History of painting
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| History of art |
|---|
The history of painting reaches back in time to artifacts and artwork created by pre-historic artists, and spans all cultures. It represents a continuous, though periodically disrupted, tradition from Antiquity. Across cultures, continents, and millennia, the history of painting consists of an ongoing river of creativity that continues into the 21st century.[1] Until the early 20th century it relied primarily on representational, religious and classical motifs, after which time more purely abstract and conceptual approaches gained favor.
Developments in Eastern painting historically parallel those in Western painting, in general, a few centuries earlier.[2] African art, Jewish art, Islamic art, Indonesian art, Indian art,[3] Chinese art, and Japanese art[4] each had significant influence on Western art, and vice versa.[5]
Initially serving utilitarian purpose, followed by imperial, private, civic, and religious patronage, Eastern and Western painting later found audiences in the aristocracy and the middle class. From the Modern era, the Middle Ages through the Renaissance painters worked for the church and a wealthy aristocracy.[6] Beginning with the Baroque era artists received private commissions from a more educated and prosperous middle class.[7] Finally in the West the idea of "art for art's sake"[8] began to find expression in the work of the Romantic painters like Francisco de Goya, John Constable, and J. M. W. Turner.[9] The 19th century saw the rise of the commercial art gallery, which provided patronage in the 20th century.[10]
Pre-history[edit]

The oldest known paintings are approximately 40,000 years old, found in both the Franco-Cantabrian region in western Europe, and in the caves in the district of Maros (Sulawesi, Indonesia). The oldest type of cave paintings are hand stencils and simple geometric shapes; the oldest undisputed examples of figurative cave paintings are somewhat younger, close to 35,000 years old.[11] In November 2018, scientists reported the discovery of the then-oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal, in the cave of Lubang Jeriji Saléh on the Indonesian island of Borneo (Kalimantan).[12][13] In December 2019, however, figurative cave paintings depicting pig hunting in the Maros-Pangkep karst in Sulawesi were estimated to be even older, at least 43,900 years old. The finding was noted to be "the oldest pictorial record of storytelling and the earliest figurative artwork in the world".[14][15] And more recently, in 2021, cave art of a pig found in an Indonesian island, and dated to over 45,500 years, has been reported.[16] There are examples of cave paintings all over the world—in Indonesia, France, India, Spain, Southern Africa, China, Australia etc.
Various conjectures have been made as to the meaning these paintings had to the people that made them. Prehistoric artists may have painted animals to "catch" their soul or spirit in order to hunt them more easily or the paintings may represent an animistic vision and homage to surrounding nature. They may be the result of a basic need of expression that is innate to human beings, or they could have been for the transmission of practical information.
- Lascaux, Horse
- Lascaux, Bulls and Horses
- Spanish cave painting of Bulls
- Petroglyphs, from Sweden, Nordic Bronze Age (painted)
- Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for Cave of the Hands) in the Santa Cruz province in Argentina, c. 7300 BC
- Gwion Gwion rock paintings found in the north-west Kimberley region of Western Australia c. 15,000 BC[17]
In Paleolithic times, the representation of humans in cave paintings was rare. Mostly, animals were painted, not only animals that were used as food but also animals that represented strength like the rhinoceros or large Felidae, as in the Chauvet Cave. Signs like dots were sometimes drawn. Rare human representations include handprints and stencils, and figures depicting human / animal hybrids. The Chauvet Cave in the Ardèche Departments of France contains the most important preserved cave paintings of the Paleolithic era, painted around 31,000 BC. The Altamira cave paintings in Spain were done 14,000 to 12,000 BC and show, among others, bisons. The hall of bulls in Lascaux, Dordogne, France, is one of the best known cave paintings and dates to about 15,000 to 10,000 BC.
If there is meaning to the paintings, it remains unknown. The caves were not in an inhabited area, so they may have been used for seasonal rituals. The animals are accompanied by signs which suggest a possible magic use. Arrow-like symbols in Lascaux are sometimes interpreted as being used as calendars or almanacs, but the evidence remains inconclusive.[18] The most important work of the Mesolithic era were the marching warriors, a rock painting at Cingle de la Mola, Castellón, Spain dated to about 7000 to 4000 BC. The technique used was probably spitting or blowing the pigments onto the rock. The paintings are quite naturalistic, though stylized. The figures are not three-dimensional, even though they overlap.
The earliest known Indian paintings were the rock paintings of prehistoric times, the petroglyphs as found in places like the Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka, and some of them are older than 5500 BC. Such works continued and after several millennia, in the 7th century, carved pillars of Ajanta, Maharashtra state present a fine example of Indian paintings. The colors, mostly various shades of red and orange, were derived from minerals.
Eastern[edit]

