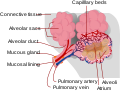
to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer to fixation via perfusion, used in histological studies. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which...
12 KB (1,408 words) - 22:40, 12 April 2025
Perfusionist (redirect from Certification in Clinical Perfusion)
perfusiologist, and occasionally a cardiopulmonary bypass doctor or clinical perfusion scientist, is a healthcare professional who operates the cardiopulmonary...
17 KB (1,755 words) - 06:29, 25 April 2025
Perfusion MRI or perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) is perfusion scanning by the use of a particular MRI sequence[which?]. The acquired data are then post-processed...
11 KB (1,260 words) - 07:59, 6 May 2024
physiology, the ventilation/perfusion ratio (V/Q ratio) is a ratio used to assess the efficiency and adequacy of the ventilation-perfusion coupling and thus the...
9 KB (1,181 words) - 18:02, 25 May 2025
Myocardial perfusion imaging or scanning (also referred to as MPI or MPS) is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle...
18 KB (1,985 words) - 13:39, 23 April 2025
respiratory system, ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) mismatch refers to the pathological discrepancy between ventilation (V) and perfusion (Q) resulting in an abnormal...
7 KB (905 words) - 06:06, 25 May 2025
A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy...
13 KB (1,215 words) - 09:48, 12 October 2024
Twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence, also called TRAP sequence, TRAPS, or acardiac twinning, is a rare complication of monochorionic twin pregnancies...
8 KB (918 words) - 19:10, 26 January 2025
Perfusion CT or CT Perfusion is a type of perfusion scanning using computed tomography. It is helpful in the evaluation of the vascularity of tissue in...
3 KB (247 words) - 03:58, 28 May 2025
Limb perfusion is a medical technique that is used to deliver drugs locally directly to a site of interest. It is commonly used in human medicine for...
11 KB (1,421 words) - 02:22, 27 May 2025
Shock (circulatory) (redirect from Decreased peripheral perfusion)
stimulation and acidosis[citation needed] Hypothermia due to decreased perfusion and evaporation of sweat[citation needed] Thirst and dry mouth, due to...
51 KB (5,486 words) - 13:03, 26 May 2025
Parasitic twin (redirect from Twin-reversed arterial perfusion)
collectively referred to as heteropagus twins. The twin reversed arterial perfusion, or TRAP sequence, results in an 'acardiac twin', a parasitic twin that...
8 KB (749 words) - 07:57, 4 April 2025
Retrograde perfusion (retroperfusion) is an artificial method of providing blood supply to an organ by delivering oxygenated blood through the veins....
1 KB (161 words) - 07:17, 3 October 2024
Pulse oximetry (redirect from Perfusion index)
between the pulsatile and baseline absorbance ("perfusion index") can be used to evaluate perfusion. SpO 2 = HbO 2 HbO 2 + Hb {\displaystyle {\ce {SpO2}}={\frac...
59 KB (6,982 words) - 22:00, 29 May 2025
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue. The practice of perfusion scanning is the process...
17 KB (2,121 words) - 07:59, 6 May 2024
Ventilation–perfusion coupling is the relationship between ventilation and perfusion in the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Ventilation is the...
22 KB (2,491 words) - 13:44, 25 December 2024
Fixation (histology) (section Perfusion)
tissue. Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the blood vessels or natural channels of an organ or organism. In tissue fixation via perfusion, the fixative...
19 KB (2,387 words) - 06:19, 26 November 2023
Machine perfusion (MP) is an artificial perfusion technique often used for organ preservation to help facilitate organ transplantation. MP works by continuously...
72 KB (9,315 words) - 08:19, 17 October 2024
Cerebral perfusion pressure, or CPP, is the net pressure gradient causing cerebral blood flow to the brain (brain perfusion). It must be maintained within...
6 KB (742 words) - 07:34, 15 May 2024
Ex vivo (section Organ perfusion)
post-mortem biochemical changes that accumulate over time. The earliest perfusion studies were conducted in the mid-19th century, and subsequent advances...
53 KB (5,582 words) - 09:16, 22 May 2025
Push–pull perfusion is an in vivo sampling method most commonly used for measuring neurotransmitters in the brain. Developed by J.H. Gaddum in 1960, this...
3 KB (362 words) - 20:49, 27 May 2025
reduced capacity of the blood to carry oxygen, compromised general or local perfusion, or inability of the affected tissues to extract oxygen from, or metabolically...
108 KB (11,681 words) - 04:10, 3 June 2025
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging perfusion (cardiac MRI perfusion, CMRI perfusion), also known as stress CMR perfusion, is a clinical magnetic resonance...
11 KB (1,412 words) - 06:00, 8 September 2024
Cardiopulmonary bypass (redirect from Artificial perfusion)
state in which the body can be maintained for up to 45 minutes without perfusion (blood flow). If blood flow is stopped at normal body temperature, permanent...
34 KB (4,057 words) - 04:58, 2 May 2025
Minusheet perfusion culture system is used for advanced cell culture experiments in combination with adherent cells and to generate specialized tissues...
20 KB (2,563 words) - 09:58, 29 May 2025
Ischemic hepatitis (redirect from Liver perfusion)
insufficient oxygen delivery) to the liver. The decreased blood flow (perfusion) to the liver is usually due to shock or low blood pressure. However,...
9 KB (743 words) - 15:28, 16 March 2025
Artificial insemination (redirect from Fallopian sperm perfusion)
moderate endometriosis. In non-tubal sub fertility, fallopian tube sperm perfusion may be the preferred technique over intrauterine insemination. Intratubal...
79 KB (9,596 words) - 03:41, 2 June 2025
Ex vivo lung perfusion (abbreviated EVLP) is a form of machine perfusion aimed at sustaining the active aerobic cellular metabolism of donor lungs outside...
33 KB (3,893 words) - 05:29, 3 May 2025
Physiology of decompression (section Perfusion)
pressure over time. Once dissolved, distribution of the dissolved gas is by perfusion, where the solvent (blood) is circulated around the diver's body, and...
114 KB (13,601 words) - 18:46, 18 April 2025