| Motor proteins are a class of molecular motors that can move along the cytoskeleton of cells. They convert chemical energy into mechanical work by the... 13 KB (1,538 words) - 23:48, 17 April 2024 |
 | Microtubule (redirect from Microtubule proteins) of the motor proteins. This allows the movement of the motor proteins along the microtubule or the microtubule moving across the motor proteins. Consequently... 64 KB (7,838 words) - 06:58, 22 February 2024 |
 | the flagellar motor switch protein (Flig) is one of three proteins in certain bacteria coded for by the gene fliG. The other two proteins are FliN coded... 5 KB (538 words) - 12:59, 21 March 2022 |
 | Kinesin (category Motor proteins) A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered... 36 KB (4,235 words) - 00:04, 25 April 2024 |
 | Molecular biophysics (redirect from Protein chemistry) A good example is the muscle protein myosin which "motors" the contraction of muscle fibers in animals. Motor proteins are the driving force behind most... 19 KB (2,012 words) - 14:04, 3 December 2023 |
 | main cytoskeletal "tracks" for transportation. Kinesin and dynein are motor proteins that move cargoes in the anterograde (forwards from the soma to the... 22 KB (2,622 words) - 07:46, 6 May 2024 |
List of gene families (section Motor proteins) typically encode functionally related proteins, and sometimes the term gene families is a shorthand for the sets of proteins that the genes encode. They may... 2 KB (184 words) - 19:03, 4 November 2022 |
 | Axon (redirect from Motor fiber) growth describing how motor proteins could affect the axon length on the molecular level. These studies suggest that motor proteins carry signaling molecules... 58 KB (6,915 words) - 23:07, 22 April 2024 |
 | Cytokinesis (section Proteins involved in cytokinesis) components, including PRC1 (microtubule-bundling protein required for cytokinesis 1) and MKLP1 (a kinesin motor protein). Originally inhibited by CDK1-mediated... 28 KB (3,533 words) - 15:18, 9 February 2024 |
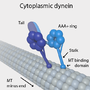 | Dynein (category Motor proteins) Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical... 29 KB (3,313 words) - 16:08, 3 December 2023 |
Motility protein A, MotA, is a bacterial protein that is encoded by the motA gene. It is a component of the flagellar motor. More specifically, MotA and... 4 KB (437 words) - 23:42, 22 October 2022 |
 | Muscle contraction (redirect from Contractile proteins) strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional... 62 KB (7,394 words) - 18:12, 1 May 2024 |
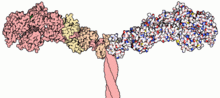 | Myosin (category Motor proteins) Myosins (/ˈmaɪəsɪn, -oʊ-/) are a superfamily of motor proteins best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes... 42 KB (4,894 words) - 05:02, 6 May 2024 |
 | centromere) via protein complexes (kinetochores). The attached microtubules depolymerise and shorten, which together with motor proteins creates movement... 6 KB (719 words) - 02:00, 2 May 2024 |
 | NDEL1 (category Human proteins) division via regulation of the dynein motor protein and its cofactor protein, Lis1. Ndel1 is a highly conserved protein and its human gene, NDEL1 is expressed... 16 KB (2,014 words) - 02:50, 6 May 2024 |