The history of Eastern painting includes a vast range of influences from various cultures and religions. Developments in Eastern painting historically parallel those in Western painting, in general a few centuries earlier.[2] African art, Jewish art, Islamic art, Indonesian art, Indian art,[19] Chinese art, Korean Art, and Japanese art[4] each had significant influence on Western art, and, vice versa.[5]
Chinese painting is one of the oldest continuous artistic traditions in the world. The earliest paintings were not representational but ornamental; they consisted of patterns or designs rather than pictures. Early pottery was painted with spirals, zigzags, dots, or animals. It was only during the Warring States period (403–221 B.C.) that artists began to represent the world around them. Japanese painting is one of the oldest and most highly refined of the Japanese arts, encompassing a wide variety of genre and styles. The history of Japanese painting is a long history of synthesis and competition between native Japanese aesthetics and adaptation of imported ideas. Korean painting, as an independent form, began around 108 B.C., around the fall of Gojoseon, making it one of the oldest in the world. The artwork of that time period evolved into the various styles that characterized the Three Kingdoms of Korea period, most notably the paintings and frescoes that adorn the tombs of Goguryeo's royalty. During the Three Kingdoms period and through the Goryeo dynasty, Korean painting was characterized primarily by a combination of Korean-style landscapes, facial features, Buddhist-centered themes, and an emphasis on celestial observation that was facilitated by the rapid development of Korean astronomy.
East Asian[edit]
See also Chinese painting, Japanese painting, Korean painting.
This section contains an unencyclopedic or excessive gallery of images. |
- A lacquerware painting from the Jingmen Tomb (Chinese: 荊門楚墓; Pinyin: Jīngmén chǔ mù) of the State of Chu (704–223 BC), depicting men riding in a two-horsed chariot
- Detail of a fresco showing the Chinese philosopher Confucius, from a Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) tomb of Dongping County, Shandong province
- A Chinese woman, fresco from a Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) tomb of Xi'an (ancient Chang'an), Shaanxi province
- Paintings on tile of guardian spirits donned in Chinese robes, from the Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD)
- Gentlemen in Conversation, tomb painting dated to the Eastern Han dynasty (25–220 AD).
- Male figure from a lacquerware painting over wood, Northern Wei period, 5th century AD
- Buddhist art of painted relief sculptures from the Yungang Grottoes, Northern Wei dynasty (386-535 AD)
- Eighty-Seven Celestials, by Wu Daozi (685–758), Tang dynasty, Chinese
- Portrait of Night-Shining White, by Han Gan, 8th century, Tang dynasty, Chinese
- Spring Outing of the Tang Court, by Zhang Xuan, 8th century, Tang dynasty, Chinese
- Servant, 8th century, Tang dynasty, Chinese
- Ladies making silk, a remake of an 8th-century original by Zhang Xuan by Emperor Huizong of Song, early 12th century, Chinese
- An illustrated sutra from the Nara period, 8th century, Japanese
- Ladies Playing Double Sixes, by Zhou Fang (730–800 AD), Tang dynasty, Chinese
- A Palace Concert, Tang dynasty, Chinese
- The Xiao and Xiang Rivers, by Dong Yuan (c. 934–962 AD), Chinese
- Night Revels, a Song dynasty remake of a 10th-century original by Gu Hongzhong.
- Court portrait of Emperor Shenzong of Song (r. 1067–1085), Chinese
- Golden Pheasant and Cotton Rose, by Emperor Huizong of Song (r.1100–1126 AD), Chinese
- Listening to the Guqin, by Emperor Huizong of Song (1100–1126 AD), Chinese
- Children Playing, by Su Han Chen, c. 1150, Chinese
- Chinese, anonymous artist of the 12th century Song dynasty
- Portrait of the Zen Buddhist Wuzhun Shifan, 1238 AD, Chinese
- Ma Lin, 1246 AD, Chinese
- A Man and His Horse in the Wind, by Zhao Mengfu (1254–1322 AD), Chinese
- Shukei-sansui (Autumn Landscape), Sesshu Toyo (1420–1506), Japanese
- Kanō Masanobu, 15th-century founder of the Kanō school, Zhou Maoshu Appreciating Lotuses, Japanese
- A White-Robed Kannon, Bodhisattva of Compassion, by Kanō Motonobu (1476–1559), Japanese
- Yi Ahm (1499–?), Mother Dog, 15th century, National Museum of Korea
- Tang Yin, A Fisher in Autumn, (1523), Chinese
- Nanban ships arriving for trade in Japan, 16th century, Japanese
- A screen painting depicting people playing Go, by Kanō Eitoku (1543–1590), Japanese
- Right panel of the Pine Trees screen (Shōrin-zu byōbu, 松林図 屏風) by Hasegawa Tōhaku (1539–1610), Japanese
- Scroll calligraphy of Bodhidharma, "Zen points directly to the human heart, see into your nature and become Buddha", Hakuin Ekaku (1686 to 1769), Japanese
- Hanging scroll 1672, Kanō Tanyū (1602–1674), Japanese
- Peonies, by Yun Shouping (1633–1690), Chinese
- Genji Monogatari, by Tosa Mitsuoki (1617–1691), Japanese
- View of Geumgang, Jeong Seon (1676–1759), 1734, Korean
- Ike no Taiga (1723–1776), Fish in Spring, Japanese
- Maruyama school, Pine, Bamboo, Plum, six-fold screen, Maruyama Ōkyo (1733–1795), Japanese
- A Cat and a Butterfly, Kim Hong-do (1745–?), 18th century, Korean
- A Boat Ride, Shin Yun-bok (1758–?), 1805, Korean
- Rimpa school, Autumn Flowers and Moon, Sakai Hoitsu (1761–1828), Japanese
- A tanuki (raccoon dog) as a tea kettle, by Katsushika Hokusai (1760–1849), Japanese
- A House amongst Apricot Trees, Jo Hee-ryong (1797–1859), Korean
- Katsushika Hokusai, The Dragon of Smoke Escaping from Mt Fuji, Japanese
- Miyagawa Isshō, untitled Ukiyo-e painting, Japanese
- Tomioka Tessai (1837–1924), Nihonga style, Two Divinities Dancing, 1924, Japanese

China, Japan and Korea have a strong tradition in painting which is also highly attached to the art of calligraphy and printmaking (so much that it is commonly seen as painting). Far east traditional painting is characterized by water based techniques, less realism, "elegant" and stylized subjects, graphical approach to depiction, the importance of white space (or negative space) and a preference for landscape (instead of the human figure) as a subject. Beyond ink and color on silk or paper scrolls, gold on lacquer was also a common medium in painted East Asian artwork. Although silk was a somewhat expensive medium to paint upon in the past, the invention of paper during the 1st century AD by the Han court eunuch Cai Lun provided not only a cheap and widespread medium for writing, but also a cheap and widespread medium for painting (making it more accessible to the public).
The ideologies of Confucianism, Daoism, and Buddhism played important roles in East Asian art. Medieval Song dynasty painters such as Lin Tinggui and his Luohan Laundering[20] (housed in the Smithsonian Freer Gallery of Art) of the 12th century are excellent examples of Buddhist ideas fused into classical Chinese artwork. In the latter painting on silk (image and description provided in the link), bald-headed Buddhist Luohan are depicted in a practical setting of washing clothes by a river. However, the painting itself is visually stunning, with the Luohan portrayed in rich detail and bright, opaque colors in contrast to a hazy, brown, and bland wooded environment. Also, the tree tops are shrouded in swirling fog, providing the common "negative space" mentioned above in East Asian Art.
In Japonisme, late 19th-century Post-Impressionists like Van Gogh and Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, and tonalists such as James McNeill Whistler, admired early 19th-century Japanese Ukiyo-e artists like Hokusai (1760–1849) and Hiroshige (1797–1858) and were influenced by them.
Chinese[edit]

The earliest surviving examples of Chinese painted artwork date to the Warring States period (481–221 BC), with paintings on silk or tomb murals on rock, brick, or stone. They were often in simplistic stylized format and in more-or-less rudimentary geometric patterns. They often depicted mythological creatures, domestic scenes, labor scenes, or palatial scenes filled with officials at court. Artwork during this period and the subsequent Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD) was made not as a means in and of itself or for higher personal expression; rather artwork was created to symbolize and honor funerary rites, representations of mythological deities or spirits of ancestors, etc. Paintings on silk of court officials and domestic scenes could be found during the Han dynasty, along with scenes of men hunting on horseback or partaking in military parade. There was also painting on three dimensional works of art like figurines and statues, such as the original-painted colors covering the soldier and horse statues of the Terracotta Army. During the social and cultural climate of the ancient Eastern Jin dynasty (316 – 420 AD) based at Nanjing in the south, painting became one of the official pastimes of Confucian-taught bureaucratic officials and aristocrats (along with music played by the guqin zither, writing fanciful calligraphy, and writing and reciting of poetry). Painting became a common form of artistic self-expression, and during this period painters at court or amongst elite social circuits were judged and ranked by their peers.

The establishment of classical Chinese landscape painting is accredited largely to the Eastern Jin dynasty artist Gu Kaizhi (344 – 406 AD), one of the most famous artists of Chinese history. Like the elongated scroll scenes of Kaizhi, Tang dynasty (618–907 AD) Chinese artists like Wu Daozi painted vivid and highly detailed artwork on long horizontal handscrolls (which were very popular during the Tang), such as his Eighty Seven Celestial People. Painted artwork during the Tang period pertained the effects of an idealized landscape environment, with sparse numbers of objects, persons, or amount of activity, as well as monochromatic in nature (example: the murals of Prince Yide's tomb in the Qianling Mausoleum). There were also figures such as early Tang-era painter Zhan Ziqian, who painted superb landscape paintings that were well ahead of his day in portrayal of realism. However, landscape art did not reach greater level of maturity and realism in general until the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960 AD). During this time, there were exceptional landscape painters like Dong Yuan (refer to this article for an example of his artwork), and those who painted more vivid and realistic depictions of domestic scenes, like Gu Hongzhong and his Night Revels of Han Xizai.

