The E1cB elimination reaction is a type of elimination reaction which occurs under basic conditions, where the hydrogen to be removed is relatively acidic... 17 KB (2,139 words) - 16:36, 25 March 2024 |
 | third type of reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the... 14 KB (1,843 words) - 07:43, 4 February 2024 |
 | E1cB-elimination reaction. Pyridynes were first postulated by Levine and Leake in 1955. In 1969 Zoltewicz and Nisi trapped 3,4-pyridyne in a reaction... 4 KB (444 words) - 22:36, 6 April 2023 |
Boord olefin synthesis (category Olefination reactions) reaction with magnesium forming an intermediate Grignard reagent. The alkoxy group is a poor leaving group and therefore an E1cB elimination reaction... 2 KB (209 words) - 19:34, 27 October 2022 |
Outline of organic chemistry (section Reactions) cyclization reaction Elimination reaction Beta elimination Cope elimination E1cB elimination reaction Hofmann elimination Organic redox reaction Cannizzaro... 8 KB (576 words) - 12:14, 30 October 2023 |
expansion reaction Duff reaction Dutt–Wormall reaction Dyotropic reaction E1cB elimination reaction Eder reaction Edman degradation Eglinton reaction Ehrlich–Sachs... 38 KB (3,433 words) - 17:07, 5 January 2024 |
 | Aldol condensation (redirect from Claisen–Schmidt reaction) the product to an enolate, which eliminates via the E1cB mechanism, while dehydration in acid proceeds via an E1 reaction mechanism. Depending on the nature... 17 KB (1,679 words) - 06:32, 22 March 2024 |
Methanesulfonyl chloride (section Reactions) via a mechanism wherein methanesulfonyl chloride first undergoes an E1cb elimination to generate the highly reactive parent sulfene (CH2=SO2), followed... 9 KB (772 words) - 03:36, 2 February 2024 |
 | Leaving group (category Reaction mechanisms) mechanism in elimination reactions. With poor leaving groups, the E1cB mechanism is favored, but as the leaving group's ability changes, the reaction shifts... 22 KB (2,532 words) - 15:42, 14 February 2024 |
Aryne (section Reactions of arynes) elimination event proceeds in two steps, deprotonation, followed by expulsion of the nucleophile. Thus, the process is formally analogous to the E1cb... 26 KB (2,936 words) - 17:42, 27 March 2024 |
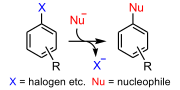 | Nucleophilic aromatic substitution (category Reaction mechanisms) pathways. SNAr (addition-elimination) mechanism aromatic SN1 mechanism encountered with diazonium salts benzyne mechanism (E1cB-AdN) free radical SRN1 mechanism... 11 KB (1,262 words) - 11:16, 17 April 2024 |
 | Glycolysis (redirect from Glucose oxidation reaction) 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate. This reaction is an elimination reaction involving an E1cB mechanism. Cofactors: 2 Mg2+, one "conformational"... 81 KB (8,782 words) - 03:47, 9 April 2024 |
O’Ferrall, R. A. (1970). "Relationships between E2 and E1cB mechanisms of beta-elimination". J. Chem. Soc. B: 274–277. doi:10.1039/J29700000274. Jencks, William... 8 KB (976 words) - 10:30, 21 April 2020 |












