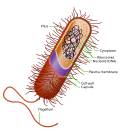
peptidoglycan, not all cell walls have the same overall structures. Since the cell wall is required for bacterial survival, but is absent in some eukaryotes, several...
35 KB (4,590 words) - 16:02, 2 May 2025
The bacterial capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed...
17 KB (1,785 words) - 22:12, 1 October 2024
This envelope is not present in the Mollicutes where the cell wall is absent. Bacterial cell envelopes fall into two major categories: a Gram-positive...
9 KB (1,169 words) - 03:12, 12 May 2024
Bacterial adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate adhesion or adherence to other cells or to surfaces, usually...
19 KB (2,245 words) - 18:49, 25 January 2025
agar, distinct from those in land plants. Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan, while archaeal cell walls vary in composition, potentially consisting...
43 KB (4,789 words) - 03:07, 24 March 2025
Prokaryote (redirect from Prokaryotic cell)
transcribe RNA to DNA). Bacterial cell structure Evolution of cells List of sequenced archaeal genomes List of sequenced bacterial genomes Marine prokaryotes...
45 KB (4,318 words) - 11:15, 30 April 2025
associated with bacterial cell structure and morphology; cell membrane homeostasis; the uptake of nutrients; protection of the cell from toxins including...
11 KB (1,300 words) - 20:43, 18 March 2025
Artificial cell Bacterial cell structure Bangstad syndrome Cell cortex Cell damage, including damage to cell membrane Cell theory Cytoneme Elasticity of cell membranes...
59 KB (6,912 words) - 02:27, 12 March 2025
Flagellum (redirect from Bacterial flagella)
outside the cell, and rotate to propel the cell. Archaeal flagella have a unique structure which lacks a central channel. Similar to bacterial type IV pilins...
66 KB (7,271 words) - 19:40, 1 May 2025
such as cell shape, Gram stain (number of lipid bilayers) or bilayer composition (see Bacterial cellular morphologies, Bacterial cell structure) Bacteria...
84 KB (9,798 words) - 02:54, 19 May 2025
same function. An example is the forelimb structure shared by cats and whales. Analogous structures - structures similar in different organisms because,...
12 KB (1,247 words) - 19:27, 8 December 2024
Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no mutation event occurs, the resulting...
18 KB (2,111 words) - 20:50, 4 March 2025
Secretion (redirect from Cell secretion)
interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their...
26 KB (2,981 words) - 12:10, 21 April 2025
Genetic transformation (redirect from Bacterial transformation)
other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a...
55 KB (6,818 words) - 22:30, 1 April 2025
Bacterial cellular morphologies are the shapes that are characteristic of various types of bacteria and often key to their identification. Their direct...
24 KB (2,335 words) - 10:50, 7 April 2025
cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, and that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells are...
59 KB (6,143 words) - 19:43, 3 May 2025
its target protein. Bacterial display is often coupled with magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) or fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) techniques...
14 KB (1,933 words) - 16:11, 8 May 2025
Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between...
22 KB (2,419 words) - 03:04, 2 January 2025
Lipopolysaccharide (category Bacterial toxins)
(in the original sense of toxins that are inside the bacterial cell that are released when the cell disintegrates) that are not related to LPS, such as...
63 KB (7,187 words) - 01:02, 11 May 2025
Gram-positive bacteria (redirect from Gram-positive bacterial infections)
through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During...
24 KB (2,652 words) - 14:02, 13 April 2025
Bacterial morphological plasticity refers to changes in the shape and size that bacterial cells undergo when they encounter stressful environments. Although...
31 KB (3,631 words) - 12:11, 27 November 2024
lipopolysaccharide layer. Other bacterial cell surface structures range from disorganised slime layers to highly structured capsules. These are made from...
109 KB (12,267 words) - 21:52, 22 April 2025
bonds of the stain with the cell wall. Gram staining is almost always the first step in the identification of a bacterial group. While Gram staining is...
27 KB (2,815 words) - 17:21, 17 May 2025
Peptidoglycan (redirect from Peptidoglycan cell wall)
the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic...
36 KB (4,018 words) - 18:24, 24 September 2024
Cytoskeleton (redirect from Cell wall skeleton)
organelles within the cell) and can be a template for the construction of a cell wall. Furthermore, it can form specialized structures, such as flagella,...
45 KB (5,117 words) - 13:29, 14 May 2025
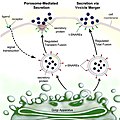
Bacterial secretion systems are protein complexes present on the cell membranes of bacteria for secretion of substances. Specifically, they are the cellular...
31 KB (3,752 words) - 11:08, 25 March 2025
Organelle (redirect from Cell organelle)
other structures such as mitochondria and plastids. While prokaryotes do not possess eukaryotic organelles, some do contain protein-shelled bacterial microcompartments...
28 KB (2,362 words) - 23:23, 16 March 2025
being washed away before infection occurs. Bacterial cells can bind to many host cell surface structures such as glycolipids and glycoproteins which...
17 KB (2,221 words) - 13:21, 30 January 2025
Antimicrobial peptides (section Bacterial resistance)
protein folding, and cell wall synthesis. The initial contact between the peptide and the target organism is electrostatic, as most bacterial surfaces are anionic...
61 KB (6,552 words) - 20:19, 10 February 2025