During the Chinese Song dynasty (960–1279 AD), not only landscape art was improved upon, but portrait painting became more standardized and sophisticated than before (for example, refer to Emperor Huizong of Song), and reached its classical age maturity during the Ming dynasty (1368–1644 AD). During the late 13th century and first half of the 14th century, Chinese under the Mongol-controlled Yuan dynasty were not allowed to enter higher posts of government (reserved for Mongols or other ethnic groups from Central Asia), and the Imperial examination was ceased for the time being. Many Confucian-educated Chinese who now lacked profession turned to the arts of painting and theatre instead, as the Yuan period became one of the most vibrant and abundant eras for Chinese artwork. An example of such would be Qian Xuan (1235–1305 AD), who was an official of the Song dynasty, but out of patriotism, refused to serve the Yuan court and dedicated himself to painting. Examples of superb art from this period include the rich and detailed painted murals of the Yongle Palace,[22][23] or "Dachunyang Longevity Palace", of 1262 AD, a UNESCO World Heritage site. Within the palace, paintings cover an area of more than 1000 square meters, and hold mostly Daoist themes. It was during the Song dynasty that painters would also gather in social clubs or meetings to discuss their art or others' artwork, the praising of which often led to persuasions to trade and sell precious works of art. However, there were also many harsh critics of others art as well, showing the difference in style and taste amongst different painters. In 1088 AD, the polymath scientist and statesman Shen Kuo once wrote of the artwork of one Li Cheng, who he criticized as follows:
...Then there was Li Cheng, who when he depicted pavilions and lodges amidst mountains, storeyed buildings, pagodas and the like, always used to paint the eaves as seen from below. His idea was that 'one should look upwards from underneath, just as a man standing on level ground and looking up at the eaves of a pagoda can see its rafters and its cantilever eave rafters'. This is all wrong. In general the proper way of painting a landscape is to see the small from the viewpoint of the large...just as one looks at artificial mountains in gardens (as one walks about). If one applies (Li's method) to the painting of real mountains, looking up at them from below, one can only see one profile at a time, and not the wealth of their multitudinous slopes and profiles, to say nothing of all that is going on in the valleys and canyons, and in the lanes and courtyards with their dwellings and houses. If we stand to the east of a mountain its western parts would be on the vanishing boundary of far-off distance, and vice versa. Surely this could not be called a successful painting? Mr. Li did not understand the principle of 'seeing the small from the viewpoint of the large'. He was certainly marvelous at diminishing accurately heights and distances, but should one attach such importance to the angles and corners of buildings?[24]

Although high level of stylization, mystical appeal, and surreal elegance were often preferred over realism (such as in shan shui style), beginning with the medieval Song dynasty there were many Chinese painters then and afterwards who depicted scenes of nature that were vividly real. Later Ming dynasty artists would take after this Song dynasty emphasis for intricate detail and realism on objects in nature, especially in depictions of animals (such as ducks, swans, sparrows, tigers, etc.) amongst patches of brightly colored flowers and thickets of brush and wood (a good example would be the anonymous Ming dynasty painting Birds and Plum Blossoms,[25] housed in the Freer Gallery of the Smithsonian Museum in Washington, D.C.). There were many renowned Ming dynasty artists; Qiu Ying is an excellent example of a paramount Ming era painter (famous even in his own day), utilizing in his artwork domestic scenes, bustling palatial scenes, and nature scenes of river valleys and steeped mountains shrouded in mist and swirling clouds. During the Ming dynasty there were also different and rivaling schools of art associated with painting, such as the Wu School and the Zhe School.
Classical Chinese painting continued on into the early modern Qing dynasty, with highly realistic portrait paintings like seen in the late Ming dynasty of the early 17th century. The portraits of Kangxi Emperor, Yongzheng Emperor, and Qianlong Emperor are excellent examples of realistic Chinese portrait painting. During the Qianlong reign period and the continuing 19th century, European Baroque styles of painting had noticeable influence on Chinese portrait paintings, especially with painted visual effects of lighting and shading. Likewise, East Asian paintings and other works of art (such as porcelain and lacquerware) were highly prized in Europe since initial contact in the 16th century.
Chinese oil paintings[edit]
Western techniques of oil paintings began entering China in the 19th century, becoming prevalent among Chinese artists and art students in the early 20th century, coinciding with China's growing engagement with the West. Artists such as Li Tiefu, Hong Yi, Xu Beihong, Yan Wenliang, Lin Fengmian, Fang Ganmin, Pang Yuliang went abroad, predominantly to Paris and Tokyo, to learn Western art. Through them, artistic movements such as Impressionism, Cubism, Fauvism, Post-impressionism grew and thrived in China, only halted by the Second World War and the birth of the People's Republic of China, when modernistic artistic styles were seen as being inconsistent with the prevailing political ideals and realism was the only acceptable artistic form. Nonetheless, the legacy of the close engagement with Western art in the early 20th century endured. Oil paintings survived as an important medium in Chinese artistic scenes; traditional Chinese ink paintings were also changed as a result.
- Portrait of Madame Liu, (1942) Li Tiefu oil on canvas
- Portrait of Kang Youwei (1904) Li Tiefu oil on canvas
- Portrait of Madam Cheng (1941) Oil on board Xu Beihong
Japanese[edit]

