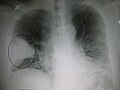
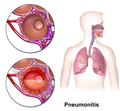
Chemical pneumonitis is inflammation of the lung caused by aspirating or inhaling irritants. It is sometimes called a "chemical pneumonia", though it... 5 KB (502 words) - 11:52, 13 March 2023 |
 | Lobar pneumonia is a form of pneumonia characterized by inflammatory exudate within the intra-alveolar space resulting in consolidation that affects a... 7 KB (720 words) - 01:48, 14 May 2022 |
Atypical pneumonia, also known as walking pneumonia, is any type of pneumonia not caused by one of the pathogens most commonly associated with the disease... 12 KB (1,224 words) - 01:05, 31 January 2024 |
Viral pneumonia is a pneumonia caused by a virus. Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in one or both of the lungs. The pulmonary alveoli... 13 KB (1,380 words) - 19:30, 5 January 2024 |
 | Fungal pneumonia is an infection of the lungs by fungi. It can be caused by either endemic or opportunistic fungi or a combination of both. Case mortality... 6 KB (618 words) - 20:13, 25 August 2022 |
 | Bronchopneumonia (redirect from Bronchial pneumonia) Bronchopneumonia is a subtype of pneumonia. It is the acute inflammation of the bronchi, accompanied by inflamed patches in the nearby lobules of the... 5 KB (409 words) - 18:15, 21 October 2023 |
 | Turpentine (category Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID) diarrhea, tachycardia, unconsciousness, respiratory failure, and chemical pneumonia. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set... 23 KB (2,237 words) - 14:07, 17 April 2024 |
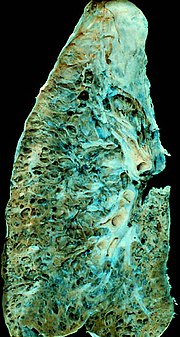 | Interstitial lung disease (redirect from Interstitial pneumonia) eosinophilic pneumonia Acute interstitial pneumonia Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia Chronic: Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia Lymphoproliferative... 23 KB (2,153 words) - 06:26, 6 January 2024 |
Mycoplasma pneumonia is a form of bacterial pneumonia caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. M. pneumoniae is known to cause a host of symptoms... 18 KB (1,963 words) - 01:37, 16 December 2023 |
 | Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the... 11 KB (1,185 words) - 01:51, 11 December 2023 |
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) refers to pneumonia (any of several lung diseases) contracted by a person outside of the healthcare system. In contrast... 36 KB (4,300 words) - 01:22, 8 January 2024 |
results in eosinophilic pneumonia. Chemicals such as sulfites, aluminum silicate, and cigarette smoke can cause eosinophilic pneumonia when inhaled. A New... 15 KB (1,740 words) - 12:26, 15 February 2022 |
 | categories. Aspiration hazard includes severe acute effects such as chemical pneumonia, varying degrees of pulmonary injury or death following aspiration... 41 KB (4,664 words) - 11:03, 24 April 2024 |
 | Chlamydia (redirect from Chlamydial pneumonia) lead to blindness; and pneumonia. Conjunctivitis due to chlamydia typically occurs one week after birth (compared with chemical causes (within hours) or... 45 KB (4,145 words) - 15:40, 11 April 2024 |
 | Pneumococcal vaccine (redirect from Pneumonia vaccine) bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. Their use can prevent some cases of pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. There are two types of pneumococcal vaccines:... 35 KB (3,344 words) - 03:01, 21 April 2024 |
 | Streptococcus pneumoniae (redirect from Streptococcus pneumonia) pathogenic bacterium S. pneumoniae was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity... 32 KB (3,364 words) - 21:23, 15 April 2024 |
Hydrocarbon pneumonitis (redirect from Hydrocarbon pneumonia) require several weeks for complete resolution. Symptoms of chemical (hydrocarbon) pneumonia may include: burning of the nose, eyes, lips, mouth, and throat... 5 KB (603 words) - 13:41, 12 February 2019 |
 | at all, to chemical pneumonitis or pneumonia, to death within minutes from asphyxiation. These consequences depend on the volume, chemical composition... 19 KB (2,101 words) - 19:44, 24 April 2024 |
 | The use of toxic chemicals as weapons dates back thousands of years, but the first large-scale use of chemical weapons was during World War I. They were... 86 KB (10,194 words) - 00:14, 20 April 2024 |