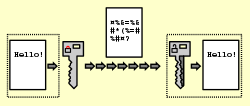
adaptive offline adversary. For randomized online algorithms competitiveness can depend upon the adversary model used. The three common adversaries are the oblivious...
3 KB (285 words) - 22:17, 14 December 2020
cryptosystem from achieving their goal Adversary model, in online algorithms, used to show competitiveness of randomized algorithms Adversarial alignment, when an...
1 KB (178 words) - 06:46, 6 June 2024
matrix representation adversary algorithm algorithm BSTW algorithm FGK algorithmic efficiency algorithmically solvable algorithm V all pairs shortest path...
35 KB (3,135 words) - 18:46, 6 May 2025
A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that employs a degree of randomness as part of its logic or procedure. The algorithm typically uses uniformly random...
33 KB (4,256 words) - 16:11, 5 August 2025
Message authentication code (redirect from Message Authentication Algorithm)
prevent forgery by adversaries without knowledge of the secret key, this is insufficient in certain scenarios. When an adversary is able to control the...
16 KB (1,918 words) - 14:30, 11 July 2025
bipartite matching Adversary model Dynamic algorithm Prophet inequality Real-time computing Streaming algorithm Sequential algorithm Online machine learning/Offline...
6 KB (708 words) - 13:17, 23 June 2025
RSA cryptosystem (redirect from RSA algorithm)
Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, who publicly described the algorithm in 1977. An equivalent system was developed secretly in 1973 at Government...
69 KB (8,479 words) - 16:34, 10 August 2025
List update problem (category Analysis of algorithms)
Performance of algorithms depend on the construction of request sequences by adversaries under various adversary models An online algorithm for this problem...
9 KB (1,339 words) - 07:23, 21 July 2025
In computer science, a selection algorithm is an algorithm for finding the k {\displaystyle k} th smallest value in a collection of ordered values, such...
45 KB (5,755 words) - 20:59, 28 January 2025
Encryption (redirect from Encryption algorithm)
encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but...
34 KB (3,645 words) - 19:23, 28 July 2025
By treating opponents as a unified adversary whose payoff is the opposite of the focal player’s payoff, the algorithm can apply branch and bound techniques...
2 KB (272 words) - 19:35, 24 May 2025
receiver confidentially, in spite of eavesdropping and intercepting adversaries. Modern standards for public-key encryption of arbitrary messages are...
36 KB (4,176 words) - 16:36, 10 August 2025
recover a cipher's key. It is defined as the probability that the adversary algorithm can guess a cipher's randomly selected key, given a fixed amount...
3 KB (329 words) - 16:51, 24 January 2025
MR 1471991, S2CID 13403194. Algorithms: Dasgupta, Papadimitriou, Vazirani Vazirani, Umesh Virkumar (1986-01-01). Randomness, Adversaries and Computation. University...
7 KB (547 words) - 02:53, 23 September 2024
The randomized weighted majority algorithm is an algorithm in machine learning theory for aggregating expert predictions to a series of decision problems...
15 KB (2,401 words) - 05:15, 30 December 2023
for on-line and randomized algorithms, which are typically data dependent. In competitive analysis, one imagines an "adversary" which deliberately chooses...
6 KB (794 words) - 12:55, 19 March 2024
oracle. Say that an adversary algorithm has access to an oracle that will apply a function to inputs that are sent to it. The algorithm sends the oracle...
2 KB (236 words) - 23:21, 18 July 2025
Theoretical computer science (section Algorithms)
parties (called adversaries). More generally, it is about constructing and analyzing protocols that overcome the influence of adversaries and that are related...
42 KB (4,801 words) - 23:57, 1 June 2025
Alpha–beta pruning (category Graph algorithms)
Alpha–beta pruning is a search algorithm that seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is an...
19 KB (2,408 words) - 13:17, 20 July 2025
cryptographic algorithms are designed around computational hardness assumptions, making such algorithms hard to break in actual practice by any adversary. While...
101 KB (11,139 words) - 05:17, 7 August 2025
Block cipher (redirect from Codebook algorithm)
In cryptography, a block cipher is a deterministic algorithm that operates on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks. Block ciphers are the elementary...
51 KB (6,569 words) - 07:54, 3 August 2025
method is an algorithmic technique most commonly used for decision making and prediction, and also widely deployed in game theory and algorithm design. The...
24 KB (3,696 words) - 01:18, 3 June 2025
Cryptographic hash function (redirect from Message-digest algorithm)
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n {\displaystyle...
49 KB (6,300 words) - 10:48, 24 July 2025
determined by an algorithm defined in advance, and known by both Bob and Alice. The correct response might be as simple as "63x83z", with the algorithm changing...
11 KB (1,540 words) - 09:38, 23 June 2025
Quantum computing (redirect from Quantum search algorithms)
security. Quantum algorithms then emerged for solving oracle problems, such as Deutsch's algorithm in 1985, the Bernstein–Vazirani algorithm in 1993, and Simon's...
114 KB (12,541 words) - 06:48, 6 August 2025
Universal hashing (category Search algorithms)
In mathematics and computing, universal hashing (in a randomized algorithm or data structure) refers to selecting a hash function at random from a family...
29 KB (4,886 words) - 10:51, 16 June 2025
Quicksort (category Divide-and-conquer algorithms)
sorting algorithm. Quicksort was developed by British computer scientist Tony Hoare in 1959 and published in 1961. It is still a commonly used algorithm for...
73 KB (10,091 words) - 13:13, 11 July 2025
Timing attack (section String comparison algorithms)
compromise a cryptosystem by analyzing the time taken to execute cryptographic algorithms. Every logical operation in a computer takes time to execute, and the...
13 KB (1,541 words) - 14:52, 6 August 2025
computer science, a distribution is pseudorandom against a class of adversaries if no adversary from the class can distinguish it from the uniform distribution...
7 KB (858 words) - 05:44, 9 January 2025
Trapdoor function (redirect from Trapdoor algorithm)
mechanism that is added to a cryptographic algorithm (e.g., a key pair generation algorithm, digital signing algorithm, etc.) or operating system, for example...
9 KB (1,316 words) - 00:34, 25 June 2024