Japanese painting (絵画) is one of the oldest and most highly refined of the Japanese arts, encompassing a wide variety of genres and styles. As with Japanese arts in general, Japanese painting developed through a long history of synthesis and competition between native Japanese aesthetics and adaptation of imported ideas. Ukiyo-e, or "pictures of the floating world," is a genre of Japanese woodblock prints (or "woodcuts") and paintings produced between the 17th and 20th centuries, featuring motifs of landscapes, theater, and courtesan districts. It is the main artistic genre of Japanese woodblock printing. Japanese printmaking, especially from the Edo period, exerted enormous influence on French painting over the 19th century. While in the 19th century, Japanese painters developed a new painting technique called yōga that borrowed heavily from western painting techniques and materials, such notable artists include Harada Naojirō, Fujishima Takeji, and Kuroda Seiki.
Korean[edit]
Korean painting, as an independent form, began around 108 B.C., around the fall of Gojoseon, making it one of the oldest in the world. The artwork of that time period evolved into the various styles that characterized the Three Kingdoms of Korea period, most notably the paintings and frescoes that adorn the tombs of Goguryeo's royalty. During the Three Kingdoms period and through the Goryeo dynasty, Korean painting was characterized primarily by a combination of Korean-style landscapes, facial features, Buddhist-centered themes, and an emphasis on celestial observation that was facilitated by the rapid development of Korean astronomy. It wasn't until the Joseon dynasty that Confucian themes began to take root in Korean paintings, used in harmony with indigenous aspects.
The history of Korean painting has been characterized by the use monochromatic works of black brushwork, often on mulberry paper or silk. This style is evident in "Min-Hwa", or colorful folk art, tomb paintings, and ritual and festival arts, both of which incorporated an extensive use of colour.
South Asian[edit]
- Floating Figures Dancing, a mural of c. 850.
- Deccan painting; the young Ibrahim Adil Shah II hawking, c. 1590
- Mughal, Yudishthira wrestling with Karna, 1598
- Emperor Shah Jahan and sons, c. 1628 or later. Mughal portraits normally use profile views.
- A Lady Listening to Music, c. 1750.
- Bahsoli painting of Radha and Krishna in Discussion, c. 1730.
- Deccan painting, Sultan Ibrahim Adil Shah II of Bijapur, c. 1590. A three-quarter view which gives a powerful and lively impression of the sitter, despite lacking both Mughal precision, and very coherent modelling of the surfaces.
- Mughal portrait of Raja Jagat Singh of Nurpur (reigned 1618–1646), probably 1619
- Pahari painting, Chamba, c. 1665, a warrior mounts his horse
- Portrait of the Govardhân Chand, Pahari painting style, c. 1750.
- Ravana kills Jathayu; the captive Sita despairs, by Raja Ravi Varma
- Akbar and Tansen Visit Haridas in Vrindavan, Rajasthan style, c. 1750.
- Krishna Summoning the Cows, Pahari painting, Bilaspur, 18th century
- A man with children, Pahari painting style, 1760.
- Company style, 1770s, Crimson Horned Pheasant (Satyr Tragapan)
- Râdhâ arrests Krishna, Pahari painting style, 1770.
- Rama and Sita in the Forest, Pahari painting style, 1780.
- Late Rajput painting, Kota, c. 1830s, Ram Singh II Tiger Hunting
Indian[edit]

Indian paintings historically revolved around the religious deities and kings. Indian art is a collective term for several different schools of art that existed in the Indian subcontinent. The paintings varied from large frescoes of Ajanta to the intricate Mughal miniature paintings to the metal embellished works from the Tanjore school. The paintings from the Gandhar–Taxila are influenced by the Persian works in the west. The eastern style of painting was mostly developed around the Nalanda school of art. The works are mostly inspired by various scenes from Indian mythology.
History[edit]

The earliest Indian paintings were the rock paintings of prehistoric times, the petroglyphs as found in places like the Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka, and some of them are older than 5500 BC. Such works continued and after several millennia, in the 7th century, carved pillars of Ajanta, Maharashtra state present a fine example of Indian paintings, and the colors, mostly various shades of red and orange, were derived from minerals.
Ajanta Caves in Maharashtra, India are rock-cut cave monuments dating back to the 2nd century BCE and containing paintings and sculpture considered to be masterpieces of both Buddhist religious art[27] and universal pictorial art.[28]
- Madhubani painting
Madhubani painting is a style of Indian painting, practiced in the Mithila region of Bihar state, India. The origins of Madhubani painting are shrouded in antiquity.
Mughal[edit]

Mughal painting is a particular style of Indian painting, generally confined to illustrations on the book and done in miniatures, and which emerged, developed and took shape during the period of the Mughal Empire 16th −19th centuries.
Rajput[edit]

Rajput painting evolved and flourished during the 18th century, in the royal courts of Rajputana, India. Each Rajput kingdom evolved a distinct style, but with certain common features. Rajput paintings depict a number of themes, events of epics like the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, Krishna's life, beautiful landscapes, and humans. Miniatures were the preferred medium of Rajput painting, but several manuscripts also contain Rajput paintings, and paintings were even done on the walls of palaces, inner chambers of the forts, havelies, particularly, the havelis of Shekhawait.
The colors extracted from certain minerals, plant sources, conch shells, and were even derived by processing precious stones, gold and silver were used. The preparation of desired colors was a lengthy process, sometimes taking weeks. Brushes used were very fine.
Tanjore[edit]
Tanjore painting is an important form of classical South Indian painting native to the town of Tanjore in Tamil Nadu. The art form dates back to the early 9th century, a period dominated by the Chola rulers, who encouraged art and literature. These paintings are known for their elegance, rich colors, and attention to detail. The themes for most of these paintings are Hindu Gods and Goddesses and scenes from Hindu mythology. In modern times, these paintings have become a much sought after souvenir during festive occasions in South India.
The process of making a Tanjore painting involves many stages. The first stage involves the making of the preliminary sketch of the image on the base. The base consists of a cloth pasted over a wooden base. Then chalk powder or zinc oxide is mixed with water-soluble adhesive and applied on the base. To make the base smoother, a mild abrasive is sometimes used. After the drawing is made, decoration of the jewellery and the apparels in the image is done with semi-precious stones. Laces or threads are also used to decorate the jewellery. On top of this, the gold foils are pasted. Finally, dyes are used to add colors to the figures in the paintings.
Madras School[edit]
During British rule in India, the crown found that Madras had some of the most talented and intellectual artistic minds in the world. As the British had also established a huge settlement in and around Madras, Georgetown was chosen to establish an institute that would cater to the artistic expectations of the royal family in London. This has come to be known as the Madras School of Art. At first traditional artists were employed to produce exquisite varieties of furniture, metal work, and curios and their work was sent to the royal palaces of the Queen.
Unlike the Bengal School where 'copying' is the norm of teaching, the Madras School flourishes on 'creating' new styles, arguments and trends.
Bengal School[edit]

