The Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) was one of the largest particle accelerators ever constructed. It was built at CERN, a multi-national centre...
14 KB (1,767 words) - 09:24, 7 June 2025
The Circular Electron Positron Collider (CEPC) is a proposed Chinese electron positron collider for experimenting on the Higgs boson. It would be the world's...
5 KB (598 words) - 15:32, 24 May 2025
Electron–positron annihilation occurs when an electron (e− ) and a positron (e+ , the electron's antiparticle) collide. At low energies, the result of...
7 KB (825 words) - 12:36, 12 June 2025
the antiparticle (antimatter counterpart) of the electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at...
35 KB (3,839 words) - 06:25, 2 June 2025
designs for proposed linear electron/positron colliders such as the International Linear Collider and the Compact Linear Collider. The study explores the...
84 KB (5,758 words) - 09:10, 30 May 2025
The Beijing Electron–Positron Collider II (BEPC II) is a Chinese electron–positron collider, a type of particle accelerator, located in Shijingshan District...
6 KB (574 words) - 19:23, 1 July 2025
the LEP program. As its name implies, the Large Electron–Positron Collider collided electrons with positrons. The three most important ways in which such...
56 KB (6,324 words) - 10:27, 17 November 2024
CERN (section Large Hadron Collider)
collider (the SppS collider), and for accelerating high energy electrons and positrons which were injected into the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP)...
120 KB (10,760 words) - 21:01, 21 July 2025
collision when compared to striking a static target with an electron. The Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) at CERN, which was operational from 1989 to 2000...
155 KB (15,851 words) - 08:43, 12 July 2025
Circular Electron Positron Collider Compact Linear Collider Future Circular Collider International Linear Collider Very Large Hadron Collider "The Large Hadron...
110 KB (10,977 words) - 20:31, 20 July 2025
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (redirect from Stanford Linear Collider)
collected by the SLAC Large Detector, which came online in 1991. Although largely overshadowed by the Large Electron–Positron Collider at CERN, which began...
33 KB (2,861 words) - 20:08, 18 July 2025
colliders Fixed-target experiment Large Electron–Positron Collider Large Hadron Collider Very Large Hadron Collider Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider International...
13 KB (1,343 words) - 02:59, 17 December 2024
Look up LEP in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. LEP is the Large Electron–Positron Collider, a particle accelerator. LEP or Lep may also refer to: Laser...
1 KB (184 words) - 21:34, 21 April 2024
pre-existing engineering infrastructure and 27 km long cavern of the Large Electron–Positron Collider, and its use of a different, innovative magnet design to bend...
32 KB (3,432 words) - 19:08, 18 July 2025
VEPP in Russia, SLAC in the US, and the Large Electron–Positron Collider at CERN. Some of these lepton colliders are still running. Hadrons are compound...
36 KB (3,964 words) - 09:09, 30 May 2025
LEP Pre-Injector (redirect from Electron Positron Accumulator)
initial source that provided electrons and positrons to CERN's accelerator complex for the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) from 1989 until 2000....
10 KB (1,230 words) - 08:53, 30 May 2025
ISABELLE (section Colliding beam accelerators)
first high energy hadron collider. The SPEAR collider at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, a 3+3 GeV electron-positron system, was completed in...
8 KB (880 words) - 16:42, 3 May 2022
Identification) was one of the four main detectors of the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) at CERN, one of the largest particle accelerators ever...
19 KB (2,030 words) - 09:49, 30 June 2025
of the LHC surpassed existing experimental limits from the Large Electron–Positron Collider and Tevatron and partially excluded the aforementioned expected...
68 KB (7,569 words) - 13:49, 12 July 2025
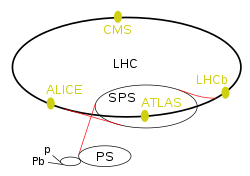
This is a list of experiments at CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The LHC is the most energetic particle collider in the world, and is used to test the...
13 KB (614 words) - 15:32, 8 April 2025
heavy particles—hadron colliders such as the LHC for protons or, alternatively, for lead nuclei. An electron–positron collider of the same size would...
22 KB (2,492 words) - 06:56, 17 June 2025
most energetic collider of heavy ions after it began colliding lead ions. Earlier facilities include the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP), which was...
42 KB (4,288 words) - 08:00, 11 July 2025
and Hadron Identification), one of the four detectors of the Large Electron-Positron Collider at CERN Delphi method, a forecasting technique which relies...
2 KB (266 words) - 00:15, 17 June 2025
CTF3 (redirect from CERN Linear Electron Accelerator for Research)
used to inject electrons and positrons into the CERN accelerator complex, to be ultimately delivered to Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP). Following...
10 KB (1,059 words) - 11:31, 3 May 2025
Neutrino (section Collider neutrinos)
from the Large Electron–Positron Collider. In the 1960s, the now-famous Homestake experiment made the first measurement of the flux of electron neutrinos...
146 KB (14,449 words) - 23:21, 21 July 2025
largest experiments using were three of the experiments at the Large Electron-Positron collider, including ALEPH, L3 and OPAL. It was also a key tool in the...
4 KB (429 words) - 16:16, 16 July 2025
extensive search for the Higgs boson was conducted at the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) at CERN in the 1990s. At the end of its service in 2000...
247 KB (27,027 words) - 20:07, 25 July 2025
List of accelerators in particle physics (redirect from List of particle colliders)
Undulator Radiation Collider: An Energy Efficient Design for a s = 15 GeV {\displaystyle {\sqrt {s}}=15~{\text{GeV}}} Collider". arXiv:1704.04469 [physics...
33 KB (657 words) - 10:46, 22 June 2025
decay widths, particularly at the Stanford Linear Collider (SLC) and Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) experiments.: 241–243 : 138 The decay rate...
42 KB (4,301 words) - 17:12, 25 May 2025
1.6×10−19 J/eV = 2.7×10−14 J "electron mass energy equivalent". NIST. Retrieved 4 November 2011. "CODATA Value: electron mass energy equivalent in MeV"...
141 KB (9,784 words) - 08:05, 23 July 2025