El Tambor Fault
| El Tambor Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla El Tambor | |
| Etymology | Cerro El Tambor |
| Coordinates | 02°46′04″N 77°18′20″W / 2.76778°N 77.30556°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Pacific/Chocó |
| State | Cauca, Valle del Cauca |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Western Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean oblique faults |
| Length | 117.5 km (73.0 mi) |
| Strike | 026.1 ± 09 |
| Dip | East |
| Dip angle | High |
| Displacement | <0.2 mm (0.0079 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Oblique thrust fault |
| Movement | Dextral reverse |
| Age | Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
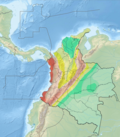
The El Tambor Fault (Spanish: Falla El Tambor) is an inactive dextral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Cauca and Valle del Cauca in Colombia. The fault has a total length of 117.5 kilometres (73.0 mi) and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 026.1 ± 09 to the west of the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
Etymology[edit]
The fault is named after Cerro El Tambor, Timbiquí, Cauca.[1][2]
Description[edit]
The El Tambor Fault borders the western slope of the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes, west of the Farallones de Cali.[3] Through most of its trace, the fault places Cretaceous volcanic and sedimentary rocks on the east, against Neogene rocks on the west, which commonly crops out across most of the plains of the Pacific Coast. The fault displays strong linear topographic features, tectonic control of drainage, and deflected stream channels and was active in the Late Pleistocene or Early Holocene.[4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Bibliography[edit]
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000a. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions, 1–66. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Maps[edit]
- Marín, P.; G. Paris; A. Orrego, and M.E. López. 1979. Mapa Geológico de Cauca 1:350,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-09-21.
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000b. Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions, 1. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch