| units, luminosity is measured in joules per second, or watts. In astronomy, values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the luminosity of the... 24 KB (3,039 words) - 15:48, 7 April 2024 |
In astronomy, a luminosity function gives the number of stars or galaxies per luminosity interval. Luminosity functions are used to study the properties... 7 KB (957 words) - 18:57, 1 March 2024 |
The Eddington luminosity, also referred to as the Eddington limit, is the maximum luminosity a body (such as a star) can achieve when there is balance... 26 KB (2,792 words) - 07:33, 6 May 2024 |
yacht Luminosity — Ignite the Night!, a former Cedar Point amusement park show that was shown from 2012 to 2017. Luminosity function (astronomy), a function... 1 KB (229 words) - 17:11, 7 February 2022 |
In astrophysics, the mass–luminosity relation is an equation giving the relationship between a star's mass and its luminosity, first noted by Jakob Karl... 16 KB (2,427 words) - 18:16, 3 December 2023 |
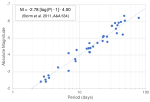
 | intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and the extinction reducing its brightness. The absolute magnitude (M) describes the intrinsic luminosity emitted by... 26 KB (2,958 words) - 14:44, 30 April 2024 |
 | Star (redirect from Star (astronomy)) as will the star's temperature and luminosity. The Sun, for example, is estimated to have increased in luminosity by about 40% since it reached the main... 146 KB (16,321 words) - 04:24, 9 May 2024 |
 | Stellar classification (redirect from Luminosity class) older Harvard spectral classification, which did not include luminosity) and a luminosity class using Roman numerals as explained below, forming the star's... 103 KB (11,333 words) - 00:13, 12 April 2024 |
 | Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (redirect from Color-luminosity diagram) same spectral classification. He took this as an indication of greater luminosity for the narrow-line stars, and computed secular parallaxes for several... 23 KB (2,771 words) - 02:01, 9 April 2024 |
higher than normal luminosity over some part of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not produced by stars... 160 KB (18,354 words) - 13:10, 19 April 2024 |
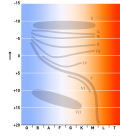 | Supergiant (section Spectral luminosity class) the definition of spectral luminosity classes, with class I referring to supergiant stars. The same system of MK luminosity classes is still used today... 37 KB (5,067 words) - 04:41, 9 May 2024 |
classification Luminosity comparison: LS, L☉ - luminosity of the Sun Luminosity of certain object: Lacc - accretion luminosity Lbol - bolometric luminosity Mass... 5 KB (483 words) - 01:09, 6 February 2024 |
 | star sensor. The X-ray luminosity of Lx = 1031 erg·s−1 (1024 W) is four orders of magnitude above the Sun's X-ray luminosity. Coronal stars, or stars... 65 KB (8,115 words) - 13:32, 13 April 2024 |
Absolute magnitude (redirect from Absolute luminosity) In astronomy, absolute magnitude (M) is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's... 49 KB (5,751 words) - 22:31, 5 November 2023 |
 | List of most luminous stars (category Lists of superlatives in astronomy) bolometric luminosity in multiples of the luminosity of the Sun (L☉) and the bolometric absolute magnitude. As with all magnitude systems in astronomy, the... 168 KB (10,338 words) - 06:32, 5 May 2024 |
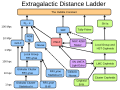 | Cosmic distance ladder (redirect from Distance (astronomy)) Planetary nebula luminosity function (PNLF) Globular cluster luminosity function (GCLF) Surface brightness fluctuation (SBF) In galactic astronomy, X-ray bursts... 54 KB (7,874 words) - 13:49, 26 April 2024 |
 | Sun (redirect from Sun (astronomy)) remains, contributing to the increased luminosity, which will eventually reach more than 1,000 times its present luminosity. When the Sun enters its red-giant... 164 KB (18,503 words) - 21:02, 8 May 2024 |
 | radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or dwarf) star of the same surface temperature. They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the... 16 KB (2,321 words) - 14:49, 20 April 2024 |
Surface brightness (category Observational astronomy) depends on its surface luminosity density, i.e., its luminosity emitted per unit surface area. In visible and infrared astronomy, surface brightness is... 9 KB (1,079 words) - 02:02, 9 February 2024 |
 | Stephenson 2 DFK 1 (section Luminosity) giving a relatively modest luminosity of 90,000 L☉. 2 years later, a new calculation for finding the bolometric luminosity by fitting the Spectral Energy... 24 KB (2,773 words) - 10:35, 4 May 2024 |
 | Main sequence (category Concepts in astronomy) times the solar luminosity. At metallicity Z=0.01 the luminosity is 1.34 times solar luminosity. At metallicity Z=0.04 the luminosity is 0.89 times the... 60 KB (6,813 words) - 07:50, 7 April 2024 |
 | Tully–Fisher relation (category Extragalactic astronomy) In astronomy, the Tully–Fisher relation (TFR) is a widely verified empirical relationship between the mass or intrinsic luminosity of a spiral galaxy... 7 KB (871 words) - 16:52, 9 January 2024 |
 | Canopus (redirect from Canopus (astronomy)) essentially white when seen with the naked eye. It has a luminosity over 10,000 times the luminosity of the Sun, is eight times as massive, and has expanded... 62 KB (7,275 words) - 08:37, 9 May 2024 |
 | VY Canis Majoris (section Luminosity) of the luminosity based on an assumed distance of 1.5 kpc (4,900 ly) gave luminosities between 200,000 and 560,000 times the Sun's luminosity (L☉). This... 64 KB (6,620 words) - 21:56, 30 April 2024 |