The carbonate compensation depth (CCD) is the depth, in the oceans, at which the rate of supply of calcium carbonates matches the rate of solvation. That... 11 KB (1,363 words) - 16:25, 7 December 2023 |
the consequent rise of the carbonate compensation depth (CCD) and a crisis of carbonate precipitation (e.g. demise of carbonate platforms in the western... 43 KB (4,985 words) - 07:10, 15 April 2024 |
 | Lysocline (section Calcite compensation depth) The lysocline is the depth in the ocean dependent upon the carbonate compensation depth (CCD), usually around 5 km, below which the rate of dissolution... 6 KB (682 words) - 12:45, 28 November 2023 |
 | Ocean acidification (redirect from Carbonate compensation) Below this depth, Ω has a value less than 1, and CaCO 3 will dissolve. The carbonate compensation depth is the ocean depth at which carbonate dissolution... 139 KB (14,781 words) - 22:23, 17 April 2024 |
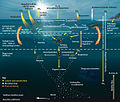 | Biological pump (redirect from Carbonate pump) as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calculations... 145 KB (16,299 words) - 20:02, 23 April 2024 |
 | Dissolved inorganic carbon (section Carbonate pump) simple compounds such as carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate, and carbonate (CO2, H2CO3, HCO− 3, CO2− 3 respectively). Dissolved inorganic carbon... 12 KB (1,233 words) - 22:48, 9 June 2023 |
conditions with respect to calcium carbonate) and above the carbonate compensation depth (below which there is no calcium carbonate preservation). In a supersaturated... 49 KB (5,362 words) - 12:23, 19 April 2024 |
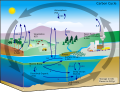
 | carbonate–silicate geochemical cycle, also known as the inorganic carbon cycle, describes the long-term transformation of silicate rocks to carbonate... 21 KB (2,540 words) - 10:01, 13 August 2023 |
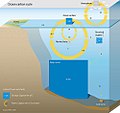 | Oceanic carbon cycle (section Carbonate pump) through the oceans. These three pumps are: (1) the solubility pump, (2) the carbonate pump, and (3) the biological pump. The total active pool of carbon at... 57 KB (6,298 words) - 17:07, 10 January 2024 |
 | type of ooze accumulates on the ocean floor at depths above the carbonate compensation depth. It accumulates more rapidly than any other pelagic sediment... 9 KB (919 words) - 20:09, 1 March 2023 |
cameras .ccd, the filename extension for CloneCD's CD image file Carbonate compensation depth, a property of oceans Colony collapse disorder, a phenomenon... 3 KB (420 words) - 02:56, 14 February 2024 |
 | crust by injecting it into the subsurface, or in the form of insoluble carbonate salts. This is because they are removing carbon from the atmosphere and... 51 KB (5,731 words) - 08:49, 11 April 2024 |
 | latter representing the amount of non-organic carbon, like carbon in carbonate minerals. Subtracting the inorganic carbon from the total carbon yields... 30 KB (3,901 words) - 15:16, 9 January 2024 |
 | carbonate compensation depth aragonite compensation depth lysocline calcareous ooze Carbonate pump Marine biogenic calcification snowline: the depth at... 60 KB (6,029 words) - 21:10, 4 January 2024 |