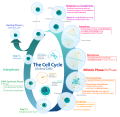
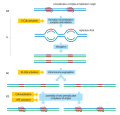
G2-M DNA damage checkpoint is an important cell cycle checkpoint in eukaryotic organisms that ensures that cells don't initiate mitosis until damaged...
18 KB (2,233 words) - 13:06, 29 October 2024
the G2/M checkpoint transition. Similar to S Phase, G2 experiences a DNA damage checkpoint. The cell is once more examined for sites of DNA damage or incomplete...
34 KB (4,587 words) - 15:21, 9 December 2024
Restriction point (redirect from G1 checkpoint)
cell cycle checkpoints, the other two being the G2-M DNA damage checkpoint and the spindle checkpoint. Originally, Howard Martin Temin showed that chicken...
22 KB (2,746 words) - 16:27, 12 April 2025
vulnerable to DNA damage than any other part of the cell cycle. G2 checkpoint checks for damaged DNA and DNA replication completeness. Damage to DNA that occurs...
81 KB (10,126 words) - 14:39, 24 June 2025
the damage before continuing to divide. DNA damage checkpoints occur at the G1/S and G2/M boundaries. An intra-S checkpoint also exists. Checkpoint activation...
132 KB (16,142 words) - 16:06, 11 June 2025
G2-M DNA damage checkpoint M spindle checkpoint, prevents anaphase onset until all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle Immune checkpoint...
3 KB (391 words) - 22:23, 29 September 2024
G2. In particular, the G2 checkpoint arrests cells in G2 in response to DNA damage through inhibitory regulation of CDK1. During mitotic S phase, DNA...
22 KB (2,818 words) - 07:39, 3 June 2024
Artemis (protein) (section Repair of DNA breaks)
phosphorylation target of ATM and ATR and is involved in the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint response". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (20): 9207–20. doi:10.1128/MCB...
15 KB (1,937 words) - 16:28, 9 December 2024
CHEK2 (redirect from CHK2 checkpoint homolog)
CHEK2 (Checkpoint kinase 2) is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the protein CHK2, a serine-threonine kinase. CHK2 is involved in DNA repair, cell...
28 KB (2,797 words) - 17:32, 21 June 2025
single-stranded DNA tracts is important in initiating the checkpoint pathways downstream of replication damage. Once single-stranded DNA becomes sufficiently...
121 KB (14,916 words) - 04:06, 3 January 2025
purpose for this checkpoint is to check for appropriate cell size and any DNA damage . The second check point is in the G2 phase, this checkpoint also checks...
41 KB (4,767 words) - 06:08, 15 June 2025
Cell cycle (redirect from M phase)
checkpoints to ensure that damaged or incomplete DNA is not passed on to daughter cells. Three main checkpoints exist: the G1/S checkpoint, the G2/M checkpoint...
78 KB (9,148 words) - 19:21, 26 May 2025
S phase (section DNA damage checkpoints)
(Synthesis phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is...
15 KB (1,681 words) - 15:45, 29 October 2023
Induced cell cycle arrest (section DNA damage repair)
CDC2 unable to arrest in G2 in response to DNA damage, indicating the gene product is involved in G2 arrest. M: A mutant screen of budding yeasts with mitotic...
27 KB (3,291 words) - 03:25, 21 April 2025
needed to replicate DNA are made. After G1, the cells enter S phase during which the DNA is replicated. After S, the cell will enter G2 where the proteins...
13 KB (2,128 words) - 19:25, 12 April 2025
CHEK1 (section G2/M transition)
maintenance of DNA replication fork stability. In response to DNA damage, Chk1 is an important signal transducer for G2/M checkpoint activation. Activation...
30 KB (3,340 words) - 01:47, 26 March 2024
CUL4A (section DNA damage and repair)
suppression, DNA replication and embryonic development, HIV-1 "hijacks" the ubiquitin ligase complex to induce arrest of the cell cycle in G2 phase. The...
36 KB (4,418 words) - 04:39, 25 December 2024
MDC1 (section Role in DNA damage response)
regulator of the Intra-S phase and the G2/M cell cycle checkpoints and recruits repair proteins to the site of DNA damage. It is involved in determining cell...
24 KB (3,123 words) - 21:25, 27 March 2024
relicensing of replication origins and to activate cell cycle and DNA damage checkpoints. DNA rereplication must be strictly regulated to ensure that genomic...
22 KB (2,860 words) - 19:01, 24 March 2024
alternative RFC (replacing RFC1 with Rad24) plays a role in the DNA damage checkpoint. The presence of an alternative RFC in the cohesion pathway can...
18 KB (2,292 words) - 09:34, 3 December 2023
different DNA damage checkpoints, which inhibit the next or maintain the current cell cycle step. There are two main checkpoints, the G1/S and the G2/M, during...
50 KB (5,695 words) - 13:00, 26 February 2025
two G0/G1 cells has the same total content of DNA and thus the same fluorescence intensity as a single G2/M cell. Unless recognized as such the G0/G1 doublets...
13 KB (1,531 words) - 03:37, 29 December 2023
TP53BP1 (section DNA repair)
Carpenter PB, Bonner WM, Chen J, Nussenzweig A (Dec 2002). "DNA damage-induced G2-M checkpoint activation by histone H2AX and 53BP1". Nature Cell Biology...
15 KB (1,857 words) - 09:36, 2 March 2025
the cell grows, and the S phase, during which DNA is replicated. It is governed by cell cycle checkpoints to ensure cell cycle integrity and the subsequent...
17 KB (2,136 words) - 14:28, 17 December 2024
include the G1 and G2 phases, DNA replication or S phase, and the actual process of cell division, mitosis or M phase. During the M phase, the chromosomes...
50 KB (6,678 words) - 21:54, 13 July 2024
H2AFX (category DNA repair)
Carpenter PB, Bonner WM, Chen J, Nussenzweig A (Dec 2002). "DNA damage-induced G2-M checkpoint activation by histone H2AX and 53BP1". Nature Cell Biology...
22 KB (2,783 words) - 00:32, 30 May 2025
leads to the DNA damage checkpoint activation. The pathway of choice in DNA repair is highly regulated to guarantee that cells in the S/G2 and G1 phase...
18 KB (2,277 words) - 13:23, 26 November 2023
G1 phase (section The G1/S checkpoint)
are three checkpoints in the cell cycle: the G1/S Checkpoint or the Start checkpoint in yeast; the G2/M checkpoint; and the spindle checkpoint. During G1...
10 KB (1,235 words) - 04:21, 13 April 2025
mechanisms of meiotic prophase I arrest and resumption and the mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint: CDC14B-based activation of APC-CDH1 in arrest and CDC25B-based...
76 KB (8,983 words) - 17:20, 9 June 2025
Prophase (section Cell checkpoints)
material occurs properly, there are cellular checkpoints in place. The meiotic checkpoint network is a DNA damage response system that controls double strand...
19 KB (2,105 words) - 19:09, 1 April 2025