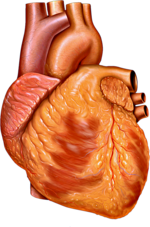
| Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and... 42 KB (5,108 words) - 13:34, 28 April 2024 |
 | smooth, and cardiac (cardiomyocytes). A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells develop... 37 KB (4,515 words) - 23:27, 19 March 2024 |
 | new "Start" of the cardiac cycle. Throughout the cardiac cycle, blood pressure increases and decreases. The movements of cardiac muscle are coordinated by... 20 KB (1,882 words) - 12:31, 3 April 2024 |
 | Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group... 46 KB (5,430 words) - 18:10, 24 April 2024 |
 | types of striated muscle: Cardiac muscle (heart muscle) Skeletal muscle (muscle attached to the skeleton) Striated muscle tissue contains T-tubules which... 8 KB (944 words) - 19:41, 19 January 2024 |
Muscular system (redirect from Muscle system) muscular system is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates... 15 KB (1,733 words) - 09:20, 10 March 2024 |
 | Troponin (section Cardiac conditions) T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-specific troponins I and... 30 KB (3,649 words) - 19:25, 19 April 2024 |
GLUT4 (section Cardiac muscle) transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac). The first evidence for this distinct glucose transport protein... 25 KB (2,937 words) - 17:58, 15 January 2024 |
occur at each ventricular systole. Cardiac muscle tissue has autorhythmicity, the unique ability to initiate a cardiac action potential at a fixed rate... 47 KB (5,784 words) - 11:54, 12 June 2023 |
Syncytium (section Cardiac muscle) syncytium of cardiac muscle is important because it allows rapid coordinated contraction of muscles along their entire length. Cardiac action potentials... 18 KB (2,042 words) - 16:03, 26 November 2023 |
 | Intercalated disc (category Cardiac anatomy) Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated... 6 KB (548 words) - 15:50, 14 February 2024 |
 | of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. With membranes that contain large concentrations of ion channels... 25 KB (3,239 words) - 08:24, 3 March 2024 |
 | Troponin I is a cardiac and skeletal muscle protein family. It is a part of the troponin protein complex, where it binds to actin in thin myofilaments... 18 KB (2,154 words) - 07:37, 20 April 2024 |
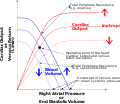
Myocardial contractility (redirect from Cardiac contractility) Myocardial contractility represents the innate ability of the heart muscle (cardiac muscle or myocardium) to contract. The ability to produce changes in force... 7 KB (842 words) - 18:26, 28 December 2023 |
Cardiac fibrosis commonly refers to the excess deposition of extracellular matrix in the cardiac muscle, but the term may also refer to an abnormal thickening... 25 KB (2,834 words) - 02:11, 15 November 2023 |
 | moderator band (also known as septomarginal trabecula) is a band of cardiac muscle found in the right ventricle of the heart. It is well-marked in sheep... 4 KB (380 words) - 10:09, 29 February 2024 |
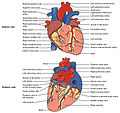 | Coronary circulation (redirect from Cardiac vessels) veins that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood... 16 KB (1,977 words) - 21:49, 28 November 2023 |
 | Atrial natriuretic peptide (section Cardiac) increasing renal sodium excretion. ANP is synthesized and secreted by cardiac muscle cells in the walls of the atria in the heart. These cells contain volume... 32 KB (3,832 words) - 00:31, 24 March 2024 |