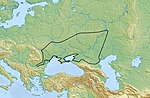
| The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the... 76 KB (8,518 words) - 22:15, 5 May 2024 |
particular archaeological culture or other typological unit, which is often named after it. For example, discoveries at La Tène and Hallstatt led scholars to divide... 4 KB (428 words) - 06:34, 2 March 2024 |
 | the Hallstatt culture – as supported by the known homelands of La Tène culture. The culture came to an end with the advent of the Hallstatt culture. Atlantic... 6 KB (715 words) - 12:06, 5 March 2024 |
 | Salzkammergut (redirect from Hallstatt-Dachstein / Salzkammergut Cultural Landscape) in use at least since the days of the Celtic Hallstatt culture, centered at the mining town of Hallstatt. These operations were continued by the Romans... 15 KB (1,563 words) - 17:11, 6 April 2024 |
the period of the Hallstatt culture (Ha D) as well as the early La Tène culture (Lt A and B). The expression “Hunsrück-Eifel culture” was coined in 1914... 6 KB (770 words) - 09:32, 4 February 2024 |
 | Etruscan civilization (redirect from Etruscan culture) in common with Hallstatt-Celtic skulls from North Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg but rather with Hallstatt-Celtic skulls from Hallstatt in Austria. Compared... 100 KB (10,734 words) - 12:14, 1 May 2024 |
 | Villanovan culture to the Central European Urnfield culture (c. 1300–750 BC) and Celtic Hallstatt culture that succeeded the Urnfield culture. It is not... 18 KB (1,527 words) - 17:19, 1 May 2024 |
 | The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished c. 2000–1150 BC, spanning from the southern Urals to the... 63 KB (7,041 words) - 15:09, 4 May 2024 |
 | with a likely Celtic substratum given the similarities with the Hallstatt culture. He made several trips there bringing back to France part of the Abbot... 20 KB (2,182 words) - 22:30, 7 April 2024 |
 | Celts (redirect from Ancient Celtic culture) Age Hallstatt culture which followed it (c. 1200–500 BC), named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria, and with the following La Tène culture (c... 146 KB (16,575 words) - 03:51, 31 March 2024 |
completely new to the area and was a typical example of the western Hallstatt culture. The name comes from the locality of Canegrate in Lombardy, south... 13 KB (1,455 words) - 07:57, 8 April 2024 |
Iron Age Europe (category CS1 German-language sources (de)) Central Europe the Urnfield culture had already given way to the Hallstatt culture. In north Italy the Villanovan culture is regarded as the start of... 33 KB (4,327 words) - 18:47, 5 April 2024 |
 | Kurgan hypothesis (redirect from Kurgan culture) prehistoric cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave) culture and its predecessors. In the 2000s, David Anthony instead used the core Yamnaya culture and... 34 KB (3,825 words) - 14:41, 30 April 2024 |
 | the Hallstatt culture, this amber found its way to the Villanovan culture. In return, the Germanic peoples imported salt from the Hallstatt culture. The... 124 KB (15,692 words) - 16:31, 7 May 2024 |
 | by F. Klopfleisch; however, he incorrectly dated the monument to the Hallstatt during the Iron Age. In subsequent years, a main cluster of Úněticean... 77 KB (8,228 words) - 14:54, 5 May 2024 |
Afanasievo culture, or Afanasevo culture (Afanasevan culture) (Russian: Афанасьевская культура Afanas'yevskaya kul'tura), is an early archaeological culture of... 62 KB (6,043 words) - 04:42, 11 May 2024 |
 | Italic peoples (redirect from Italic culture) Indo-European cultures. The burial characteristics relate the Proto-Villanovan culture to the Central European Urnfield culture and Celtic Hallstatt culture that... 24 KB (2,599 words) - 17:19, 1 May 2024 |
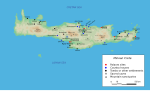 | Minoan civilization (redirect from Minoan culture) The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it... 114 KB (13,577 words) - 04:15, 28 April 2024 |
two periods based on the Hallstatt culture (early Iron Age) and La Tène (late Iron Age) cultures. Material cultures of Hallstatt and La Tène consist of... 65 KB (6,536 words) - 18:15, 25 April 2024 |
 | The Dnieper–Donets culture complex (DDCC) (ca. 5th—4th millennium BC) is a Mesolithic and later Neolithic archaeological culture found north of the Black... 22 KB (2,306 words) - 10:02, 11 April 2024 |