The Bengal school of art was an influential style of art that flourished in India during the British Raj in the early 20th century. It was associated with Indian nationalism, but was also promoted and supported by many British arts administrators.
The Bengal School arose as an avant garde and nationalist movement reacting against the academic art styles previously promoted in India, both by Indian artists such as Raja Ravi Varma and in British art schools. Following the widespread influence of Indian spiritual ideas in the West, the British art teacher Ernest Binfield Havel attempted to reform the teaching methods at the Calcutta School of Art by encouraging students to imitate Mughal miniatures. This caused immense controversy, leading to a strike by students and complaints from the local press, including from nationalists who considered it to be a retrogressive move. Havel was supported by the artist Abanindranath Tagore, a nephew of the poet Rabindranath Tagore. Tagore painted a number of works influenced by Mughal art, a style that he and Havel believed to be expressive of India's distinct spiritual qualities, as opposed to the "materialism" of the West. Tagore's best-known painting, Bharat Mata (Mother India), depicted a young woman, portrayed with four arms in the manner of Hindu deities, holding objects symbolic of India's national aspirations. Tagore later attempted to develop links with Japanese artists as part of an aspiration to construct a pan-Asianist model of art.
The Bengal School's influence in India declined with the spread of modernist ideas in the 1920s. In the post-independence period, Indian artists showed more adaptability as they borrowed freely from European styles and amalgamated them freely with the Indian motifs to new forms of art. While artists like Francis Newton Souza and Tyeb Mehta were more western in their approach, there were others like Ganesh Pyne and Maqbool Fida Husain who developed thoroughly indigenous styles of work. Today after the process of liberalization of market in India, the artists are experiencing more exposure to the international art-scene which is helping them in emerging with newer forms of art which were hitherto not seen in India. Jitish Kallat had shot to fame in the late 1990s with his paintings which were both modern and beyond the scope of generic definition. However, while artists in India in the new century are trying out new styles, themes and metaphors, it would not have been possible to get such quick recognition without the aid of the business houses which are now entering the art field like they had never before.
Modern Indian[edit]
Amrita Sher-Gil was an Indian painter, sometimes known as India's Frida Kahlo,[29] and today considered an important woman painter of 20th-century India, whose legacy stands at par with that of the Masters of Bengal Renaissance;[30][31] she is also the 'most expensive' woman painter of India.[32]
Today, she is amongst Nine Masters, whose work was declared as art treasures by The Archaeological Survey of India, in 1976 and 1979,[33] and over 100 of her paintings are now displayed at National Gallery of Modern Art, New Delhi.[34]
During the colonial era, Western influences started to make an impact on Indian art. Some artists developed a style that used Western ideas of composition, perspective and realism to illustrate Indian themes. Others, like Jamini Roy, consciously drew inspiration from folk art.
By the time of Independence in 1947, several schools of art in India provided access to modern techniques and ideas. Galleries were established to showcase these artists. Modern Indian art typically shows the influence of Western styles, but is often inspired by Indian themes and images. Major artists are beginning to gain international recognition, initially among the Indian diaspora, but also among non-Indian audiences.
The Progressive Artists' Group, established shortly after India became independent in 1947, was intended to establish new ways of expressing India in the post-colonial era. The founders were six eminent artists – K. H. Ara, S. K. Bakre, H. A. Gade, M.F. Husain, S.H. Raza and F. N. Souza, though the group was dissolved in 1956, it was profoundly influential in changing the idiom of Indian art. Almost all India's major artists in the 1950s were associated with the group. Some of those who are well-known today are Bal Chabda, Manishi Dey, Mukul Dey, V. S. Gaitonde, Ram Kumar, Tyeb Mehta, and Akbar Padamsee. Other famous painters like Jahar Dasgupta, Prokash Karmakar, John Wilkins, Narayanan Ramachandran, and Bijon Choudhuri enriched the art culture of India. They have become the icons of modern Indian art. Art historians like Prof. Rai Anand Krishna have also referred to those works of modern artistes that reflect Indian ethos. Geeta Vadhera has had acclaim in translating complex, Indian spiritual themes onto canvas like Sufi thought, the Upanishads and the Bhagwad Geeta.
Indian art got a boost with the economic liberalization of the country since the early 1990s. Artists from various fields now started bringing in varied styles of work. In post-liberalization India, many artists have established themselves in the international art market like the abstract painter Natvar Bhavsar, figurative artist Devajyoti Ray and sculptor Anish Kapoor whose mammoth postminimalist artworks have acquired attention for their sheer size. Many art houses and galleries have also opened in USA and Europe to showcase Indian artworks.
South-East Asia[edit]
Indonesian[edit]

The oldest known cave paintings are more than 44,000–50,000 years old, found in the caves in the district of Maros (Sulawesi, Indonesia). The oldest type of cave paintings are hand stencils and simple geometric shapes; the oldest undisputed examples of figurative cave paintings are somewhat younger, close to 35,000 years old.[11]
The discovery of the then-oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal, in the cave of Lubang Jeriji Saléh on the Indonesian island of Borneo. In December 2019, however, figurative cave paintings depicting pig hunting in the Maros-Pangkep karst in Sulawesi were estimated to be even older, at at least 43,900 years old. The finding was noted to be "the oldest pictorial record of storytelling and the earliest figurative artwork in the world".[14][15]

Other examples of Indonesian paintings are the Kenyah decorative art, based on endemic natural motifs such as ferns and hornbills, found decorating the walls of Kenyah longhouses. Other notable traditional art is the geometric Toraja wood carvings. Balinese paintings are initially the narrative images to depict scenes of Balinese legends and religious scripts. The classical Balinese paintings are often decorating the lontar manuscripts and also the ceilings of temples pavilion. Notable modern Indonesian painters in the European tradition include Raden Saleh, Jan Toorop, Basuki Abdullah and Abdullah Suriosubroto, their themes explore landscape and portrait painting.
- Traditional Balinese painting depicting cockfighting.
- Capture of Prince Diponegoro, 1857.
- Javanese Landscape, with Tigers Listening to the Sound of a Travelling Group, 1849.
- The Wheel of Life, I Ketut Murtika (b. 1952), Gouache on canvas
- Pre-1920 Kamasan Palindon Painting detail, an example of Kamasan-style classical painting.
- Mask Dancer (by A.A. Gde Anom Sukawati) in Puri Lukisan Museum.
- Legong dancer.
- Indonesian Temple painting.
Filipino[edit]

Filipino painting as a whole can be seen as an amalgamation of many cultural influences, though it tends to be more Western in its current form with Eastern roots.
Early Filipino painting can be found in red slip (clay mixed with water) designs embellished on the ritual pottery of the Philippines such as the Manunggul Jar. Evidence of Philippine pottery-making dated as early as 6000 BC has been found in Sanga-sanga Cave, Sulu and Laurente Cave, Cagayan. By 5000 BC the making of pottery was practiced throughout the country. Early Filipinos started making pottery before their Cambodian neighbors and at about the same time as the Thais as part of what appears to be a widespread Ice Age development of pottery technology. Further evidences of painting are manifested in the tattoo tradition of early Filipinos, in particular the Visayans, whom Spanish explorers referred to as Pintados or the 'Painted People'.[35] They decorated their bodies in various colored pigmentations with designs referencing flora and fauna and heavenly bodies. Some of the most elaborate painting done by early Filipinos that survives to the present day is manifested among the arts and architecture of the Maranao who are well known for the Nāga Dragons and the Sarimanok carved and painted in the beautiful Panolong of their Torogan or King's House.

Filipinos began creating paintings in the European tradition during the 17th-century Spanish period.[36] The earliest of these paintings were Church frescoes and religious imagery from Biblical sources as well as engravings, sculptures and lithographs featuring Christian icons and European nobility. Most of the paintings and sculptures between the 19th and 20th century were a mixture of religious, political, and landscape artwork, with qualities of sweetness, dark, and light. Early modernist painters such as Damián Domingo were associated with religious and secular paintings. The art of Juan Luna and Félix Hidalgo showed a trend toward political statement. Artists such as Fernando Amorsolo used post-modernism to produce paintings that illustrated Philippine culture, nature, and harmony. Other artists such as Fernando Zóbel used reality and abstraction in their work.
- Lila Church ceiling painting
- Lorenzo de la Rocha Icaza, Mujer filipina, 1895
- Fabián de la Rosa, Women Working in rice field, 1902
- José Honorato Lozano, Indios, 1847
Western[edit]
Egypt, Greece and Rome[edit]

