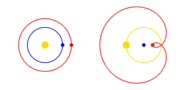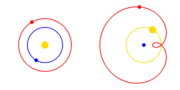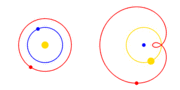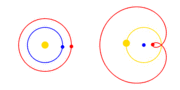
 | The Copernican Revolution was the paradigm shift from the Ptolemaic model of the heavens, which described the cosmos as having Earth stationary at the... 31 KB (3,768 words) - 15:36, 4 May 2024 |
 | Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center... 40 KB (4,778 words) - 17:39, 23 April 2024 |
 | Immanuel Kant (redirect from Copernican turn) Reason (1781/1787), his best-known work. Kant drew a parallel to the Copernican revolution in his proposal to think of the objects of experience as conforming... 153 KB (18,689 words) - 05:09, 4 May 2024 |
 | Heliocentrism (redirect from Copernican heliocentric system) astronomer, and Catholic cleric, Nicolaus Copernicus, leading to the Copernican Revolution. In the following century, Johannes Kepler introduced elliptical... 99 KB (11,812 words) - 20:54, 1 May 2024 |
 | Cosmos (section Copernican Revolution) positioned the Sun as the center of the Universe. Prior to the Copernican Revolution, the Ptolemaic system, also known as the geocentric model, was widely... 38 KB (4,479 words) - 08:11, 9 May 2024 |
The Copernican Revolution is the scientific paradigm shift from the Earth-centric model of the universe to the heliocentric model of the Solar System... 417 bytes (81 words) - 21:29, 29 January 2023 |
The Copernican Revolution is a 1957 book by the philosopher Thomas Kuhn, in which the author provides an analysis of the Copernican Revolution, documenting... 12 KB (1,406 words) - 14:51, 15 February 2024 |
 | History of astronomy (section Copernican Revolution) completely separated in Europe (see astrology and astronomy) during the Copernican Revolution starting in 1543. In some cultures, astronomical data was used for... 81 KB (10,061 words) - 14:55, 4 March 2024 |
Newton's laws of motion (category Copernican Revolution) Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide... 121 KB (15,363 words) - 05:12, 4 April 2024 |
"map" directing new research. For example, Kuhn's analysis of the Copernican Revolution emphasized that, in its beginning, it did not offer more accurate... 59 KB (7,776 words) - 15:55, 20 March 2024 |
 | Geocentric model (category Copernican Revolution) Michael J. (1990). Theories of the World from Antiquity to the Copernican Revolution. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications. ISBN 0486261735. Dreyer, J.L.E... 75 KB (8,814 words) - 19:23, 7 May 2024 |
 | Nicolaus Copernicus (category Copernican Revolution) the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution... 157 KB (18,094 words) - 23:46, 3 May 2024 |
 | Johannes Kepler (category Copernican Revolution) Lexicon, Cambridge University Press, 2016, "Inertia." Kuhn, The Copernican Revolution, pp. 238, 246–252 Frautschi, Steven C.; Olenick, Richard P.; Apostol... 100 KB (12,450 words) - 22:52, 8 May 2024 |
 | Tychonic system (category Copernican Revolution) century, which combines what he saw as the mathematical benefits of the Copernican system with the philosophical and "physical" benefits of the Ptolemaic... 21 KB (2,798 words) - 12:50, 15 April 2024 |
 | Galileo Galilei (category Copernican Revolution) sunspots. He also built an early microscope. Galileo's championing of Copernican heliocentrism was met with opposition from within the Catholic Church... 133 KB (16,374 words) - 20:58, 9 May 2024 |
 | Earth's orbit (redirect from Earth revolution) had presented his geocentric model in the second century. This "Copernican Revolution" resolved the issue of planetary retrograde motion by arguing that... 17 KB (1,834 words) - 05:28, 17 March 2024 |
 | Galileo affair (category Copernican Revolution) computations that made use of Copernicus' work." Thomas Kuhn (1957). The Copernican Revolution. Harvard University Press. p. 125. Four Treatises for the Reconsideration... 97 KB (10,397 words) - 20:32, 27 April 2024 |
emphasising that such a revolution is "incomplete." Freud, who repeatedly compared the psychoanalytic discovery to a Copernican revolution, was for Laplanche... 23 KB (2,822 words) - 15:03, 23 January 2024 |
 | And yet it moves (category Copernican Revolution) "And yet it moves" or "Although it does move" (Italian: E pur si muove or Eppur si muove [epˈpur si ˈmwɔːve]) is a phrase attributed to the Italian mathematician... 7 KB (756 words) - 21:39, 7 May 2024 |
 | Isaac Newton (category Copernican Revolution) time as a natural philosopher. He was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His pioneering book Philosophiæ Naturalis... 137 KB (14,180 words) - 10:50, 25 April 2024 |
 | Kepler's laws of planetary motion (category Copernican Revolution) Kepler's third law was published in 1619. Kepler had believed in the Copernican model of the Solar System, which called for circular orbits, but he could... 56 KB (8,294 words) - 01:32, 9 May 2024 |
 | Tycho Brahe (category Copernican Revolution) Scientific Revolution. An heir to several noble families, Tycho was well educated. He worked to combine what he saw as the geometrical benefits of Copernican heliocentrism... 96 KB (12,236 words) - 08:33, 9 May 2024 |
 | Hans Lipperhey (category Copernican Revolution) Hans Lipperhey (c. 1570 – buried 29 September 1619), also known as Johann Lippershey or Lippershey, was a German-Dutch spectacle-maker. He is commonly... 9 KB (911 words) - 00:11, 28 March 2024 |
 | Finding Our Place in the Solar System: The Scientific Story of the Copernican Revolution. Cambridge University Press. p. 33. ISBN 9781107182295. Archived... 64 KB (6,473 words) - 07:32, 23 April 2024 |
ancient times. The modern form of the concept emerged when the Copernican Revolution demonstrated that the Earth was a planet revolving around the Sun... 14 KB (1,509 words) - 20:24, 2 May 2024 |
M. A. Orr, Dante and the Medieval Astronomers (1956) Thomas Kuhn, The Copernican Revolution (1957) The Geocentric or Ptolemaic Notion of the Universe... 4 KB (465 words) - 14:12, 25 April 2024 |



