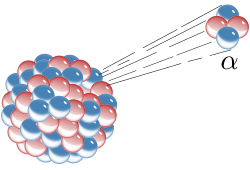
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay...
14 KB (1,522 words) - 06:37, 4 June 2025
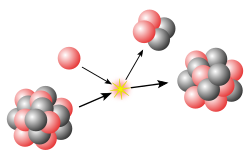
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron)...
64 KB (7,712 words) - 13:14, 19 June 2025
radiation from uranium, now called beta particles, had the same charge/mass ratio as cathode rays.: II:3 These beta particles were believed to be electrons...
43 KB (6,145 words) - 07:43, 24 May 2025
{\displaystyle \beta } radiation". After five years of additional experimental work, Rutherford and Hans Geiger determined that "the alpha particle, after it...
33 KB (4,208 words) - 06:51, 21 June 2025
Positron emission (redirect from Beta plus decay)
mediated by the weak force. The positron is a type of beta particle (β+), the other beta particle being the electron (β−) emitted from the β− decay of...
9 KB (1,145 words) - 22:57, 7 June 2025
detectable beta particles, which are electrons or positrons. The literature distinguishes between two types of double beta decay: ordinary double beta decay...
38 KB (3,818 words) - 01:51, 11 April 2025
the time. Thomson studied beta particle scattering which showed small angle deflections modelled as interactions of the particle with many atoms in succession...
94 KB (12,508 words) - 07:20, 27 June 2025
Betavoltaic device (redirect from Beta-voltaic cell)
battery) is a type of nuclear battery that generates electric current from beta particles (electrons or positrons) emitted from a radioactive source, using semiconductor...
18 KB (1,933 words) - 19:30, 25 May 2025
Neutrino (redirect from Ν particle)
considered that the new particle was emitted from the nucleus together with the electron or beta particle in the process of beta decay and had a mass similar...
146 KB (14,422 words) - 00:49, 26 June 2025
Ionizing radiation (section Beta particles)
[citation needed] Ionizing subatomic particles include alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons. These particles are created by radioactive decay, and...
61 KB (6,599 words) - 18:54, 27 June 2025
beta decay transition is the change in state of an atomic nucleus undergoing beta decay. When undergoing beta decay, a nucleus emits a beta particle and...
14 KB (2,080 words) - 22:21, 7 June 2025
W and Z bosons (redirect from W particle)
(often called a beta particle in this context) and an electron antineutrino: n0 → p+ + e− + ν e Again, the neutron is not an elementary particle but a composite...
38 KB (3,772 words) - 10:25, 4 June 2025
Radiation burn (redirect from Beta burn)
Beta burns tend to be shallow as beta particles are not able to penetrate deeply into a body; these burns can be similar to sunburn. Alpha particles can...
41 KB (4,556 words) - 22:01, 29 May 2025
Beta (UK: /ˈbiːtə/, US: /ˈbeɪtə/ ; uppercase Β, lowercase β, or cursive ϐ; Ancient Greek: βῆτα, romanized: bē̂ta or Greek: βήτα, romanized: víta) is the...
13 KB (1,461 words) - 16:00, 24 June 2025
Radiation (section Beta radiation)
and gamma radiation (γ) particle radiation consisting of particles of non-zero rest energy, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation...
48 KB (6,197 words) - 04:41, 28 June 2025
force acting on charged particles, typically alpha and beta particles, due to interaction with matter, resulting in loss of particle kinetic energy. Stopping...
30 KB (4,054 words) - 04:17, 9 June 2025
Atom (section Subatomic particles)
occurs following the emission of an alpha or a beta particle. Thus, gamma decay usually follows alpha or beta decay. Other more rare types of radioactive...
126 KB (12,975 words) - 23:44, 20 June 2025
Radioactive decay (section Alpha, beta and gamma decay)
deflection, it was clear that alpha particles were much more massive than beta particles. Passing alpha particles through a very thin glass window and...
96 KB (9,898 words) - 02:56, 20 June 2025
Radionuclide (section Beta emission only)
conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide...
31 KB (2,661 words) - 22:02, 29 May 2025
charged beta particles (high-energy positrons β+ or electrons β−; the latter being more common) high-speed electrons that are not from the beta decay process...
5 KB (616 words) - 10:17, 10 August 2023
Tritium (redirect from Triton (particle))
compared to other beta particles, the amount of bremsstrahlung generated is also lower. The unusually low energy released in the tritium beta decay makes the...
65 KB (7,638 words) - 23:21, 21 June 2025
Neutron (redirect from N particle)
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol n or n0 , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The neutron was discovered...
101 KB (11,296 words) - 14:10, 24 June 2025
Cloud chamber (category Particle detectors)
supersaturated vapor of water or alcohol. An energetic charged particle (for example, an alpha or beta particle) interacts with the gaseous mixture by knocking electrons...
15 KB (1,715 words) - 03:51, 14 June 2025
uranium-238 nuclei emit an alpha particle to become thorium-234. Next, with a short half-life, 234Th nuclei emit a beta particle to become protactinium-234...
6 KB (672 words) - 01:41, 5 December 2024
Gamma ray (redirect from Gamma particle)
property making them unlike alpha and beta rays. Gamma rays were first thought to be particles with mass, like alpha and beta rays. Rutherford initially believed...
60 KB (7,505 words) - 15:39, 16 June 2025
Linear energy transfer (section Beta particles)
(Coulomb or Rutherford scattering), much more so than heavier particles. Beta particle tracks are therefore crooked. In addition to producing secondary...
14 KB (1,858 words) - 19:50, 15 May 2024
Beta attenuation monitoring (BAM) is an air monitoring technique employing the absorption of beta radiation by solid particles extracted from air flow...
4 KB (484 words) - 02:52, 7 December 2024
Radioanalytical chemistry (section Beta-particle decay)
environment. Alpha decay is characterized by the emission of an alpha particle, a 4He nucleus. The mode of this decay causes the parent nucleus to decrease...
12 KB (1,404 words) - 21:13, 16 June 2024
particles from a radioactive layer deposited on one of the electrodes. Spacing can be either vacuum or dielectric. Negatively charged beta particles or...
25 KB (2,775 words) - 21:59, 19 June 2025
Geiger counter (category Particle detectors)
type of dosimeter. It detects ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays using the ionization effect produced in a Geiger–Müller...
24 KB (2,925 words) - 22:19, 7 June 2025