 | Reptiliomorpha (section Origin of amniotes) Pan-Amniota) is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians)... 28 KB (2,956 words) - 19:56, 21 March 2024 |
 | (/tɛˈtræpədə/). Tetrapods include all extant and extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn evolving into two major clades, the sauropsids... 101 KB (10,229 words) - 14:34, 6 April 2024 |
 | Egg (section Amniote eggs and embryos) Like amphibians, amniotes are air-breathing vertebrates, but they have complex eggs or embryos, including an amniotic membrane. Amniotes include reptiles... 41 KB (4,668 words) - 21:16, 6 January 2024 |
 | The primitive streak is a structure that forms in the early embryo in amniotes. In amphibians, the equivalent structure is the blastopore. During early... 23 KB (2,803 words) - 21:33, 7 April 2024 |
 | fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves... 16 KB (1,928 words) - 21:08, 19 April 2024 |
 | (lissamphibians, as well as the extinct temnospondyls and lepospondyls) Amniotes or true land vertebrates Sauropsids (reptiles and birds, as well as the... 77 KB (7,023 words) - 02:52, 10 April 2024 |
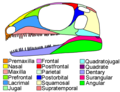 | the Taxonomic Position of Mesosaurs, and a Surprising Phylogeny of Early Amniotes" (PDF). Frontiers in Earth Science. 5: 88. Bibcode:2017FrEaS...5...88L... 13 KB (878 words) - 03:13, 19 April 2024 |
conditions. Amniotes, however, prospered due to specific key adaptations. One of the greatest evolutionary innovations of the Carboniferous was the amniote egg... 13 KB (1,145 words) - 16:23, 11 April 2024 |
 | PMID 23653398. Laurin, M.; Reisz, R.R. (1995). "A reevaluation of early amniote phylogeny". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 113 (2): 165–223... 26 KB (591 words) - 19:43, 7 February 2024 |
 | lay their eggs in aquatic environments. They are distinguished from the amniotes (reptiles, birds and mammals), which can reproduce on dry land either by... 6 KB (606 words) - 02:26, 10 April 2024 |
 | Mammal (section Evolution from older amniotes) water in. Hence, amniotes can lay eggs on dry land, while amphibians generally need to lay their eggs in water. The first amniotes apparently arose in... 212 KB (22,683 words) - 14:21, 20 April 2024 |
 | Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was... 112 KB (11,539 words) - 20:44, 26 April 2024 |
 | the only group that survived into the Cenozoic are mammals. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull... 55 KB (5,615 words) - 04:25, 24 April 2024 |
 | it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all tetrapods, excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds, and... 158 KB (17,759 words) - 16:52, 11 April 2024 |
snake in the Harry Potter series Nagini mazonense, an extinct species of amniote Nagin (disambiguation) Nagina (disambiguation) Naga (disambiguation) Ichchadhari... 662 bytes (111 words) - 15:01, 2 July 2022 |
 | bird to have ever lived, with their eggs being the largest known for any amniote. Elephant birds are palaeognaths (whose flightless representatives are... 34 KB (3,422 words) - 12:51, 15 April 2024 |














