scientific research, the null hypothesis (often denoted H0) is the claim that the effect being studied does not exist. The null hypothesis can also be described... 39 KB (5,319 words) - 17:06, 30 April 2024 |
P-value (category Statistical hypothesis testing) In null-hypothesis significance testing, the p {\displaystyle p} -value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result... 55 KB (6,739 words) - 03:28, 13 April 2024 |
-value by comparing T {\displaystyle T} to its distribution under the null hypothesis. The ranks are defined so that R i {\displaystyle R_{i}} is the number... 42 KB (7,161 words) - 22:17, 19 February 2024 |
 | statistical hypothesis testing, two hypotheses are compared. These are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the... 20 KB (2,583 words) - 12:20, 5 May 2024 |
statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when a result at least as "extreme" would be very infrequent if the null hypothesis were... 38 KB (4,077 words) - 18:43, 8 May 2024 |
Type I and type II errors (category Statistical hypothesis testing) In statistical hypothesis testing, a type I error, or a false positive, is the rejection of the null hypothesis when it is actually true. For example,... 31 KB (4,487 words) - 23:50, 2 May 2024 |
 | valid when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed under the null hypothesis, specifically Pearson's chi-squared test and variants thereof. Pearson's... 21 KB (2,361 words) - 06:28, 8 May 2024 |
the null hypothesis. The test of significance is designed to assess the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis. Usually, the null hypothesis... 8 KB (1,055 words) - 00:12, 7 May 2024 |
 | Among other contributions, the book introduced the concept of the null hypothesis in the context of the lady tasting tea experiment. A chapter is devoted... 6 KB (803 words) - 08:34, 12 January 2022 |
 | determine if the tested data has an F-distribution under the true null hypothesis, and true customary assumptions about the error term (ε). It is most... 17 KB (2,176 words) - 11:10, 5 January 2024 |
Power of a test (category Statistical hypothesis testing) statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis ( H 0 {\displaystyle H_{0}} ) when... 26 KB (4,215 words) - 03:26, 21 February 2024 |
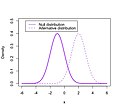 | In statistical hypothesis testing, the null distribution is the probability distribution of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is true. For example... 6 KB (836 words) - 17:38, 17 April 2021 |
different from what is to be expected under the null hypothesis; its probability (under the null hypothesis) does not exceed the significance level, i.e... 7 KB (798 words) - 09:07, 27 March 2024 |
False positive rate (category Statistical hypothesis testing) or false alarm ratio) is the probability of falsely rejecting the null hypothesis for a particular test. The false positive rate is calculated as the... 5 KB (926 words) - 09:26, 10 February 2024 |
corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. The terms are often used interchangeably... 9 KB (1,167 words) - 03:42, 26 April 2024 |
based on the ratio of their likelihoods. If the constraint (i.e., the null hypothesis) is supported by the observed data, the two likelihoods should not... 17 KB (2,090 words) - 12:36, 17 April 2024 |
test, or Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test) is a nonparametric test of the null hypothesis that, for randomly selected values X and Y from two populations, the... 44 KB (5,778 words) - 17:13, 11 April 2024 |
False discovery rate (category Statistical hypothesis testing) (FDR) is a method of conceptualizing the rate of type I errors in null hypothesis testing when conducting multiple comparisons. FDR-controlling procedures... 31 KB (4,472 words) - 14:09, 6 April 2024 |
tests. Let p = Pr(X > Y), and then test the null hypothesis H0: p = 0.50. In other words, the null hypothesis states that given a random pair of measurements... 22 KB (3,296 words) - 00:23, 29 January 2023 |
statistical hypothesis test making use of the proof by contradiction. A permutation test involves two or more samples. The null hypothesis is that all... 22 KB (2,837 words) - 20:54, 21 February 2024 |
It is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most commonly applied... 49 KB (6,665 words) - 01:08, 7 May 2024 |
Samuel Sanford Shapiro and Martin Wilk. The Shapiro–Wilk test tests the null hypothesis that a sample x1, ..., xn came from a normally distributed population... 7 KB (874 words) - 06:11, 12 April 2024 |
Misuse of p-values (category Statistical hypothesis testing) results: either the null hypothesis is rejected (which however does not prove that the null hypothesis is false), or the null hypothesis cannot be rejected... 13 KB (1,539 words) - 20:56, 25 March 2024 |
Wald test (section Nonlinear hypothesis) between the unrestricted estimate and its hypothesized value under the null hypothesis, where the weight is the precision of the estimate. Intuitively, the... 17 KB (2,232 words) - 23:13, 22 March 2024 |
null hypothesis is rejected if the observed data are significantly unlikely to have occurred if the null hypothesis were true. In this case the null hypothesis... 20 KB (2,262 words) - 13:23, 19 April 2024 |
 | null hypotheses. Suppose we have a number m of null hypotheses, denoted by: H1, H2, ..., Hm. Using a statistical test, we reject the null hypothesis if... 21 KB (2,556 words) - 15:09, 29 March 2024 |