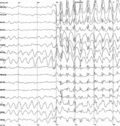
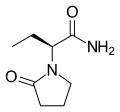
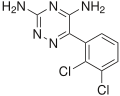
Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterized by generalized seizures that occur with no obvious cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to...
23 KB (2,570 words) - 04:48, 7 April 2025
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) is a group of epileptic disorders that are believed to have a strong underlying genetic basis. IGE is considered...
7 KB (748 words) - 02:24, 14 August 2024
Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) is a syndromic autosomal dominant disorder where affected individuals can exhibit numerous epilepsy...
35 KB (3,419 words) - 18:55, 26 February 2025
A generalized tonic–clonic seizure, commonly known as a grand mal seizure or GTCS, is a type of generalized seizure that produces bilateral, convulsive...
14 KB (1,575 words) - 03:19, 11 February 2025
Absence seizure (redirect from Absence epilepsy)
Childhood Absence Epilepsy Childhood absence epilepsy (CAE) is a type of idiopathic epilepsy characterized by its non-convulsive, generalized nature and a...
29 KB (3,533 words) - 22:11, 20 February 2025
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), also known as Janz syndrome or impulsive petit mal, is a form of hereditary, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, representing...
32 KB (3,653 words) - 22:20, 22 December 2024
seizures are grouped into four main classes: focal, generalized, unknown (whether focal or generalized), and unclassified. Focal seizures originate in one...
158 KB (17,578 words) - 16:44, 12 May 2025
into 4 groups based on epilepsy type: a. Generalized onset epilepsy syndromes. These epilepsy syndromes have only generalized-onset seizures and include...
42 KB (5,490 words) - 01:23, 21 March 2025
Levetiracetam (section Generalized epilepsy)
treatment for partial (focal) epilepsy. Levetiracetam is effective for treatment of generalized tonic-clonic epilepsy. It has been approved in the United...
37 KB (3,486 words) - 04:00, 15 May 2025
Reflex seizure (redirect from Epilepsy, reflex)
reflex epilepsy. Thinking epilepsy usually results in generalized seizures which manifest as bilateral monoclonus, absence seizures, or generalized tonic-clonic...
20 KB (2,193 words) - 12:48, 3 June 2024
epilepsy types include focal, generalized, combination focal and generalized, and unknown. Accurate classification of epilepsy will help in providing an appropriate...
63 KB (7,560 words) - 09:48, 25 September 2024
GLUT1 (section Idiopathic generalized epilepsy 12)
GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1, GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 2, idiopathic generalized epilepsy 12, dystonia 9, and stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis. Disruption...
29 KB (3,417 words) - 23:42, 4 May 2025
common triggers. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) is a prevalent and typical form of idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) syndrome. However, establishing...
16 KB (1,040 words) - 06:24, 21 March 2025
symptoms and EEG may appear like Generalized epilepsy, Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, benign childhood myoclonic epilepsy, and Huntington's disease. It is...
17 KB (1,973 words) - 00:50, 23 September 2024
Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP) refers to the sudden, unexpected death of a person with epilepsy that is not the result of trauma, drowning...
31 KB (3,407 words) - 04:40, 19 May 2025
Benign Rolandic epilepsy or self-limited epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (formerly benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS)) is...
25 KB (2,835 words) - 22:13, 22 December 2024
myoclonic-atonic seizures" in the ILAE 2017 classification, is a generalized idiopathic epilepsy. It is characterized by the development of myoclonic seizures...
8 KB (848 words) - 10:58, 19 December 2024
Childhood absence epilepsy (CAE), formerly known as pyknolepsy, is an idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndrome that begins in childhood, typically between...
12 KB (1,402 words) - 13:52, 7 May 2025
Dravet syndrome (redirect from Severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy)
are found in several epilepsies, including Childhood Absence Epilepsy, Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy, and Genetic Generalized Epilepsy. Some cases of Dravet...
33 KB (4,112 words) - 13:05, 19 May 2025
syndrome, generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+), FIRES (febrile infection–related epilepsy syndrome) Lennox-Gastaut syndrome or epilepsy of...
41 KB (4,409 words) - 20:16, 25 November 2024
Lamotrigine (section Epilepsy)
to be protective against generalized absence epilepsy and other generalized epilepsy syndromes, including primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, juvenile...
66 KB (6,694 words) - 13:40, 21 May 2025
Seizure (category Epilepsy)
unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). When available information is insufficient to determine whether a seizure is focal or generalized, it is classified...
48 KB (4,969 words) - 11:09, 13 May 2025
Spike-and-wave (section Spike-and-wave in epilepsy)
a regular, symmetrical, generalized EEG pattern seen particularly during absence epilepsy, also known as ‘petit mal’ epilepsy. The basic mechanisms underlying...
29 KB (3,692 words) - 00:09, 20 February 2025
Focal seizure (redirect from Epilepsy, complex partial)
seizures. Under the 2025 classification of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE), focal seizures are divided into three types: those with preserved...
22 KB (2,266 words) - 03:46, 12 May 2025
Vagus nerve stimulation (section Epilepsy)
identified including epilepsy onset > 12 years of age, generalized epilepsy type, non-lesional epilepsy, posttraumatic epilepsy and those who have less...
61 KB (6,697 words) - 20:45, 28 April 2025
with epilepsy (1–2%). Specifically, the hereditary rates for patients with: Any type of epilepsy is 3.5–6% Focal epilepsy is 1–5% Generalized epilepsy is...
20 KB (2,352 words) - 23:30, 8 July 2024
Myoclonus (section Epilepsy forms)
period of time. Reticular reflex myoclonus is thought to be a type of generalized epilepsy that originates in the brainstem, the part of the brain that connects...
28 KB (3,574 words) - 20:03, 28 April 2025
Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (category Epilepsy types)
Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a complex, rare, and severe childhood-onset epilepsy syndrome. It is characterized by multiple and concurrent seizure types...
30 KB (3,424 words) - 21:45, 1 May 2025
voltage-gated potassium channel gene KCNH1 cause Temple-Baraitser syndrome and epilepsy". Nature Genetics. 47 (1): 73–77. doi:10.1038/ng.3153. PMID 25420144. S2CID 52799681...
14 KB (1,121 words) - 00:49, 22 December 2024