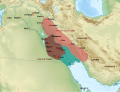
The Code of Ur-Nammu is the oldest known surviving law code. It is from Mesopotamia and is written on tablets, in the Sumerian language c. 2100–2050 BC...
15 KB (2,133 words) - 15:32, 26 May 2025
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian: 𒌨𒀭𒇉; died c. 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following...
28 KB (3,113 words) - 00:18, 18 June 2025
Ur-Nammu seems to have earned the title 'king of Sumer and Akkad.' Ur's dominance over the Neo-Sumerian Empire was consolidated with the famous Code of...
40 KB (3,877 words) - 10:31, 24 May 2025
include: The Code of Ur-Nammu of Ur. The Code of Lipit-Ishtar of Isin. The Laws of Eshnunna (written by Bilalama or by Dadusha). The "Laws of X," which,...
101 KB (10,005 words) - 09:35, 20 June 2025
code of laws, the Code of Ur-Nammu (a fragment was identified in Istanbul in 1952) is one of the oldest such documents known, preceding the Code of Hammurabi...
79 KB (9,046 words) - 23:55, 9 June 2025
a legal code written in cuneiform script in the Sumerian language. It is the second-oldest known extant legal code after the Code of Ur-Nammu. As it is...
10 KB (1,121 words) - 12:30, 13 June 2025
Trial by ordeal (redirect from Ordeal of water)
has much earlier roots, attested to as far back as the Code of Hammurabi and the Code of Ur-Nammu. In pre-industrial society, the ordeal typically ranked...
46 KB (5,841 words) - 08:06, 10 June 2025
Shulgi (redirect from Shulgi of ur)
He also wrote a law code, now known as the Code of Ur-Nammu because it was originally thought to have been authored by Ur-Nammu. He also built or rebuilt...
36 KB (3,950 words) - 16:40, 17 February 2025
Hammurabi (category 18th-century BC kings of Babylon)
as the Code of Ur-Nammu, which had focused on compensating the victim of the crime, the Law of Hammurabi was one of the first law codes to place greater...
38 KB (4,139 words) - 02:02, 26 May 2025
of a code of law was found at Ebla, in modern Syria (c. 2400 BC). The Sumerian Code of Ur-Nammu (c. 2100–2050 BC), then the Babylonian Code of Hammurabi...
4 KB (481 words) - 08:46, 3 July 2024
earliest surviving civil code is the Code of Ur-Nammu, written around 2100–2050 BC. The Corpus Juris Civilis, a codification of Roman law produced between 529...
29 KB (2,323 words) - 12:24, 5 March 2025
of a law code, dating back to 2400 BC. In addition, The UrukAgina Law Code (2380–2360 BC), the Sumerian Code of Ur-Nammu (c. 2100–2050 BC), the Code of...
11 KB (1,302 words) - 14:29, 13 June 2025
Sumerian literature (redirect from Literature of sumer)
Correspondence of the Kings of Ur as well as Isin, Larsa, and other dynasties. The Code of Ur-Nammu is attributed to Ur-Nammu, founder of the Third Dynasty of Ur Code...
9 KB (1,026 words) - 04:33, 26 October 2024
This contrasts with the Sumerian Code of Ur-Nammu (c. 2100–2050 BCE), and the Babylonian Code of Hammurabi (c. 1760 BCE, of which almost half concerns contract...
16 KB (2,251 words) - 00:57, 15 June 2025
in lieu of their right of revenge. One of the oldest-known prohibitions against murder appears in the Sumerian Code of Ur-Nammu written sometime between...
96 KB (10,150 words) - 20:35, 24 May 2025
Cuneiform law (category Codes of conduct)
2060 BC – Code of Ur-Nammu (or Shulgi?) of Ur – Neo-Sumerian (Ur-III). Earliest code of which fragments have been discovered. The code speaks of witchcraft...
4 KB (542 words) - 18:50, 11 January 2025
Lagash (redirect from Second dynasty of Lagash)
prologue of the Code of Ur-Nammu it states "He slew Nam-ha-ni the ensi of Lagash". A number of his inscriptions were defaced and the statues of Nam-mahani...
66 KB (7,046 words) - 01:23, 26 May 2025
built a large part of their wealth on slaves acquired through conquest. The Code of Ur-Nammu, the oldest known surviving law code, written c. 2100 – 2050...
16 KB (2,086 words) - 09:51, 13 January 2025
Codification (law) (redirect from Codification of Law)
statute law. Ancient Sumer's Code of Ur-Nammu was compiled circa 2050–1230 BC, and is the earliest known surviving civil code. Three centuries later, the...
27 KB (3,309 words) - 13:51, 24 May 2025
Truth (redirect from Epistemic theory of truth)
falsehoods; the oldest surviving law text, the Code of Ur-Nammu, lists penalties for false accusations of sorcery or adultery, as well as for committing...
100 KB (12,622 words) - 15:22, 5 June 2025
Tigris, north of Ur. Eshnunna became politically important after the fall of the third dynasty of Ur, founded by Ur-Nammu. This collection of laws is not...
6 KB (800 words) - 23:11, 5 March 2025
Criminal law (redirect from History of criminal law)
first written codes of law were designed by the Sumerians. Around 2100–2050 BC Ur-Nammu, the Neo-Sumerian king of Ur, enacted written legal code whose text...
34 KB (4,514 words) - 18:05, 10 June 2025
Sumer (redirect from Ancient Sumer (Eight Features of Civilization))
Lyres of Ur. Sumerian culture was male-dominated and stratified. The Code of Ur-Nammu, the oldest such codification yet discovered, dating to the Ur III...
109 KB (12,435 words) - 06:59, 18 June 2025
Iran–Iraq relations (redirect from History of Iran–Iraq relations)
of the dynasty is its establishment of the earliest known law code after the Code of Urukagina—the Code of Ur-Nammu.[citation needed] During King Shulgi's...
53 KB (6,445 words) - 08:35, 1 June 2025
Crime (redirect from History of crime)
code was the Code of Ur-Nammu (c. 2100 – c. 2050 BC), and the first known criminal code that incorporated retaliatory justice was the Code of Hammurabi....
48 KB (5,892 words) - 19:59, 9 June 2025
Constitution (redirect from Principles of the constitution)
Code of Ur-Nammu of Ur (c. 2050 BC). Some of the better-known ancient law codes are the code of Lipit-Ishtar of Isin, the code of Hammurabi of Babylonia...
100 KB (11,018 words) - 22:30, 25 May 2025
the Code of Ur-Nammu, one of the earliest known law codes (three centuries before the more famous Code of Hammurabi). Around 2000 BC, the power of Ur waned...
55 KB (6,357 words) - 01:29, 26 May 2025
Ten Commandments (redirect from Commandments of God (The Ten Commandments))
Secular and humanist alternatives to the biblical lists Code of Hammurabi (1772 BC) Code of Ur-Nammu (2050 BC) Divine command theory Five Precepts (Taoism)...
128 KB (13,575 words) - 03:56, 18 June 2025
passage from the code of Ur-Nammu published in 2011, which explicitly places the nugig among women professionally taking care of children of other people...
11 KB (1,422 words) - 20:37, 22 June 2024
Ancient economic thought (category Economy of ancient Greece)
cities include the codex of Ur-Nammu, king of Ur (c. 2050 BC), the laws of Eshnunna (c. 1930 BC) and the code of Lipit-Ishtar of Isin (c. 1870 BC). Some...
44 KB (5,285 words) - 04:39, 25 May 2025