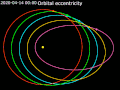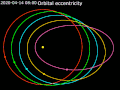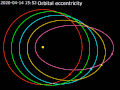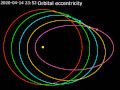
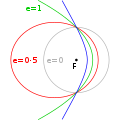
A circular orbit is an orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter; that is, in the shape of a circle. In this case, not only the distance, but also...
8 KB (1,286 words) - 11:32, 5 December 2024
shielding. A medium Earth orbit is sometimes called mid Earth orbit or intermediate circular orbit (ICO). Two medium Earth orbits are particularly significant...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
the same area. For orbits with small eccentricity, the length of the orbit is close to that of a circular one, and the mean orbital speed can be approximated...
11 KB (1,411 words) - 23:02, 25 April 2025
innermost stable circular orbit (often called the ISCO) is the smallest marginally stable circular orbit in which a test particle can stably orbit a massive...
8 KB (1,343 words) - 22:25, 22 April 2025
Higher orbits include medium Earth orbit (MEO), sometimes called intermediate circular orbit (ICO), and further above, geostationary orbit (GEO). Orbits higher...
19 KB (2,117 words) - 21:11, 17 March 2025
A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1...
27 KB (2,870 words) - 10:05, 8 May 2025
orbits can be either open or closed. Circular orbit: An orbit that has an eccentricity of 0 and whose path traces a circle. Elliptic orbit: An orbit with...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is: T = 2 π a 3 G M {\displaystyle T=2\pi {\sqrt {\frac {a^{3}}{GM}}}} where: a is the orbit's semi-major...
17 KB (2,080 words) - 13:46, 24 March 2025
a satellite's orbit from low Earth orbit to geostationary orbit. In the idealized case, the initial and target orbits are both circular and coplanar....
27 KB (3,642 words) - 22:55, 25 April 2025
resultant orbit will be less than that of the original circular orbit. Thrust applied in the direction of the satellite's motion creates an elliptical orbit with...
40 KB (5,763 words) - 07:34, 23 May 2025
elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity...
19 KB (2,744 words) - 16:48, 20 March 2025
value is sometimes given the symbol q. For perfectly circular orbits, there are no points on the orbit that can be described as either the apoapsis or periapsis...
39 KB (5,783 words) - 01:52, 25 April 2025
the orbit, and μ is the standard gravitational parameter of the planet (398600.440 km3/s2 for Earth); as p ≈ a for a circular or almost circular orbit, it...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 19:06, 16 March 2025
can stably orbit at arbitrary distances from a central object. In general relativity, however, there exists an innermost stable circular orbit (often called...
165 KB (18,730 words) - 21:57, 16 May 2025
orbit, the most significant effect is atmospheric drag. Due to atmospheric drag, the lowest altitude above the Earth at which an object in a circular...
14 KB (1,962 words) - 05:37, 19 May 2025
same on every pass. Circular orbit An orbit that has an eccentricity of 0 and whose path traces a circle. Elliptic orbit An orbit with an eccentricity...
17 KB (1,997 words) - 15:59, 21 April 2025
elliptical, not circular (or epicyclic), as had previously been believed, and that the Sun is not located at the center of the orbits, but rather at one...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 06:52, 24 April 2025
body is assumed rigid. Examples of circular motion include: special satellite orbits around the Earth (circular orbits), a ceiling fan's blades rotating...
33 KB (4,233 words) - 03:34, 27 March 2025
Bi-elliptic transfer (category Orbital maneuvers)
r_{1}} is the radius of the initial circular orbit, r 2 {\displaystyle r_{2}} is the radius of the final circular orbit, r b {\displaystyle r_{b}} is the...
15 KB (2,056 words) - 20:50, 7 July 2024
Photon sphere (redirect from Photon orbit)
circular orbit, thus forming a photon circle and hence in aggregation a photon sphere. The circular photon orbit is said to be the last photon orbit....
13 KB (1,819 words) - 14:24, 17 April 2025
In orbital mechanics, a transfer orbit is an intermediate elliptical orbit that is used to move a spacecraft in an orbital maneuver from one circular, or...
1 KB (124 words) - 17:27, 11 October 2023
Mercury (planet) (redirect from Mercury's orbit)
to complete an orbit. The diagram illustrates the effects of the eccentricity, showing Mercury's orbit overlaid with a circular orbit having the same...
156 KB (16,132 words) - 19:06, 22 May 2025
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35,786 km (22,236 mi) in altitude...
49 KB (4,893 words) - 06:24, 20 May 2025
True anomaly (category Orbits)
(segment FP in the figure) of the orbiting body. For circular orbits the true anomaly is undefined, because circular orbits do not have a uniquely determined...
11 KB (1,872 words) - 14:25, 5 May 2025
Samuil Kaplan in 1949 has shown that there is a minimum radius for the circular orbit to be stable in Schwarzschild metric. An exact solution to the Einstein...
65 KB (12,088 words) - 15:40, 25 March 2025
Lagrange point (redirect from Lagrange orbit)
solutions, the collinear and the equilateral, for any three masses, with circular orbits. The five Lagrange points are labeled and defined as follows: The L1...
51 KB (5,817 words) - 13:33, 24 May 2025
phasing burn complete. Dragon and the @inspiration4x crew have reached a circular orbit of 585km – a new Dragon altitude record" (Tweet). Archived from the...
287 KB (12,588 words) - 00:50, 8 May 2025
of the distance (such as gravity), has an orbit that is a conic section (i.e. circular orbit, elliptic orbit, parabolic trajectory, hyperbolic trajectory...
8 KB (1,317 words) - 19:17, 9 December 2024
Parabolic trajectory (redirect from Escape orbit)
closely related to the orbital velocity of a body in a circular orbit of the radius equal to the radial position of orbiting body on the parabolic trajectory:...
7 KB (1,091 words) - 22:08, 14 October 2024
satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that...
11 KB (1,470 words) - 02:33, 8 May 2025