Second Level Address Translation (SLAT), also known as nested paging, is a hardware-assisted virtualization technology which makes it possible to avoid...
17 KB (1,805 words) - 18:35, 6 March 2025
can hardware accelerate the address translation of Guest Virtual Address-spaces by using second level address translation provided by the CPU, referred...
47 KB (4,025 words) - 00:09, 22 March 2025
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of...
43 KB (5,559 words) - 21:58, 12 May 2025
support for VT-x with Extended Page Tables (EPT), also called Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). The Core 2-branded CPUs include: Conroe/Allendale (dual-core...
17 KB (1,151 words) - 09:25, 17 March 2025
a naval anti-torpedo system, on FREMM multipurpose frigate Second Level Address Translation, a computer technology Software Liberty Association of Taiwan...
2 KB (280 words) - 19:37, 11 September 2023
time taken to access a user memory location. It can be called an address-translation cache. It is a part of the chip's memory-management unit (MMU). A...
24 KB (3,328 words) - 08:42, 3 April 2025
Page table (redirect from Page translation table)
be read and written during the virtual address translation process by the memory management unit or by low-level system software or firmware. In operating...
17 KB (2,462 words) - 20:30, 8 April 2025
also requires a processor that supports Client Hyper-V and Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). The Visual Studio Express 2015 editions are: Express...
22 KB (1,893 words) - 20:20, 26 January 2025
X86 virtualization (redirect from Function level reset)
OS-level virtualization Timeline of virtualization development Virtual machine List of IOMMU-supporting hardware Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)...
41 KB (3,747 words) - 12:37, 15 February 2025
productivity and social features and updates to security and accessibility, addressing some of the deficiencies of Windows 10. The Microsoft Store, which serves...
131 KB (11,014 words) - 12:41, 16 May 2025
CPU cache (redirect from Virtual-to-physical address translation)
independent levels of caches (L1, L2 and L3) and different types of caches: Translation lookaside buffer (TLB) Used to speed up virtual-to-physical address translation...
97 KB (13,332 words) - 15:03, 7 May 2025
created and run using Hyper-V. The server's CPU must support Second Level Address Translation (SLAT), and have it enabled. For Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1...
13 KB (1,369 words) - 19:15, 3 April 2025
IPv6 transition mechanism (redirect from Network Address Translation/Protocol Translation algorithm)
application-level gateway (DNS-ALG) implementation. While almost identical to NAT-PT, Network Address Port Translation + Protocol Translation, which is...
24 KB (3,160 words) - 13:45, 26 April 2025
A prefix for locally translated IPv4/IPv6 addresses. Addresses with this prefix can be used for multiple IPv4/IPv6 translation mechanisms like NAT64...
61 KB (8,455 words) - 17:41, 13 May 2025
automate translation or to mechanically aid the human translator. More recently, the rise of the Internet has fostered a world-wide market for translation services...
167 KB (21,191 words) - 01:21, 13 May 2025
technologies, including network address translation (NAT), Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) in 1993, and IPv6 in 1998. The top-level exhaustion occurred on...
65 KB (6,434 words) - 06:29, 18 May 2025
Virtual memory (redirect from Virtual address translation)
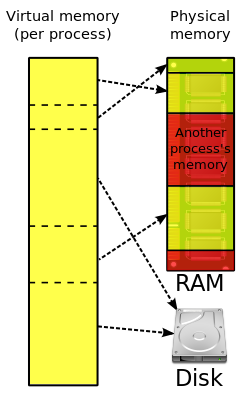
memory. Address translation hardware in the CPU, often referred to as a memory management unit (MMU), automatically translates virtual addresses to physical...
43 KB (5,334 words) - 00:27, 19 January 2025
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as 192.0.2.1 that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses...
32 KB (4,384 words) - 12:21, 27 March 2025
Single-letter second-level domains are domains in which the second-level domain of the domain name consists of only one letter, such as x.com. In 1993...
23 KB (1,153 words) - 09:35, 22 April 2025
references to memory, and translates the memory addresses being referenced, known as virtual memory addresses, into physical addresses in main memory. In modern...
49 KB (7,099 words) - 18:50, 8 May 2025
INT 13h and 28-bit CHS numbering used by ATA. The translation scheme was called large or bit shift translation. This method would remap 16:4:8 bit ATA cylinders...
18 KB (1,980 words) - 12:49, 13 May 2025
a numerical IP address that is used to route communications between nodes. Normally if the server does not know a requested translation it will ask another...
12 KB (1,517 words) - 20:44, 29 April 2025
"High-level language" refers to the higher level of abstraction from machine language. Rather than dealing with registers, memory addresses, and call...
17 KB (2,028 words) - 12:12, 8 May 2025
Address terms are linguistic expressions used by a speaker to start conversation or call someone. George Yule defines address form as a word or phrase...
99 KB (12,618 words) - 17:09, 4 May 2025
Memory segmentation (redirect from Segmented address space)
between address spaces; this bit is set to optimize TLB use Each of IBM's DAT implementations includes a translation cache, which IBM called a Translation Lookaside...
19 KB (2,278 words) - 07:00, 16 October 2024
Memory-mapped I/O and port-mapped I/O (redirect from I/O address)
same address space to address both main memory and I/O devices. The memory and registers of the I/O devices are mapped to (associated with) address values...
17 KB (2,288 words) - 01:44, 18 November 2024
following groups of top-level domains: Infrastructure top-level domain (ARPA): This group consists of one domain, the Address and Routing Parameter Area...
29 KB (3,029 words) - 19:54, 21 April 2025
.arpa (redirect from Address and Routing Parameter Area)
DNS lookup of IP addresses.: §3.5 Originally, the IETF intended that new infrastructure databases would be created in the top-level domain int. In May...
11 KB (1,647 words) - 06:12, 12 May 2025
X86 memory segmentation (redirect from Segmented address)
Requested Privilege Level (RPL), a 1-bit Table Indicator (TI), and a 13-bit index. When attempting address translation of a given logical address, the processor...
23 KB (3,302 words) - 22:29, 14 May 2025
Proxy server (redirect from Translation proxy server)
by the translated content as it passes back through the proxy. The translations used in a translation proxy can be either machine translation, human translation...
47 KB (5,574 words) - 02:23, 4 May 2025