| webs, detrital food webs, marine food webs, aquatic food webs, soil food webs, Arctic (or polar) food webs, terrestrial food webs, and microbial food... 83 KB (8,618 words) - 00:25, 11 March 2024 |
 | Plankton (redirect from Marine plankton) provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales. Marine plankton include bacteria... 62 KB (6,455 words) - 06:05, 26 April 2024 |
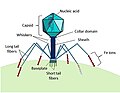
 | Viral shunt (section Effect on the marine food web) on food webs across marine environments as well as on a more macro scale on the global carbon budget. Viral shunt influences carbon cycling in marine environments... 33 KB (4,090 words) - 04:46, 19 February 2024 |
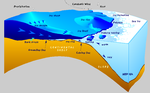 | foundation of the marine food web, polynyas are a critical food source for a variety of organisms such as fish, birds, and marine mammals. Listed below... 16 KB (1,892 words) - 15:08, 4 March 2024 |
 | The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how... 27 KB (3,653 words) - 11:27, 1 April 2024 |
 | Zooplankton (section Role in food webs) levels in marine food webs, zooplankton also play an important role as “recyclers” of carbon and other nutrients that significantly impact marine biogeochemical... 76 KB (7,030 words) - 05:39, 28 April 2024 |
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically... 17 KB (1,932 words) - 11:04, 27 April 2024 |
 | Microbial loop (section In marine ecosystems) efficiency of the marine food web via the utilization of dissolved organic matter (DOM), which is typically unavailable to most marine organisms. In this... 27 KB (3,094 words) - 16:09, 14 March 2024 |
 | The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may... 26 KB (3,055 words) - 22:34, 13 March 2024 |
The microbial food web refers to the combined trophic interactions among microbes in aquatic environments. These microbes include viruses, bacteria, algae... 3 KB (337 words) - 02:30, 14 March 2023 |
toxic to either one or many members of the marine food web. This page focuses on phycotoxins produced by marine microalgae; however, freshwater algae and... 27 KB (2,521 words) - 16:29, 25 September 2023 |
 | Sustainable fishery (section Marine protected areas) predecessor; and that changes will occur in the trophic balance (fishing down marine food webs). Global wild fisheries are believed to have peaked and begun a decline... 60 KB (6,205 words) - 05:25, 9 February 2024 |
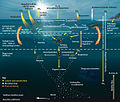 | Biological pump (section Marine snow) levels in marine food webs, zooplankton also play an important role as "recyclers" of carbon and other nutrients that significantly impact marine biogeochemical... 145 KB (16,299 words) - 20:02, 23 April 2024 |
 | of the microscopic plants (phytoplankton) that are the basis of the marine food web. Typically iron(III) salts, like the "chloride" are aquo complexes... 8 KB (1,036 words) - 18:39, 10 March 2024 |