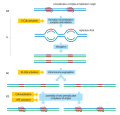
multiple origins of replication on multiple chromosomes simultaneously so that the duration of S phase is not limited by the total amount of DNA. This flexibility...
15 KB (2,036 words) - 10:21, 19 February 2025
DNA replication (redirect from Amplification of DNA)
within the termination region of the chromosome. Within eukaryotes, DNA replication is controlled within the context of the cell cycle. As the cell grows...
61 KB (7,458 words) - 14:41, 28 July 2025
caused by duplication of the gene encoding peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) on chromosome 17. Insertions: A portion of one chromosome has been deleted...
43 KB (4,578 words) - 10:31, 28 July 2025
Potocki–Lupski syndrome (redirect from Duplication 17p11.2 syndrome)
2 or duplication 17p11.2 syndrome, is a contiguous gene syndrome involving the microduplication of band 11.2 on the short arm of human chromosome 17 (17p11...
16 KB (1,550 words) - 06:59, 19 July 2025
accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. This...
113 KB (12,563 words) - 21:58, 15 June 2025
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that carry...
31 KB (3,702 words) - 01:08, 22 July 2025
chromosome is a replicon. The chromosomes of archaea and eukaryotes can have multiple origins of replication, and so their chromosomes may consist of...
6 KB (634 words) - 15:08, 18 July 2025
from the other parent may result in duplication or deletion of genetic material based on segregation of chromosomes during meiosis. This can lead to infertility...
46 KB (4,505 words) - 09:33, 30 July 2025
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination...
81 KB (7,977 words) - 07:45, 3 August 2025
Segmental duplication Tandem exon duplication Virtual karyotype McCarroll SA, Altshuler DM (July 2007). "Copy-number variation and association studies of human...
46 KB (5,325 words) - 21:58, 12 April 2025
Isodicentric 15 (redirect from Isodicentric chromosome 15 syndrome)
also called marker chromosome 15 syndrome, idic(15), partial tetrasomy 15q, or inverted duplication 15 (inv dup 15), is a chromosome abnormality in which...
20 KB (2,370 words) - 00:49, 18 July 2025
Turner syndrome (redirect from Ring chromosome X)
a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy)...
80 KB (9,406 words) - 20:58, 19 July 2025
Homologous chromosomes or homologs are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis. Homologs...
24 KB (2,766 words) - 17:33, 16 July 2025
Trisomy 18 (redirect from Chromosome 18, trisomy)
is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born...
21 KB (1,954 words) - 18:41, 17 July 2025
DNA polymerase epsilon is a member of the DNA polymerase family of enzymes found in eukaryotes. It is composed of the following four subunits: POLE (central...
3 KB (336 words) - 03:59, 2 December 2024
intellectual disability. The cause of M2DS is a duplication of the MECP2 or Methyl CpG binding protein 2 gene located on the X chromosome (Xq28). The MeCP2 protein...
9 KB (849 words) - 17:23, 17 July 2025
1q21.1 duplication syndrome. Similar observations were done for chromosome 16 on 16p11.2 (deletion: autism/duplication: schizophrenia), chromosome 22 on...
21 KB (2,031 words) - 19:58, 29 October 2024
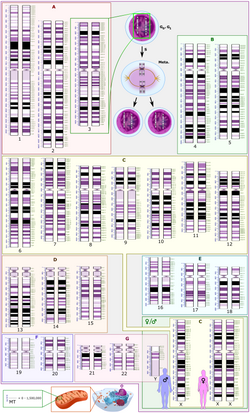
Karyotype (redirect from Chromosome banding)
six pairs of chromosomes, yet V. faba chromosomes are many times larger. These differences probably reflect different amounts of DNA duplication. Differences...
59 KB (7,006 words) - 02:34, 19 July 2025
Xp11.2 duplication is a genomic variation marked by the duplication of an X chromosome region on the short arm p at position 11.2, defined by standard...
27 KB (3,280 words) - 07:54, 19 July 2025
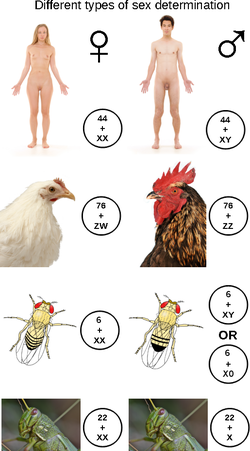
Sex-determination system (redirect from Evolution of sex-determination systems)
animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual differentiation...
78 KB (9,020 words) - 06:26, 15 July 2025
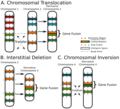
a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome becomes inverted within its original position. An inversion occurs when a chromosome undergoes...
18 KB (1,977 words) - 04:32, 1 August 2025
Diprosopus (redirect from Craniofacial duplication)
[neuter], "face", "person"; with Latin ending), also known as craniofacial duplication (cranio- from Greek κρανίον, "skull", the other parts Latin), is an extremely...
22 KB (2,466 words) - 18:54, 24 May 2025
Chromosome 15 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 15 spans about 99.7 million...
34 KB (3,031 words) - 16:54, 16 July 2025
Gene family (section Duplication)
families which duplicate to form superfamilies spanning multiple chromosomes. Whole genome duplication doubles the number of copies of every gene and...
16 KB (2,025 words) - 21:21, 18 November 2024
chromosomes are duplicated or deleted. More specifically, CIN refers to the increase in rate of addition or loss of entire chromosomes or sections of...
34 KB (4,006 words) - 10:27, 23 July 2025
Down syndrome (redirect from History of Down syndrome)
trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with developmental delays...
151 KB (14,999 words) - 15:24, 30 July 2025
Meiosis (redirect from Tetrad (chromosomal formation))
copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed...
77 KB (9,027 words) - 13:27, 27 July 2025
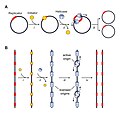
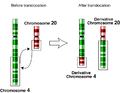
Fusion gene (category Modification of genetic information)
a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia...
17 KB (1,920 words) - 16:29, 19 July 2025
POLE (gene) (category Genes on human chromosome 12)
C (Aug 1994). "Localization of the gene for DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE) to human chromosome 12q24.3 and rat chromosome 12 by somatic cell hybrid panels...
9 KB (1,103 words) - 06:58, 19 July 2025
Cell division (redirect from Daughter chromosome)
part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell...
41 KB (4,776 words) - 23:11, 21 July 2025