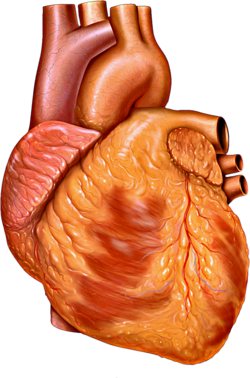
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q {\displaystyle Q} , Q ˙ {\displaystyle {\dot...
76 KB (9,417 words) - 13:58, 28 May 2025
the cardiac output, the amount of blood that flows from the heart each minute, and the cardiac index, a hemodynamic parameter that relates the cardiac output...
25 KB (2,843 words) - 02:43, 26 May 2025
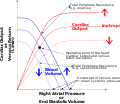
A cardiac function curve is a graph showing the relationship between right atrial pressure (x-axis) and cardiac output (y-axis).[citation needed] Superimposition...
5 KB (389 words) - 15:52, 26 May 2025
The cardiac index (CI) is a hemodynamic measure that represents the cardiac output (CO) of an individual divided by their body surface area (BSA), expressed...
13 KB (1,476 words) - 17:50, 23 May 2025
High-output heart failure is a heart condition that occurs when the cardiac output is higher than normal because of increased peripheral demand. There...
2 KB (236 words) - 02:07, 25 May 2023
Heart failure (redirect from Cardiac failure)
cardiac output with high systemic vascular resistance or high cardiac output with low vascular resistance (low-output heart failure vs. high-output heart...
144 KB (15,674 words) - 03:06, 15 June 2025
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the...
17 KB (1,855 words) - 12:50, 16 May 2025
blood stretches cardiac muscle, leading to an increase in the force of contraction. The Frank-Starling mechanism allows the cardiac output to be synchronized...
17 KB (1,918 words) - 19:32, 24 May 2025
changes in the volume of each pulse). Blood pressure is influenced by cardiac output, systemic vascular resistance, blood volume and arterial stiffness,...
84 KB (8,951 words) - 07:53, 9 June 2025
Hemodynamics (section Cardiac output)
port. Cardiac output is mathematically expressed by the following equation: C O = S V × H R {\displaystyle CO=SV\times HR} where CO = cardiac output (L/sec)...
48 KB (6,468 words) - 18:39, 30 January 2025
bloodstream and to guide treatment. Other helpful measurements include cardiac output and superior vena cava oxygen saturation. People with sepsis need preventive...
125 KB (13,631 words) - 21:25, 15 June 2025
of blood flow back to the heart. It normally limits cardiac output. Superposition of the cardiac function curve and venous return curve is used in one...
8 KB (901 words) - 13:02, 24 May 2025
without lowering cardiac output demands, amlodipine increases the cardiac output response concomitantly with increased functional cardiac load. Amlodipine...
45 KB (4,049 words) - 19:56, 29 May 2025
systole). Apex beat Cardiac action potential Cardiac output Pulse Pollock JD, Makaryus AN (3 October 2022). "Physiology: Cardiac cycle". StatPearls Publishing...
20 KB (1,873 words) - 14:26, 2 June 2025
decrease in cardiac input and output. A further decrease of cardiac input and output is typical in phase III of the progression of cardiac tamponade. This...
24 KB (2,440 words) - 18:16, 11 June 2025
physiologically relevant hemodynamic parameters such as stroke volume, cardiac output, ejection fraction, myocardial contractility, etc. can be determined...
21 KB (2,725 words) - 09:22, 18 March 2025
structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another. The heart...
47 KB (5,787 words) - 15:46, 21 August 2024
cardiodynamic parameters, such as stroke volume (SV), heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), ventricular ejection time (VET), and pre-ejection period; it then...
20 KB (2,160 words) - 01:59, 7 June 2025
calculated by taking the cardiac output (measured in liters per minute) and dividing it by the heart rate (to give output per cardiac cycle) and then dividing...
12 KB (1,290 words) - 14:54, 8 December 2023
[citation needed] Aortic stenosis hinders circulation by obstructing the cardiac output.[citation needed] Hypertrophic sub-aortic stenosis is overly thick ventricular...
51 KB (5,494 words) - 13:27, 6 June 2025
Blunt trauma (section Blunt cardiac trauma)
as hypoxia, ventilation-perfusion mismatch, hypovolemia, and reduced cardiac output due to the way the thoracic organs may have been affected. Blunt thoracic...
37 KB (4,117 words) - 22:19, 28 May 2025
Vasodilation acts to increase cardiac output by decreasing afterload, −one of the four determinants of cardiac output. By expanding available area for...
44 KB (4,096 words) - 22:53, 25 October 2024
values are obtained during exertion at a maximal effort. Here Q is the cardiac output of the heart, CaO2 is the arterial oxygen content, and CvO2 is the venous...
33 KB (3,465 words) - 16:47, 21 May 2025
Diving reflex (section Bradycardia and cardiac output)
cardiac output remain higher than normal during immersion. The increased respiratory and cardiac workload causes increased blood flow to the cardiac and...
24 KB (2,592 words) - 17:40, 7 May 2025
contraction force (by the Frank–Starling law of the heart) and thus a rise in cardiac output. In heart failure, this mechanism fails, as the ventricle is loaded...
16 KB (2,166 words) - 05:57, 27 January 2023
predict volume-responsiveness (i.e. whether more fluid will improve cardiac output). However, there is increasing evidence that CVP, whether as an absolute...
6 KB (642 words) - 09:20, 9 November 2024
(1829–1901), the Fick principle has been applied to the measurement of cardiac output. Its underlying principles may also be applied in a variety of clinical...
8 KB (1,061 words) - 16:01, 10 June 2025
quantium Medical Cardiac Output (qCO) uses impedance cardiography in a simple, continuous, and non-invasive way to estimate the cardiac output (CO) and other...
33 KB (3,550 words) - 05:05, 27 December 2023
cause, however the common theme is that of a high cardiac output with a low or normal afterload. The output may be high due to the inefficiency in valve disease...
4 KB (412 words) - 10:41, 7 February 2023