Ancient Egypt, a civilization with very strong traditions of architecture and sculpture (both originally painted in bright colours) also had many mural paintings in temples and buildings, and painted illustrations on papyrus manuscripts. Egyptian wall painting and decorative painting is often graphic, sometimes more symbolic than realistic. Egyptian painting depicts figures in bold outline and flat silhouette, in which symmetry is a constant characteristic. Egyptian painting has close connection with its written language – called Egyptian hieroglyphs. Painted symbols are found amongst the first forms of written language. The Egyptians also painted on linen, remnants of which survive today. Ancient Egyptian paintings survived due to the extremely dry climate. The ancient Egyptians created paintings to make the afterlife of the deceased a pleasant place. The themes included journey through the afterworld or their protective deities introducing the deceased to the gods of the underworld. Some examples of such paintings are paintings of the gods and goddesses Ra, Horus, Anubis, Nut, Osiris and Isis. Some tomb paintings show activities that the deceased were involved in when they were alive and wished to carry on doing for eternity. In the New Kingdom and later, the Book of the Dead was buried with the entombed person. It was considered important for an introduction to the afterlife.
- Sennedjem plows his fields with a pair of oxen, c. 1200 BC
- Ancient Egypt, Queen Nefertari
- Ancient Egypt, papyrus
- Fresco of an ancient Macedonian soldier (thorakitai) wearing chainmail armor and bearing a thureos shield, 3rd century BC
- Fresco depicting sacrifice of Iphigenia
- Roman art showing Dirce's punishment
- Roman art showing Pirithous and Hippodamia
- Roman art, Pompeii, Villa of the Mysteries, c. 60-50 BC
- Roman art, Villa Boscoreale frescos, c. 40 BC
- Roman art, Pompeii
- The Three Graces, fresco from Pompeii
- The Fall of Icarus, fresco from Pompeii, 40-79 AD
- Roman art, Pompeii
- Roman art, Fayum mummy portraits from Roman Egypt
- Roman art from the House of the Vettii, Pompeii, 1st century AD
- Roman fresco with a seated Venus, the so-called "Dea Barberini", 4th century AD
To the north of Egypt was the Minoan civilization centered on the island of Crete. The wall paintings found in the palace of Knossos are similar to that of the Egyptians but much more free in style. Mycenaean Greece, beginning around 1600 BC, produced similar art to that of Minoan Crete. Ancient Greek art during the Greek Dark Age became far less complex, but the renewal of Greek civilization throughout the Mediterranean during Archaic Greece brought about new forms of Greek art with the Orientalizing style.

Ancient Greece had skilled painters, sculptors (though both endeavours were regarded as mere manual labour at the time), and architects. The Parthenon is an example of their architecture that has lasted to modern days. Greek marble sculpture is often described as the highest form of Classical art. Painting on pottery of Ancient Greece and ceramics gives a particularly informative glimpse into the way society in Ancient Greece functioned. Black-figure vase painting and Red-figure vase painting gives many surviving examples of what Greek painting was. Some famous Greek painters on wooden panels who are mentioned in texts are Apelles, Zeuxis and Parrhasius, however few examples of Ancient Greek panel painting survive, mostly just written descriptions by their contemporaries or later Romans. Zeuxis lived in 5–6 BC and was said to be the first to use sfumato. According to Pliny the Elder, the realism of his paintings was such that birds tried to eat the painted grapes. Apelles is described as the greatest painter of Antiquity for perfect technique in drawing, brilliant color and modeling.
Roman art was influenced by Greece and can in part be taken as a descendant of ancient Greek painting. However, Roman painting does have important unique characteristics. Surviving Roman paintings include wall paintings and frescoes, many from villas in Campania, in Southern Italy at sites such as Pompeii and Herculaneum. Such painting can be grouped into four main "styles" or periods[37] and may contain the first examples of trompe-l'œil, pseudo-perspective, and pure landscape.[38] Almost the only painted portraits surviving from the Ancient world are a large number of coffin-portraits of bust form found in the Late Antique cemetery of Al-Fayum. Although these were neither of the best period nor the highest quality, they are impressive in themselves, and give an idea of the quality that the finest ancient work must have had. A very small number of miniatures from Late Antique illustrated books also survive, and a rather larger number of copies of them from the Early Medieval period.
Middle Ages[edit]
- Byzantine icon, 6th century
- Byzantine art mosaics in Ravenna
- Byzantine, 6th century
- The Capture of Jerusalem during the First Crusade, c. 1099
- The Morgan Leaf, from the Winchester Bible 1160–75, Scenes from the life of David
- Yaroslavl Gospels c. 1220s
- Carolingian Saint Mark
- Bonaventura Berlinghieri, St Francis of Assisi, 1235
- Rogier van der Weyden, (c. 1435)
- Rogier van der Weyden, St Ivo (c. 1450)
The rise of Christianity imparted a different spirit and aim to painting styles. Byzantine art, once its style was established by the 6th century, placed great emphasis on retaining traditional iconography and style, and gradually evolved during the thousand years of the Byzantine Empire and the living traditions of Greek and Russian Orthodox icon-painting. Byzantine painting has a hieratic feeling and icons were and still are seen as a representation of divine revelation. There were many frescos, but fewer of these have survived than mosaics. Byzantine art has been compared to contemporary abstraction, in its flatness and highly stylised depictions of figures and landscape. Some periods of Byzantine art, especially the so-called Macedonian art of around the 10th century, are more flexible in approach. Frescos of the Palaeologian Renaissance of the early 14th century survive in the Chora Church in Istanbul.

