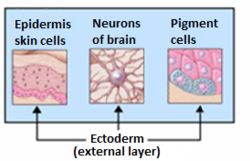
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a structure that forms from the ectodermal cells at the distal end of each limb bud and acts as a major signaling...
25 KB (3,322 words) - 01:37, 27 May 2025
between specialized ectodermal cells and the underlying mesoderm. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions between the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) and the underlying...
21 KB (2,617 words) - 01:17, 6 July 2024
anemia and TAR syndrome.Other possible causes are an injury to the apical ectodermal ridge during upper limb development, intrauterine compression, or maternal...
11 KB (1,457 words) - 07:36, 25 May 2025
be a result of a wedge-shaped defect of the apical ectoderm of the limb bud (AER: apical ectodermal ridge). Polydactyly, syndactyly and cleft hand can...
29 KB (3,031 words) - 15:31, 26 May 2025
and positive feedback retention of two signaling regions: the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) and the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) with the mesenchymal...
24 KB (2,943 words) - 19:33, 27 May 2025
different genes, signals, and a unique region of ectoderm called the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). Research by Saunders and Gasseling in 1948 identified the...
15 KB (2,075 words) - 12:02, 28 December 2024
formation of an organizer at the end of the limb bud, called the apical ectodermal ridge (AER), which guides further development and controls cell death...
36 KB (4,234 words) - 18:27, 25 May 2025
been made using chicken embryos, such as the discovery of the apical ectodermal ridge and the zone of polarizing activity. The chicken was the first...
69 KB (6,519 words) - 02:36, 11 June 2025
ectoderm to form an important organizing structure called the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). The AER reciprocatively secretes FGF8 and FGF4 which maintains...
6 KB (674 words) - 07:16, 25 May 2025
Poland syndrome. Abnormality of an embryonic structure called the apical ectodermal ridge, which helps direct early limb development, may also be involved...
25 KB (2,639 words) - 06:14, 19 June 2025
parietal layer of lateral plate mesoderm. Ectodermal cells at the distal end of the buds form the apical ectodermal ridge, which creates an area of rapidly proliferating...
43 KB (5,261 words) - 01:14, 11 April 2025
distal end, the differentiation of skeletal elements occurs in an apical ectodermal ridge (AER) which expands in rays. A Zone of Polarizing Activity (ZPA)...
8 KB (1,002 words) - 01:04, 31 May 2025
endoplasmic reticulum, a cell organelle Albumin Excretion Rate Apical ectodermal ridge, critical component of vertebrate limb development Administrative...
2 KB (334 words) - 07:03, 20 January 2025
morphogen called fibroblast growth factors must be secreted from the apical ectodermal ridge. Sonic hedgehog has also been shown to act as an axonal guidance...
63 KB (7,452 words) - 18:46, 28 May 2025
progress zone is a layer of mesodermal cells immediately beneath the apical ectodermal ridge in the developing limb bud. The fate of the mesodermal cells is...
2 KB (208 words) - 08:53, 25 April 2023
develop. Saunders researched the vertebrate limb and studied the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). This research was critical in recognizing growth factors...
25 KB (3,334 words) - 18:08, 22 May 2025
involves many signaling molecules such as FGF, BMP, SHH and WNT. The apical ectodermal ridge is a structure found at the distal most tip which becomes a key...
11 KB (1,320 words) - 23:52, 2 December 2024
eventually becomes an apical ectodermal cap (AEC) that forms on the tip of the stump. This is similar to the embryonic apical ectodermal ridge, which forms during...
16 KB (1,692 words) - 07:51, 20 May 2024
early skeletogenesis, where nerves grow into the limb bud and the apical ectodermal ridge (AER), a structure that ensures proper limb development, appears...
84 KB (9,890 words) - 00:37, 3 June 2025
In 1969, a scientist named John Saunders established that the apical ectodermal ridge (AER)--a transparent rim along limb buds—plays an important role...
18 KB (1,857 words) - 00:01, 6 January 2025
lacrimal gland, tarsal glands, and the conjunctiva of the eye The apical ectodermal ridge, which induces the development of the limb buds of the embryo List...
2 KB (207 words) - 16:54, 8 May 2024
glycosyltransferases. The gene products of radical fringe stimulate the Apical Ectodermal Ridge in limb-bud formation. The mouse and human Fringe family members...
2 KB (225 words) - 07:15, 9 April 2025
posterior structures such as the hindgut. FGF8 is secreted by the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) at the distal end of limb buds and is essential for limb...
21 KB (2,541 words) - 04:13, 9 June 2025
that zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) requires maintenance of apical ectodermal ridge (AER). The dependence of ZPA on ARE indicates the linkage between...
7 KB (925 words) - 04:41, 26 February 2024
patterning of the limb and has been implicated in the formation of the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). The AER is essential for the distal patterning of the limb...
3 KB (477 words) - 13:32, 11 September 2022
; Vogel A.; Booth I.; Martin G.R. (1993). "FGF-* replaces the apical ectodermal ridge and directs outgrowth and patterning of the limb". Cell. 75 (3):...
16 KB (1,935 words) - 09:06, 13 September 2024
These transcription factors are Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER) specific in limb development. The Apical Ectodermal Ridge signaling is important for specification...
7 KB (936 words) - 23:10, 4 April 2024
Top expressed in sclerotome Apical ectodermal ridge surface ectoderm rhombic lip thoracic vertebral column hair ventral tegmental area lumbar subsegment...
9 KB (1,168 words) - 00:49, 3 December 2023
phase by functioning as an autocrine or paracrine ligand. In the apical ectodermal ridge (AER), FGF4 plays a key role in initiating and sustaining limb...
16 KB (1,874 words) - 16:09, 30 March 2025
EI (1998). "JAGGED2: a putative Notch ligand expressed in the apical ectodermal ridge and in sites of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions". Mech. Dev...
8 KB (1,018 words) - 22:07, 28 December 2023