist André Dupont-Sommer (1900-1983) at Tell Halaf the former Aramean city-state of Bit Bahiani which is located on the border...
5 KB (529 words) - 13:13, 22 April 2025
cities Amrit Arpad Bit Bahiani Coba Höyük Gidara Hama Qarqar Ruhizzi Sam'al Tell Aran Tell Halaf Til Barsip Upu Zobah Sources Aramaic inscriptions v t e...
9 KB (839 words) - 00:05, 9 April 2025
same name for the circular houses belonging to the Neolithic culture of Tell Halaf (Iraq, Syria and Turkey), there is no relationship between them. In Greece...
13 KB (1,702 words) - 23:17, 14 February 2025
of the hilani type buildings at the top on page 146 (fig.1 ""Tell Ta'yinat", "Tell Halaf", "Zinjirli" and "Sakje Guezi") in Podium Structures with Lateral...
11 KB (1,268 words) - 14:13, 24 April 2025
Five Mountain System, a Japanese network of Zen temples (Gozan Seidō) Tell Halaf, a Syrian archeological site near the city of Guzana or Gozan This disambiguation...
344 bytes (82 words) - 07:22, 2 February 2020
Ugarit (redirect from Ugrarit (Tell Shamra))
chalcolithic = RS 4 A-B (with some RS 3) Stratum 13 - 4000 - 3400 BC - Halaf chalcolithic = RS 4-C (4 A-B) Stratum 14 - c. 4000 BC - Neolithic with pottery...
51 KB (6,787 words) - 19:51, 4 June 2025
Ancient Aramean six-winged deity, from Tell Halaf (10th century BCE)...
40 KB (4,918 words) - 11:24, 18 May 2025
Anatolia). It as well as other early Neolithic sites, such as Samarra and Tell Halaf were in northern Mesopotamia; later settlements in southern Mesopotamia...
55 KB (6,357 words) - 01:29, 26 May 2025
city-state kingdom (c. 1200 – 808 BC) with its capital at Guzana (modern day Tell Halaf). Bit Baḫiani was ruled by King Kapara. There were at least five kings...
2 KB (122 words) - 17:28, 25 January 2022
at Tell es-Sakan – a site located south of the present-day Gaza City – which began as an Ancient Egyptian fortress built in Canaanite territory. Tell es-Sakan...
88 KB (9,932 words) - 09:12, 25 May 2025
disappeared from visual arts after the Bronze Age, but a relief from Tell Halaf is presumed to be a first millennium BCE example, and according to Gary...
68 KB (9,386 words) - 19:12, 23 May 2025
Cavustepe, Ayanis, Armavir, Erebuni, Bastam) and Neo-Hittite sites (Karkamis, Tell Halaf, Karatepe). Houses are mostly known from Old Babylonian remains at Nippur...
90 KB (10,426 words) - 23:47, 2 June 2025
portal Halaf culture Cities of the ancient Near East Fieldwork campaign: Tell Sabi Abyad (Syria) universiteitleiden.nl Peter M. M. G. Akkermans. “Tell Sabi...
17 KB (1,894 words) - 16:43, 21 January 2025
During excavations in 1979, the famous Tell Fekheriye bilingual inscription was found. The nearby town of Tell Halaf is also a former site of an Aramean...
27 KB (2,498 words) - 20:53, 29 April 2025
Tel Hazor (redirect from Tell Waqqas)
Greek: Άσώρ), and in Arabic Tell Waqqas or Tell Qedah el-Gul (Arabic: تل القدح, romanized: Tell el-Qedah), is an archaeological tell at the site of ancient...
39 KB (4,695 words) - 13:58, 4 June 2025
Urkesh (redirect from Tell Mozan)
(Akkadian: 𒌨𒆧𒆠 UR.KIŠKI, 𒌨𒋙𒀭𒄲𒆠 UR.KEŠ3KI; modern Tell Mozan; Arabic: تل موزان), is a tell, or settlement mound, located in the foothills of the Taurus...
16 KB (1,915 words) - 17:03, 25 December 2024
Dietrich Opitz located it under the largely unexcavated mound of Tell el Fakhariya, near Tell Halaf in Syria. This position was supported by M. Oppenheim and...
12 KB (1,430 words) - 18:47, 4 May 2025
2025-04-11. Albright, W. F. (1956). "The Date of the Kapara Period at Gozan (Tell Halaf)". Anatolian Studies. 6: 75–85. doi:10.2307/3642402. ISSN 0066-1546. JSTOR 3642402...
19 KB (1,345 words) - 06:03, 26 May 2025