physics, an electromagnetic electron wave is a wave in a plasma which has a magnetic field component and in which primarily the electrons oscillate. In...
8 KB (1,336 words) - 20:50, 26 May 2025
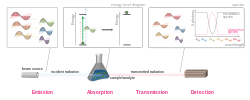
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space...
85 KB (10,023 words) - 00:11, 25 May 2025
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate...
47 KB (4,685 words) - 15:35, 12 May 2025
to the stationary magnetic field. Finally, for perpendicular electromagnetic electron waves, the perturbed electric field can be parallel or perpendicular...
6 KB (489 words) - 04:01, 19 March 2025
Photon (redirect from Locating an electron with an ideal microscope)
of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force....
104 KB (11,301 words) - 23:08, 20 June 2025
practical, matter exhibits wave-like behavior. For example, a beam of electrons can be diffracted just like a beam of light or a water wave. The concept that matter...
70 KB (8,040 words) - 16:42, 22 May 2025
physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is...
38 KB (4,163 words) - 22:48, 18 March 2025
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic...
38 KB (4,084 words) - 04:01, 13 June 2025
Wave–particle duality is the concept in quantum mechanics that fundamental entities of the universe, like photons and electrons, exhibit particle or wave...
28 KB (2,963 words) - 22:12, 22 May 2025
density at which the plasma frequency equals the frequency of an electromagnetic electron wave in plasma This disambiguation page lists articles associated...
385 bytes (81 words) - 06:15, 8 March 2025
individual electrons as well as electron plasma by the use of electromagnetic fields. Special telescopes can detect electron plasma in outer space. Electrons are...
155 KB (15,859 words) - 20:24, 29 May 2025
Electric current (redirect from Electron current)
even though the electrons in the wires only move back and forth over a tiny distance. The ratio of the speed of the electromagnetic wave to the speed of...
36 KB (4,347 words) - 23:29, 13 June 2025
Speed of electricity (category Electromagnetism)
devices, the signals travel as electromagnetic waves typically at 50%–99% of the speed of light in vacuum. The electrons themselves move much more slowly...
9 KB (1,287 words) - 22:57, 20 May 2025
An electromagnetic cavity is a cavity that acts as a container for electromagnetic fields such as photons, in effect containing their wave function inside...
2 KB (298 words) - 12:53, 29 July 2023
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also referred to as a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. The origin...
31 KB (3,715 words) - 21:23, 1 June 2025
Electron optics is a mathematical framework for the calculation of electron trajectories in the presence of electromagnetic fields. The term optics is...
11 KB (1,279 words) - 07:33, 25 May 2025
absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy—and so transforms electromagnetic energy...
9 KB (806 words) - 11:47, 20 April 2025
effect is the emission of electrons from a material caused by electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner are...
59 KB (7,023 words) - 00:56, 15 June 2025
Transverse wave Dyakonov surface wave Dyakonov–Voigt wave Earth–ionosphere waveguide, in radio transmission Electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic wave equation...
61 KB (7,810 words) - 14:42, 3 June 2025
electromagnetic waves, the electromagnetic spectrum. An electromagnetic field very far from currents and charges (sources) is called electromagnetic radiation...
22 KB (2,564 words) - 15:25, 17 April 2025
the gravitational equivalent of electromagnetic waves. In 1916, Albert Einstein demonstrated that gravitational waves result from his general theory of...
106 KB (12,709 words) - 23:49, 19 June 2025
Evanescent field (redirect from Evanescent Wave)
oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the...
23 KB (3,164 words) - 17:09, 6 September 2024
piezoelectric surface, the strain wave generates an electromagnetic potential. The potential minima can then trap single electrons, allowing them to be individually...
34 KB (4,073 words) - 14:27, 25 May 2025
equation connecting the electron's spin with its electromagnetic properties. Reduction of the Dirac equation for an electron in a magnetic field to its...
23 KB (3,393 words) - 14:44, 8 June 2025
Whistler (radio) (redirect from Whistler wave)
it is called 2−, and so on. Dawn chorus (electromagnetic) Electromagnetic electron wave Hiss (electromagnetic) Atmospheric noise Radio atmospheric Helicon...
13 KB (1,514 words) - 09:10, 25 May 2025
relies on the beam being deflected by electromagnetic fields. In the classical case, the fast electrons in the electron beam is deflected by the Lorentz force...
37 KB (4,263 words) - 23:40, 22 May 2025
light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled...
74 KB (9,420 words) - 14:38, 20 June 2025
Wavelength (redirect from Wave length)
for wave phenomena is called a spectrum. The name originated with the visible light spectrum but now can be applied to the entire electromagnetic spectrum...
36 KB (4,299 words) - 20:17, 15 May 2025
Radiation (section Radio waves)
form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: electromagnetic radiation consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves...
48 KB (6,186 words) - 07:40, 21 June 2025
Wavenumber (redirect from Wave number)
wave scattering, such as X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, electron diffraction, and elementary particle physics. For quantum mechanical waves,...
15 KB (1,940 words) - 20:14, 4 June 2025