In post-Antique Catholic Europe the first distinctive artistic style to emerge that included painting was the Insular art of the British Isles, where the only surviving examples are miniatures in Illuminated manuscripts such as the Book of Kells.[39] These are most famous for their abstract decoration, although figures, and sometimes scenes, were also depicted, especially in Evangelist portraits. Carolingian and Ottonian art also survives mostly in manuscripts, although some wall-painting remain, and more are documented. The art of this period combines Insular and "barbarian" influences with a strong Byzantine influence and an aspiration to recover classical monumentality and poise.
Walls of Romanesque and Gothic churches were decorated with frescoes as well as sculpture and many of the few remaining murals have great intensity, and combine the decorative energy of Insular art with a new monumentality in the treatment of figures. Far more miniatures in Illuminated manuscripts survive from the period, showing the same characteristics, which continue into the Gothic period.
Panel painting becomes more common during the Romanesque period, under the heavy influence of Byzantine icons. Towards the middle of the 13th century, Medieval art and Gothic painting became more realistic, with the beginnings of interest in the depiction of volume and perspective in Italy with Cimabue and then his pupil Giotto. From Giotto on, the treatment of composition by the best painters also became much more free and innovative. They are considered to be the two great medieval masters of painting in western culture. Cimabue, within the Byzantine tradition, used a more realistic and dramatic approach to his art. His pupil, Giotto, took these innovations to a higher level which in turn set the foundations for the western painting tradition. Both artists were pioneers in the move towards naturalism.
Churches were built with more and more windows and the use of colorful stained glass become a staple in decoration. One of the most famous examples of this is found in the cathedral of Notre Dame de Paris. By the 14th century Western societies were both richer and more cultivated and painters found new patrons in the nobility and even the bourgeoisie. Illuminated manuscripts took on a new character and slim, fashionably dressed court women were shown in their landscapes. This style soon became known as International style and tempera panel paintings and altarpieces gained importance.
Renaissance and Mannerism[edit]
- Robert Campin, c. 1425
- Jan van Eyck, 1434
- Rogier van der Weyden, c. 1435
- Hugo van der Goes, c. 1470
- Dieric Bouts, 1464–1467
- Hans Memling, c. 1466–1473
- Petrus Christus, c. 1470
- Hieronymus Bosch, c. 1480–1505
- Fra Angelico, 1425–1428
- Paolo Uccello, c. 1470
- Masaccio, 1426–1427
- Jean Fouquet, 1450
- Andrea Mantegna, c. 1458–1460
- Piero della Francesca, 1463–1465
- Sandro Botticelli, 1483–1485
- Leonardo da Vinci, 1503–1506
- Raphael, 1505–1506
- Michelangelo, c. 1511
- Lucas Cranach the Elder, c. 1530
- Albrecht Dürer, 1500
- Matthias Grünewald, 1512–1516
- Giovanni Bellini, c. 1480
- Giorgione, c. 1505
- Titian, 1520–1523
- École de Fontainebleau, 1530
- Bronzino, 1540–1545
- Pieter Bruegel, 1565
- Hans Holbein the Younger, 1527
- Jacopo Tintoretto, 1582
- Paolo Veronese, 1562–1563
- Joachim Wtewael, 1595
- El Greco, 1596–1600
The Renaissance (French for 'rebirth'), a cultural movement roughly spanning the 14th through the mid-17th century, heralded the study of classical sources, as well as advances in science which profoundly influenced European intellectual and artistic life. In the Low Countries, especially in modern day Flanders, a new way of painting was established in the beginning of the 15th century. In the footsteps of the developments made in the illumination of manuscripts, especially by the Limbourg Brothers, artists became fascinated by the tangible in the visible world and began representing objects in an extremely naturalistic way.[40] The adoption of oil painting whose invention was traditionally, but erroneously, credited to Jan van Eyck, made possible a new verisimilitude in depicting this naturalism. The medium of oil paint was already present in the work of Melchior Broederlam, but painters like Jan van Eyck and Robert Campin brought its use to new heights and employed it to represent the naturalism they were aiming for. With this new medium the painters of this period were capable of creating richer colors with a deep intense tonality. The illusion of glowing light with a porcelain-like finish characterized Early Netherlandish painting and was a major difference to the matte surface of tempera paint used in Italy.[40] Unlike the Italians, whose work drew heavily from the art of Ancient Greece and Rome, the northerners retained a stylistic residue of the sculpture and illuminated manuscripts of the Middle Ages (especially its naturalism). The most important artist of this time was Jan van Eyck, whose work ranks among the finest made by artists who are now known as Early Netherlandish painters or Flemish Primitives (since most artists were active in cities in modern day Flanders). The first painter of this period was the Master of Flémalle, nowadays identified as Robert Campin, whose work follows the art of the International Gothic. Another important painter of this period was Rogier van der Weyden, whose compositions stressed human emotion and drama, demonstrated for instance in his Descent from the Cross, which ranks among the most famous works of the 15th century and was the most influential Netherlandish painting of Christ's crucifixion. Other important artists from this period are Hugo van der Goes (whose work was highly influential in Italy), Dieric Bouts (who was among the first northern painters to demonstrate the use of a single vanishing point),[40] Petrus Christus, Hans Memling and Gerard David.
In Italy, the art of Classical antiquity inspired a style of painting that emphasized the ideal. Artists such as Paolo Uccello, Masaccio, Fra Angelico, Piero della Francesca, Andrea Mantegna, Filippo Lippi, Sandro Botticelli, Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo Buonarroti, and Raphael took painting to a higher level through the use of perspective, the study of human anatomy and proportion, and through their development of an unprecedented refinement in drawing and painting techniques. A somewhat more naturalistic style emerged in Venice. Painters of the Venetian school, such as Giovanni Bellini, Giorgione, Titian, Tintoretto, and Veronese, were less concerned with precision in their drawing than with the richness of color and unity of effect that could be achieved by a more spontaneous approach to painting.
Flemish, Dutch and German painters of the Renaissance such as Hans Holbein the Younger, Albrecht Dürer, Lucas Cranach, Matthias Grünewald, Hieronymus Bosch, and Pieter Bruegel represent a different approach from their Italian colleagues, one that is more realistic and less idealized. Genre painting became a popular idiom amongst the Northern painters like Pieter Bruegel.
The French tradition of International Gothic, will develop a new style by integrating the strong chromatic tones of Gothic with the Italian perspective and volumes of the Quattrocento, as well as the naturalistic innovations of the Flemish primitives, called the École de Tours. Its main representatives are Jean Fouquet, Barthélemy d'Eyck from the Netherlands, Jean and François Clouet, Jean Perreal, Nicolas Froment and the École de Fontainebleau.
Renaissance painting reflects the revolution of ideas and science (astronomy, geography) that occurred in this period, the Reformation, and the invention of the printing press. Dürer, considered one of the greatest of printmakers, states that painters are not mere artisans but thinkers as well. With the development of easel painting in the Renaissance, painting gained independence from architecture. Easel paintings—movable pictures which could be hung easily on walls—became a popular alternative to paintings fixed to furniture, walls or other structures. Following centuries dominated by religious imagery, secular subject matter slowly returned to Western painting. Artists included visions of the world around them, or the products of their own imaginations in their paintings. Those who could afford the expense could become patrons and commission portraits of themselves or their family.
The High Renaissance gave rise to a stylized art known as Mannerism. In place of the balanced compositions and rational approach to perspective that characterized art at the dawn of the 16th century, the Mannerists sought instability, artifice, and doubt. The unperturbed faces and gestures of Piero della Francesca and the calm Virgins of Raphael are replaced by the troubled expressions of Pontormo and the emotional intensity of El Greco. Restless and unstable compositions, often extreme or disjunctive effects of perspective, and stylized poses are characteristic of Italian Mannerists such as Tintoretto, Pontormo, and Bronzino, and appeared later in the work of Northern Mannerists such as Hendrick Goltzius, Bartholomeus Spranger, and Joachim Wtewael.
Baroque and Rococo[edit]
- Caravaggio, 1595–1597
- Artemisia Gentileschi, 1614–1620
- Peter Paul Rubens, 1632–1635
- Frans Hals, 1624
- Judith Leyster, 1630
- Rembrandt van Rijn, 1642
- Pieter de Hooch, 1658
- Johannes Vermeer, c. 1660
- Jan Steen, c. 1665
- Jacob van Ruisdael, 1670
- Willem Claesz. Heda, 1631
- Diego Velázquez, 1656–1657
- Jusepe de Ribera, 1620–1624
- Nicolas Poussin, c. 1637–1638
- Georges de La Tour, 1640s
- Guido Reni, 1625
- Salvator Rosa, c. 1645
- Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, c. 1650–1655
- Claude Lorrain, 1648
- Anthony van Dyck, 1635–1636
- Canaletto, 1723
- Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, c. 1752–1753
- Antoine Watteau, c. 1720
- Jean-Honoré Fragonard, c. 1767–1768
- François Boucher, 1751
- Élisabeth Louise Vigée-Le Brun, after 1782
- Maurice Quentin de La Tour, c. 1761
- Thomas Gainsborough, c. 1770
- Joshua Reynolds, 1769
- Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin, c. 1728
- William Hogarth, c. 1757
- Angelica Kauffman, c. 1780
Baroque painting is associated with the Baroque cultural movement, a movement often identified with Absolutism and the Counter Reformation or Catholic Revival;[41][42] the existence of important Baroque painting in non-absolutist and Protestant states also, however, underscores its popularity, as the style spread throughout Western Europe.[43]
Baroque painting is characterized by great drama, rich, deep color, and intense light and dark shadows. Baroque art was meant to evoke emotion and passion instead of the calm rationality that had been prized during the Renaissance. During the period beginning around 1600 and continuing throughout the 17th century, painting is characterized as Baroque. Among the greatest painters of the Baroque are Caravaggio, Rembrandt, Frans Hals, Rubens, Velázquez, Poussin, and Johannes Vermeer. Caravaggio is an heir of the humanist painting of the High Renaissance. His realistic approach to the human figure, painted directly from life and dramatically spotlit against a dark background, shocked his contemporaries and opened a new chapter in the history of painting. Baroque painting often dramatizes scenes using light effects; this can be seen in works by Rembrandt, Vermeer, Le Nain, La Tour, and Jusepe de Ribera.

