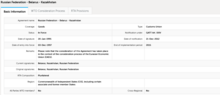
Single Economic Space of the Eurasian Economic Union
Eurasian Economic Space | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Policy of | |
| Type | Single market |
| Member states | |
| Establishment | 1 January 2012 |
| Area | |
• Total | 20,260,431 km2 (7,822,596 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2013 estimate | 182,519,270[1][2][3][4][5] |
• Density | 9.01/km2 (23.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | $4.1 trillion[6] |
• Per capita | $22,000 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | $2.4 trillion[7] |
• Per capita | $13,000 |

The Eurasian Economic Space or Single Economic Space is a single market that provides for the free movement of persons, goods, services and capital within the Eurasian Economic Union. The Single Economic Space was established in 2012 with the goal of creating an integrated single market. It is inspired by the European Internal market and the European Economic Area.
The Eurasian Economic Space initially consisted of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia, and was enlarged to include Armenia and Kyrgyzstan from 1 January 2015.[11] The original treaty establishing the Single Economic Space was terminated by the agreement establishing the Eurasian Economic Union, signed in 2014, which incorporated the economic space into the EEU's legal framework.
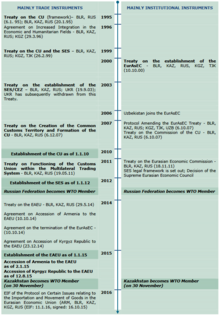
The Economic Space was established after Belarus, Kazakhstan and Russia had removed all customs borders in July 2011 through the Eurasian Customs Union. The Single Economic Space aimed to promote further economic integration. The creation of the Eurasian Economic Space was guaranteed by 3 different treaties. The first treaty in 2003 guaranteeing its creation, the second in 2007 guaranteeing its formation and the third in 2011 announced the establishment of the economic space and the formation of the common market.
Member states of the Eurasian Economic Space[edit]
- Armenia (2015)
- Belarus (2012)
- Kazakhstan (2012)
- Kyrgyzstan (2015)
- Russia (2012)
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Archived copy Archived 1 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The World Factbook". 6 October 2022.
- ^ "О демографической ситуации в январе-сентябре 2014 г". Archived from the original on 16 November 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.armstat.am.
- ^ "Census data". www.stat.kg.
- ^ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ https://docsonline.wto.org/dol2fe/Pages/SS/directdoc.aspx?filename=q:/WT/REG/358-1.pdf&Open=True
- ^ https://rtais.wto.org/UI/PublicShowMemberRTAIDCard.aspx?rtaid=857
- ^ https://rtais.wto.org/UI/PublicShowMemberRTAIDCard.aspx?rtaid=909
- ^ Kyrgyzstan and Armenia will officially enter the Eurasian Customs Union that was created by Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan, on the January 1, 2015., Kyrgyzstan, Armenia officially enter Eurasian Economic Union Archived 2016-06-11 at the Wayback Machine, 24.kg. Retrieved 11 January 2014.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch