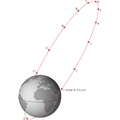
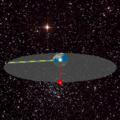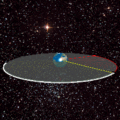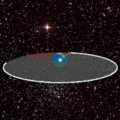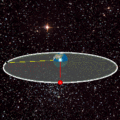
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours...
33 KB (3,236 words) - 12:26, 4 June 2025
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35,786 km (22,236 mi) in altitude...
49 KB (4,893 words) - 06:24, 20 May 2025
transfer orbit (GTO) or geosynchronous transfer orbit is a highly elliptical type of geocentric orbit, usually with a perigee as low as low Earth orbit (LEO)...
13 KB (1,789 words) - 19:22, 30 March 2025
This is a list of satellites in geosynchronous orbit (GSO). These satellites are commonly used for communication purposes, such as radio and television...
67 KB (729 words) - 03:23, 7 December 2024
graveyard orbit is a supersynchronous orbit well beyond geosynchronous orbit. Some satellites are moved into such orbits at the end of their operational life...
9 KB (1,039 words) - 13:01, 7 June 2025
Thus, a geostationary orbit is defined as a geosynchronous orbit at zero inclination. Geosynchronous (and geostationary) orbits have a semi-major axis...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
Space elevator (redirect from Geosynchronous orbital tether)
design's passenger climber would be able to reach the level of geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO) after an 8-day trip. Further details were published in...
89 KB (10,325 words) - 17:43, 30 May 2025
to geosynchronous orbit, into a HEO transfer orbit and then a final stage or engine circularizes the payload in the intended geosynchronous orbit. When...
5 KB (604 words) - 01:51, 5 June 2025
areosynchronous orbits (ASO) are the synchronous orbits for artificial satellites around the planet Mars. They are the martian equivalent of the geosynchronous orbits...
3 KB (374 words) - 00:13, 28 May 2025
A geosynchronous satellite is a satellite in geosynchronous orbit, with an orbital period the same as the Earth's rotation period. Such a satellite returns...
9 KB (1,035 words) - 18:52, 28 March 2025
A high Earth orbit is a geocentric orbit with an apogee farther than that of the geosynchronous orbit, which is 35,786 km (22,236 mi) away from Earth....
9 KB (790 words) - 11:14, 26 April 2025
have an inclined orbit around the Sun if it has an angle other than 0° to the ecliptic plane. A geosynchronous orbit is an inclined orbit with an altitude...
3 KB (338 words) - 20:20, 12 June 2024
200 mi) and that of the geosynchronous orbit at 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Geosynchronous orbit (GSO) Geocentric circular orbit with an altitude of 35,786 km...
17 KB (1,997 words) - 14:10, 7 June 2025
the boundary between MEO and HEO is the particular altitude of a geosynchronous orbit, in which a satellite takes 24 hours to circle the Earth, the same...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
Orbital Sciences Corporation; their capabilities and development and construction budgets are classified. They operate in "near-geosynchronous orbit"...
8 KB (593 words) - 14:19, 8 June 2025
Altitude (section In satellite orbits)
200 mi) and that of the geosynchronous orbit at 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Geosynchronous orbit (GSO) Geocentric circular orbit with an altitude of 35,786 km...
26 KB (3,069 words) - 03:28, 26 April 2025
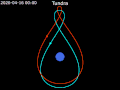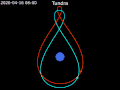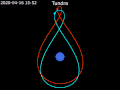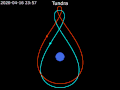
Tundra orbit (Russian: орбита «Тундра») is a highly elliptical geosynchronous orbit with a high inclination (approximately 63.4°), an orbital period of...
18 KB (1,850 words) - 04:02, 25 May 2025
but not all geosynchronous orbits are geostationary. A geostationary orbit stays exactly above the equator, whereas a geosynchronous orbit may swing north...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 08:45, 4 June 2025
Sun-synchronous frozen orbits. Orbital perturbation analysis (spacecraft) Analemma Geosynchronous orbit Geostationary orbit List of orbits Polar orbit World Geodetic...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 19:06, 16 March 2025
than would be required from a geosynchronous orbit. Low Earth orbit A low Earth orbit (LEO) typically is a circular orbit about 160 to 2,000 kilometres...
50 KB (5,997 words) - 02:56, 9 May 2025
scheduled for a Satcom 3 transponder but that satellite failed to reach geosynchronous orbit upon its launch on 7 December 1979. Shortly after its launch, Satcom...
8 KB (612 words) - 20:07, 21 December 2024
FYP and will be launched in the beginning of 13th FYP (2018–23) in geosynchronous orbit of 42° inclination. Also, the development of space-qualified Indian...
64 KB (5,319 words) - 09:49, 11 June 2025
continuing past LEO, or satellites travelling at medium Earth orbit (MEO) or geosynchronous orbit (GEO). The catastrophic scenarios predict an increase in...
44 KB (4,746 words) - 19:03, 12 June 2025
Earth orbit for master sergeants, medium Earth orbit for senior master sergeants, and geosynchronous orbit for chief master sergeants. These orbital chevrons...
171 KB (12,285 words) - 12:18, 15 June 2025
Synthetic-aperture radar (section Application: geosynchronous orbit synthetic-aperture radar (GEO-SAR))
positions at different times. When the radar is carried by an aircraft or an orbiting vehicle, those positions are functions of a single variable, distance along...
79 KB (11,260 words) - 07:13, 27 May 2025
Non-rocket spacelaunch (section Orbital ring)
minimal power and would be in a circular orbit. The concept of a structure reaching to geosynchronous orbit was first conceived by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky...
49 KB (5,489 words) - 13:58, 26 May 2025
three different orbits, including 24 satellites in medium-circle orbits (covering the world), 3 satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbits (covering the...
68 KB (5,866 words) - 01:18, 2 June 2025
geostationary orbit. The more general case, when the orbit is inclined to Earth's equator or is non-circular is called a geosynchronous orbit. The corresponding...
8 KB (813 words) - 03:33, 1 June 2025
discuss] A geostationary orbit is a particular type of equatorial orbit, one which is geosynchronous. A satellite in a geostationary orbit appears stationary...
5 KB (689 words) - 18:00, 15 March 2025
Space-based solar power (redirect from Orbital power satellite)
electricity. The program looked both at systems in Sun-synchronous orbit and geosynchronous orbit. Some of SERT's conclusions: The increasing global energy demand...
112 KB (12,829 words) - 12:05, 13 June 2025