 | Charon (/ˈkɛərɒn, -ən/ KAIR-on, -ən or /ˈʃærən/ SHAIR-ən), known as (134340) Pluto I, is the largest of the five known natural satellites of the dwarf... 51 KB (5,207 words) - 23:18, 30 April 2024 |
 | Moons of Pluto (redirect from Pluto's Natural Satellite) planet Pluto has five natural satellites. In order of distance from Pluto, they are Charon, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. Charon, the largest, is mutually... 38 KB (3,586 words) - 02:33, 26 April 2024 |
 | of dwarf planets, Charon has the largest ratio, being 0.52 the diameter and 12.2% the mass of Pluto. The first known natural satellite was the Moon, but... 43 KB (3,565 words) - 13:50, 26 March 2024 |
 | Pluto (redirect from Pluto-Charon system) thought before Charon was discovered. The discovery of Pluto's satellite Charon in 1978 enabled a determination of the mass of the Pluto–Charon system by application... 162 KB (14,009 words) - 10:33, 19 April 2024 |
 | Hydra (moon) (redirect from Hydra (satellite)) × 40 km (34 mi × 25 mi). List of natural satellites The instantaneous force at Hydra's distance in the Pluto–Charon–Hydra alignment case is 4.62% larger than... 26 KB (2,599 words) - 08:42, 26 September 2023 |
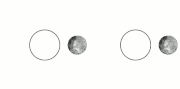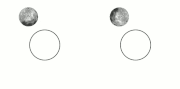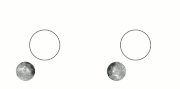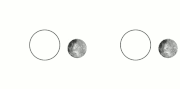 | example is the dwarf planet Pluto and its satellite Charon. They have already reached a state where Charon is visible from only one hemisphere of Pluto... 47 KB (5,074 words) - 18:11, 26 April 2024 |
 | Dysnomia (moon) (redirect from Dysnomia (satellite)) Eris and is the second-largest known moon of a dwarf planet, after Pluto I Charon. It was discovered in September 2005 by Mike Brown and the Laser Guide Star... 21 KB (1,965 words) - 09:46, 4 March 2024 |
 | Kerberos (moon) (redirect from Kerberos (satellite)) {\textstyle P_{C}=6.3872304\,d} is Charon's period. Showalter, M. R.; Hamilton, D. P. (20 July 2011). "New Satellite of (134340) Pluto: S/2011 (134340)... 21 KB (1,926 words) - 15:18, 10 April 2024 |
 | Dwarf planet (section Charon) The IAU currently says Charon is not considered a dwarf planet but rather a satellite of Pluto, though the idea that Charon might qualify as a dwarf... 96 KB (8,944 words) - 14:11, 27 April 2024 |
 | Moon (redirect from Luna (satellite)) the minor-planet moon Charon of the Pluto-Charon system is larger relative to Pluto, the Moon is the largest natural satellite of the Solar System relative... 255 KB (24,730 words) - 03:09, 1 May 2024 |
 | Styx (moon) (redirect from Styx (satellite)) them Charon, Styx, and Cerberus. Upon discovery, Styx received the minor planet designation S/2012 (134340) 1 because it was the first satellite (S) discovered... 20 KB (1,732 words) - 00:27, 26 September 2023 |
 | Nix (moon) (redirect from Nix (satellite)) Leslie A.; Stern, S. Alan (2006). "Orbits and Photometry of Pluto's Satellites: Charon, S/2005 P1, and S/2005 P2". The Astronomical Journal. 132 (1): 290–298... 28 KB (2,605 words) - 07:52, 8 February 2024 |
 | Moons of Neptune (redirect from Satellite of Neptune) body in question. Binary objects, objects with moons such as the Pluto–Charon system, are quite common among the larger trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs)... 50 KB (4,349 words) - 01:16, 1 May 2024 |
 | Minor-planet moon (category Minor planet satellites) binary after Pluto–Charon, 1998 WW31, was optically resolved in 2002. In 2005, the asteroid 87 Sylvia was discovered to have two satellites, making it the... 132 KB (2,467 words) - 01:34, 30 April 2024 |
 | its moon Charon. The barycenter of those two bodies is always outside Pluto's surface. This has led some astronomers to call the Pluto–Charon system a... 3 KB (351 words) - 01:58, 22 October 2023 |
 | James W. Christy (redirect from Discoverer of Charon) (born September 15, 1938) is an American astronomer known for discovering Charon, the largest moon of the dwarf planet Pluto. Christy was born in 1938 in... 7 KB (609 words) - 21:46, 1 September 2023 |
 | Orbital resonance (redirect from Satellite resonances) of Charon's orbit (see Pluto's natural satellites for details). The near resonances may be maintained by a 15% local fluctuation in the Pluto-Charon gravitational... 97 KB (10,244 words) - 23:04, 2 April 2024 |
 | Vanth (moon) (redirect from Vanth (satellite)) which the two bodies revolve around the barycenter, much like the Pluto–Charon system. It is hypothesized that both systems formed similarly, most likely... 35 KB (3,367 words) - 16:47, 15 April 2024 |
 | Hiʻiaka (moon) (redirect from Hi'iaka (satellite)) after Pluto I Charon, Eris I Dysnomia, Orcus I Vanth, and possibly Varda I Ilmarë and Salacia I Actaea. Hiʻiaka was the first satellite discovered around... 6 KB (520 words) - 21:09, 3 December 2023 |
 | Planetary-mass moon (redirect from Satellite planet) moons (Umbriel, Ariel and Miranda) is unclear, as is that of Pluto's moon Charon. The TNO moons Eris I Dysnomia, Orcus I Vanth, and possibly Varda I Ilmarë... 29 KB (2,200 words) - 16:39, 2 April 2024 |
 | Actaea (moon) (redirect from Actaea (satellite)) is about the sixth-biggest known moon of a trans-Neptunian object, after Charon (1212 km), Dysnomia (700 km), Vanth (443 km), Ilmarë (326 km) and Hiʻiaka... 7 KB (604 words) - 01:53, 6 March 2024 |
 | 90482 Orcus (section Satellite) trans-Neptunian object or icy satellite of the outer planets other than Miranda. The 1.65 μm band on Orcus is broad and deep (12%), as on Charon, Quaoar, Haumea, and... 42 KB (3,832 words) - 23:33, 25 April 2024 |
moon Charon. Much more commonly, synchronous orbits are employed by artificial satellites used for communication, such as geostationary satellites. For... 5 KB (574 words) - 15:28, 6 August 2023 |
 | Io (moon) (redirect from Satellite Io) designation (a system introduced by Galileo) as "Jupiter I", or as "the first satellite of Jupiter". The customary English pronunciation of the name is /ˈaɪoʊ/... 112 KB (12,388 words) - 03:07, 26 April 2024 |
 | Titan (moon) (redirect from Titan (satellite)) Titan was the first known moon of Saturn, and the sixth known planetary satellite (after Moon Earth's moon and the four Galilean moons of Jupiter). Titan... 173 KB (16,586 words) - 21:24, 1 May 2024 |




