In geology, a deformation mechanism is a process occurring at a microscopic scale that is responsible for changes in a material's internal structure,... 32 KB (4,137 words) - 16:44, 31 March 2024 |
 | that operate under high stresses or high temperatures. Creep is a deformation mechanism that may or may not constitute a failure mode. For example, moderate... 64 KB (8,899 words) - 18:38, 8 May 2024 |
Different deformation modes may occur under different conditions, as can be depicted using a deformation mechanism map. Permanent deformation is irreversible;... 17 KB (2,320 words) - 19:45, 2 May 2024 |
Superplasticity (redirect from Superplastic deformation) beyond its usual breaking point, usually over about 400% during tensile deformation. Such a state is usually achieved at high homologous temperature. Examples... 35 KB (5,237 words) - 12:41, 12 February 2024 |
 | as the statues. Upon removal from seawater, the mechanism was not treated, resulting in deformational changes. On 17 May 1902, archaeologist Valerios... 126 KB (13,070 words) - 21:57, 6 May 2024 |
 | Coble creep (section Deformation mechanism maps) of diffusion creep, is a mechanism for deformation of crystalline solids. Contrasted with other diffusional creep mechanisms, Coble creep is similar to... 10 KB (1,729 words) - 19:09, 23 January 2022 |
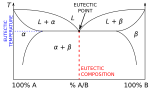 | Eutectic system (section Strengthening mechanisms) eutectic phases to resist deformation at high temperatures (see creep deformation) is more convoluted as the primary deformation mechanism changes depending on... 25 KB (3,479 words) - 00:37, 28 March 2024 |
Dislocation creep is a deformation mechanism in crystalline materials. Dislocation creep involves the movement of dislocations through the crystal lattice... 21 KB (3,101 words) - 17:02, 12 January 2024 |
 | Plasticity (physics) (redirect from Plastic Deformation) Plastic deformation is observed in most materials, particularly metals, soils, rocks, concrete, and foams. However, the physical mechanisms that cause... 29 KB (3,521 words) - 03:10, 16 April 2024 |
 | Zirconium alloys (section Deformation) doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00190-2. Tenckhoff, E (2005). "Review of Deformation Mechanisms, Texture, and Mechanical Anisotropy in Zirconium and Zirconium Base... 41 KB (4,650 words) - 03:08, 21 January 2024 |
River anticline (section Deformation mechanism) hot, thin, dry, crust to form areas of extreme uplift and exhumation. Deformation caused by tectonic aneurysms are similar to aneurysms in blood vessels... 25 KB (3,272 words) - 11:15, 31 March 2024 |
the grain – crystal scale. Strain partitioning of deformation mechanisms incorporates those mechanisms which occur both simultaneously and/or subsequently... 15 KB (1,401 words) - 13:10, 20 November 2023 |
Changed Tribological and Mechanical properties impact Scratch's deformation Mechanisms (microscopic effects of deforming a material), Scratch visibility... 18 KB (1,947 words) - 21:17, 3 January 2024 |
 | and diagenesis, pressure solution or pressure dissolution is a deformation mechanism that involves the dissolution of minerals at grain-to-grain contacts... 4 KB (395 words) - 20:46, 22 July 2023 |
 | Ductility (category Deformation (mechanics)) ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is an important consideration... 24 KB (3,084 words) - 09:18, 9 February 2024 |
 | Ductility (Earth science) (section Deformation) Crystal-Plastic Deformation Crystal-Plastic Deformation occurs at the atomic scale and is governed by its own set of specific mechanisms that deform crystals... 12 KB (1,633 words) - 09:36, 1 August 2022 |
 | Work hardening (category Strengthening mechanisms of materials) strain hardening, is the strengthening of a metal or polymer by plastic deformation. Work hardening may be desirable, undesirable, or inconsequential, depending... 19 KB (2,493 words) - 03:05, 16 April 2024 |
 | Grain boundary sliding (category Deformation (mechanics)) Grain boundary sliding (GBS) is a material deformation mechanism where grains slide against each other. This occurs in polycrystalline material under... 22 KB (2,860 words) - 09:11, 9 February 2024 |
Converter, a type of renewable energy device White etching cracks, a deformation mechanism in bearings This disambiguation page lists articles associated with... 2 KB (246 words) - 20:25, 10 March 2024 |
 | Shear zone (redirect from Zone of deformation) different deformation mechanisms reigning in the crust, i.e. the changeover from brittle (fracturing) at or near the surface to ductile (flow) deformation with... 12 KB (1,515 words) - 20:29, 5 April 2024 |
Strength of materials (category Deformation (mechanics)) material. Creep (deformation) – Tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under mechanical stress Deformation mechanism map – Microscopic... 25 KB (3,682 words) - 07:57, 12 April 2024 |
 | Grain boundary strengthening (category Strengthening mechanisms of materials) Hall–Petch the dominant deformation mechanism is intragrain dislocation motion while in inverse Hall–Petch the dominant mechanism is grain boundary sliding... 33 KB (4,204 words) - 05:53, 26 June 2023 |
another deformation mechanism that becomes easier, i.e. grain boundary sliding. At this point, all dislocation related hardening mechanisms become irrelevant... 6 KB (812 words) - 12:18, 8 March 2022 |
of fault rocks was the first to include an understanding of the deformation mechanisms involved and all subsequent schemes have been based on this. Fault... 6 KB (716 words) - 01:17, 2 February 2024 |
 | Crystal twinning (redirect from Deformation twinning) The third is deformation twinning, in which twinning develops in a crystal in response to a shear stress, and is an important mechanism for permanent... 51 KB (5,846 words) - 08:21, 9 May 2024 |
 | The interlocking of bricks of nacre has large impact on both the deformation mechanism as well as its toughness. Tensile, shear, and compression tests... 36 KB (3,894 words) - 03:30, 25 February 2024 |




