 | Oxidative phosphorylation (redirect from ATP generation) energy gradient, through a large enzyme called ATP synthase in a process called chemiosmosis. The ATP synthase uses the energy to transform adenosine diphosphate... 85 KB (9,411 words) - 21:47, 31 March 2024 |
 | ATPase (redirect from ATP monophosphatase) F0F1-ATP Synthase) is a charge-transferring complex that catalyzes ATP to perform ATP synthesis by moving ions through the membrane. The coupling of ATP hydrolysis... 18 KB (2,143 words) - 23:05, 27 February 2024 |
electrochemical gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP via coupling with oxidative phosphorylation with ATP synthase. In eukaryotic organisms, the electron transport... 33 KB (4,063 words) - 12:57, 22 April 2024 |
 | Thylakoid (section ATP synthase) Cytochrome b6f complex ATP synthase Photosystem II is located mostly in the grana thylakoids, whereas photosystem I and ATP synthase are mostly located in... 37 KB (4,369 words) - 00:37, 13 March 2024 |
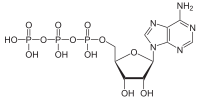
 | Adenosine triphosphate (redirect from ATP thermochemistry) electron transport chain and result in the generation of additional ATP by ATP synthase. The pyruvate generated as an end-product of glycolysis is a substrate... 46 KB (5,062 words) - 17:08, 19 April 2024 |
Proton pump (section ATP-driven proton pumps) potential that the ATP synthase of mitochondria then uses to synthesize ATP.[citation needed] Proton pumps driven by adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (also referred... 13 KB (1,530 words) - 01:29, 14 January 2024 |
 | of the cell involves the synthesis of ATP by an enzyme called ATP synthase. In aerobic respiration, ATP synthase is coupled with an electron transport... 8 KB (715 words) - 07:52, 16 January 2024 |
'ligase'. ATP synthase Citrate synthase Tryptophan synthase Pseudouridine synthase Fatty acid synthase Cellulose synthase (UDP-forming) Cellulose synthase (GDP-forming)... 1 KB (120 words) - 21:07, 7 February 2024 |
 | force, used by ATP synthase to form ATP. In cyclic photophosphorylation, cytochrome b6f uses electrons and energy from PSI to create more ATP and to stop... 28 KB (3,452 words) - 22:04, 10 April 2024 |
ATP synthase. The ATP synthase works by a rotary mechanism. The ATP generated will be dependent on the amount of ATP produced per rotation of the ATP... 5 KB (761 words) - 15:26, 11 October 2023 |
 | Photophosphorylation (section ATP and reactions) NADPH. Both the structure of ATP synthase and its underlying gene are remarkably similar in all known forms of life. ATP synthase is powered by a transmembrane... 11 KB (1,381 words) - 01:30, 25 March 2024 |
 | Gamma subunit of ATP synthase F1 complex forms the central shaft that connects the Fo rotary motor to the F1 catalytic core. F-ATP synthases (also known as... 3 KB (405 words) - 06:48, 2 January 2021 |
 | MT-ATP6 (redirect from ATP synthase chain A) with the full name 'mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase membrane subunit 6' that encodes the ATP synthase Fo subunit 6 (or subunit/chain A). This subunit... 24 KB (3,097 words) - 07:09, 15 April 2024 |
both cellular respiration and photosynthesis by ATP synthase. ATP synthase couples the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate with an electrochemical... 24 KB (2,528 words) - 15:02, 22 February 2024 |
 | 'mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase membrane subunit 8' that encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase, ATP synthase Fo subunit 8 (or subunit... 24 KB (2,791 words) - 07:10, 15 April 2024 |
membrane through ATP synthase. Using their kinetic energy to escape, the protons will spin the ATP synthase which in turn will create ATP. This happens in... 11 KB (1,500 words) - 09:09, 18 September 2023 |
 | complex is the main transmembrane subunit of V-type, A-type and F-type ATP synthases. Subunit C (also called subunit 9, or proteolipid in F-ATPases, or... 6 KB (789 words) - 19:26, 3 December 2022 |
 | produce a bisbenzyl ketone. DCC is a classical inhibitor of ATP synthase. DCC inhibits ATP synthase by binding to one of the c subunits and causing steric... 11 KB (993 words) - 15:48, 14 April 2024 |
 | ATP citrate synthase (also ATP citrate lyase (ACLY)) is an enzyme that in animals represents an important step in fatty acid biosynthesis. By converting... 13 KB (1,471 words) - 11:45, 12 March 2024 |









