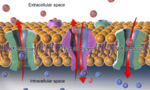
| Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of... 63 KB (7,837 words) - 11:44, 5 November 2023 |
membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting membrane potential, and this is called hyperpolarisation. To generate an action potential,... 22 KB (2,705 words) - 08:12, 8 January 2024 |
 | They produce roughly 60–100 action potentials every minute. The action potential passes along the cell membrane causing the cell to contract, therefore... 46 KB (5,430 words) - 18:10, 24 April 2024 |
biological membrane, the reversal potential is the membrane potential at which the direction of ionic current reverses. At the reversal potential, there is... 8 KB (865 words) - 18:59, 14 March 2024 |
Postsynaptic potentials are changes in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse. Postsynaptic potentials are graded potentials, and... 6 KB (808 words) - 05:31, 4 January 2024 |
 | Depolarization (redirect from Membrane depolarization) to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization... 19 KB (2,313 words) - 10:21, 7 March 2024 |
 | Mitochondrion (redirect from Mitochondrial membrane) there is a membrane potential across the inner membrane, formed by the action of the enzymes of the electron transport chain. Inner membrane fusion is... 158 KB (17,629 words) - 08:47, 19 April 2024 |
Hyperpolarization (biology) (category Membrane biology) change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization. It inhibits action potentials by increasing the... 9 KB (1,079 words) - 05:36, 13 October 2022 |
 | membrane potential can be measured. Typically, the resting membrane potential of a healthy cell will be -60 to -80 mV, and during an action potential... 38 KB (4,430 words) - 00:47, 3 April 2024 |
often bring the membrane potential of the sensory receptor towards the threshold for triggering an action potential. Receptor potential can work to trigger... 3 KB (366 words) - 05:24, 4 April 2023 |
 | Repolarization (category Membrane biology) in membrane potential that returns it to a negative value just after the depolarization phase of an action potential which has changed the membrane potential... 21 KB (2,413 words) - 13:09, 2 December 2023 |
A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such... 25 KB (2,649 words) - 12:33, 13 March 2024 |
needed] Many cells have resting membrane potentials that are unstable. It is usually due to ion channels in the cell membrane that spontaneously open and... 9 KB (1,125 words) - 08:56, 17 September 2023 |
 | cell's membrane potential back to its resting membrane potential. When the cell's membrane voltage overshoots its resting membrane potential (near -60... 11 KB (1,302 words) - 06:37, 23 March 2024 |
 | cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that... 59 KB (6,906 words) - 21:19, 12 April 2024 |
differences in osmotic potential if a semipermeable membrane exists between the zones of high and low osmotic potential. A semipermeable membrane is necessary because... 13 KB (1,858 words) - 18:04, 10 January 2024 |