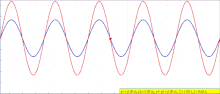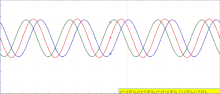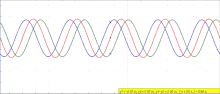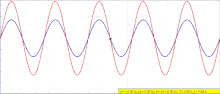
| A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or... 21 KB (2,384 words) - 21:00, 5 April 2024 |
 | A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster... 10 KB (1,050 words) - 18:26, 27 April 2024 |
 | Earthquake (redirect from Seismic activity) resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot... 81 KB (8,850 words) - 18:27, 27 April 2024 |
measurements of an earthquake's seismic waves as recorded on a seismogram. Magnitude scales vary based on what aspect of the seismic waves are measured and how they... 53 KB (5,868 words) - 04:28, 6 April 2024 |
 | Seismology (redirect from Detection of seismic waves) causation of seismic events and geodetic motions had come together in the now well-established theory of plate tectonics. Seismic waves are elastic waves that... 35 KB (3,975 words) - 07:49, 13 April 2024 |
 | k is the wave number. Earthquake Early Warning (Japan) Lamb waves Longitudinal wave Love wave P wave Rayleigh wave Seismic wave Shear wave splitting... 12 KB (1,574 words) - 06:06, 7 March 2024 |
 | Reflection seismology (redirect from Seismic reflection) reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite or Tovex blast, a specialized air gun or a seismic vibrator... 77 KB (10,213 words) - 21:43, 26 November 2023 |
 | Tsunami (redirect from Seismic sea wave) generally encouraged the use of the term seismic sea wave rather than tidal wave. However, like tidal wave, seismic sea wave is not a completely accurate term... 63 KB (7,338 words) - 19:53, 21 April 2024 |
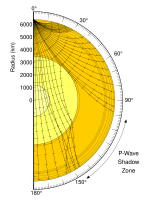 | Shadow zone (redirect from Seismic shadowing) A seismic shadow zone is an area of the Earth's surface where seismographs cannot detect direct P waves and/or S waves from an earthquake. This is due... 15 KB (1,901 words) - 09:56, 13 January 2024 |
 | Earth's inner core (section Seismic wave velocity) mantle. Information about Earth's core mostly comes from analysis of seismic waves and Earth's magnetic field. The inner core is believed to be composed... 60 KB (7,191 words) - 13:05, 19 April 2024 |
Seismic tomography or seismotomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth with seismic waves produced by earthquakes or explosions... 22 KB (2,796 words) - 18:51, 15 April 2024 |
Attenuation (redirect from Seismic attenuation) medium in question. Attenuation also occurs in earthquakes; when the seismic waves move farther away from the hypocenter, they grow smaller as they are... 21 KB (2,645 words) - 17:24, 21 March 2024 |
 | compressional (P-waves) while it absorbs the transverse or shear waves (S-waves). Outside the seismic shadow zone, both types of wave can be detected but... 13 KB (1,426 words) - 16:52, 24 April 2024 |
of the source event, such as measured by various seismic magnitude scales. The type of seismic wave generated, and its orientation. The depth of the event... 11 KB (1,127 words) - 10:45, 6 April 2024 |
focal depth can be calculated from measurements based on seismic wave phenomena. As with all wave phenomena in physics, there is uncertainty in such measurements... 12 KB (1,370 words) - 01:18, 5 April 2024 |
 | Seismometer (redirect from Seismic station) less noisy and gives better records of some seismic waves.[citation needed] The foundation of a seismic station is critical. A professional station is... 44 KB (5,546 words) - 09:09, 22 April 2024 |
gravitational waves and may cause shifts in the atoms. Hence, the magnitude of seismic waves can be detected by a relative shift in the gravitational waves. The... 21 KB (2,922 words) - 10:11, 14 March 2024 |
 | Travel time in seismology means time for the seismic waves to travel from the focus of an earthquake through the crust to a certain seismograph station... 3 KB (360 words) - 21:19, 24 June 2023 |
Moment magnitude scale (category Articles using seismic moment M0) and surface wave magnitude (Ms ) scales. Subtypes of the moment magnitude scale (Mww , etc.) reflect different ways of estimating the seismic moment. At... 47 KB (5,924 words) - 13:59, 6 April 2024 |
 | Geophysics (section Electromagnetic waves) mantle convection. Recording of seismic waves from controlled sources provides information on the region that the waves travel through. If the density... 50 KB (5,268 words) - 05:57, 9 April 2024 |
 | waves mathematically in 1911. They form a distinct class, different from other types of seismic waves, such as P-waves and S-waves (both body waves)... 7 KB (1,119 words) - 23:49, 6 April 2023 |