In Italy, the Baroque style is epitomized by religious and mythological paintings in the Grand Manner by artists such as the Carracci, Guido Reni, and Luca Giordano. Illusionistic church ceiling frescoes by Pietro da Cortona seemed to open to the sky. A much quieter type of Baroque emerged in the Dutch Republic, where easel paintings of everyday subjects were popular with middle-class collectors, and many painters became specialists in genre, others in landscape or seascape or still life. Vermeer, Gerard ter Borch, and Pieter de Hooch brought great technical refinement to the painting of domestic scenes, as did Willem Claesz. Heda to still life. In contrast, Rembrandt excelled in painting every type of subject, and developed an individual painterly style in which the chiaroscuro and dark backgrounds derived from Caravaggio and the Utrecht Caravaggists lose their theatrical quality.
During the 18th century, Rococo followed as a lighter extension of Baroque, often frivolous and erotic. Rococo developed first in the decorative arts and interior design in France. Louis XV's succession brought a change in the court artists and general artistic fashion. The 1730s represented the height of Rococo development in France exemplified by the works of Antoine Watteau and François Boucher. Rococo still maintained the Baroque taste for complex forms and intricate patterns, but by this point, it had begun to integrate a variety of diverse characteristics, including a taste for Oriental designs and asymmetric compositions.
The Rococo style spread with French artists and engraved publications. It was readily received in the Catholic parts of Germany, Bohemia, and Austria, where it was merged with the lively German Baroque traditions. German Rococo was applied with enthusiasm to churches and palaces, particularly in the south, while Frederician Rococo developed in the Kingdom of Prussia.
The French masters Watteau, Boucher and Fragonard represent the style, as do Giovanni Battista Tiepolo and Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin who was considered by some as the best French painter of the 18th century – the Anti-Rococo. Portraiture was an important component of painting in all countries, but especially in England, where the leaders were William Hogarth, in a blunt realist style, and Francis Hayman, Angelica Kauffman (who was Swiss), Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds in more flattering styles influenced by Anthony van Dyck. In France during the Rococo era Jean-Baptiste Greuze (the favorite painter of Denis Diderot),[44] excelled in portraits and history paintings, and Maurice Quentin de La Tour and Élisabeth Vigée-Lebrun were highly accomplished portrait painters. La Tour specialized in pastel painting, which became a popular medium during this period.
William Hogarth helped develop a theoretical foundation for Rococo beauty. Though not intentionally referencing the movement, he argued in his Analysis of Beauty (1753) that the undulating lines and S-curves prominent in Rococo were the basis for grace and beauty in art or nature (unlike the straight line or the circle in Classicism). The beginning of the end for Rococo came in the early 1760s as figures like Voltaire and Jacques-François Blondel began to voice their criticism of the superficiality and degeneracy of the art. Blondel decried the "ridiculous jumble of shells, dragons, reeds, palm-trees and plants" in contemporary interiors.[45]
By 1785, Rococo had passed out of fashion in France, replaced by the order and seriousness of Neoclassical artists like Jacques-Louis David.
19th century: Neo-classicism, History painting, Romanticism, Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, Symbolism[edit]
- Jacques-Louis David 1787
- John Constable 1802
- Antoine-Jean Gros, 1804
- Francisco de Goya 1814
- Théodore Géricault 1819
- Caspar David Friedrich c.1822
- Eugène Delacroix 1830
- J. M. W. Turner 1838
- Gustave Courbet 1849–1850
- Ivan Aivazovsky 1850
- Albert Bierstadt 1866
- Camille Corot c.1867
- Ilya Repin 1870–1873
- Camille Pissarro 1872
- Claude Monet 1872
- Edgar Degas 1876
- Édouard Manet 1882
- Thomas Eakins 1884–1885
- Georges Seurat 1884–1886
- Valentin Serov 1887
- Vincent van Gogh 1889
- Albert Pinkham Ryder 1890
- Paul Gauguin 1897–1898
- Winslow Homer 1899
- Paul Cézanne 1906
After Rococo there arose in the late 18th century, in architecture, and then in painting severe neo-classicism, best represented by such artists as David and his heir Ingres. Ingres' work already contains much of the sensuality, but none of the spontaneity, that was to characterize Romanticism. This movement turned its attention toward landscape and nature as well as the human figure and the supremacy of natural order above mankind's will. There is opposition to Enlightenment ideals, as humanity is seen being at the whim of nature's chaos. The idea that human beings are not above the forces of Nature is in contradiction to Ancient Greek and Renaissance ideals where mankind was above all things and owned his fate. This thinking led romantic artists to depict the sublime, ruined churches, shipwrecks, massacres and madness.
By the mid-19th-century painters became liberated from the demands of their patronage to only depict scenes from religion, mythology, portraiture or history. The idea "art for art's sake" began to find expression in the work of painters like Francisco de Goya, John Constable, and J.M.W. Turner. Romantic painters saw landscape painting as an important genre to express the vanity of mankind in opposition to the grandeur of nature. Until then, landscape painting wasn't considered the most important genre for painters (like portraiture or history painting). But painters like J.M.W. Turner and Caspar David Friedrich managed to elevate landscape painting to an eminence rivalling history painting. Some of the major painters of this period are Eugène Delacroix, Théodore Géricault, J. M. W. Turner, Caspar David Friedrich and John Constable. Francisco de Goya's late work demonstrates the Romantic interest in the irrational, while the work of Arnold Böcklin evokes mystery and the paintings of Aesthetic movement artist James McNeill Whistler evoke both sophistication and decadence. In the United States the Romantic tradition of landscape painting was known as the Hudson River School:[46] exponents include Thomas Cole, Frederic Edwin Church, Albert Bierstadt, Thomas Moran, and John Frederick Kensett. Luminism was a movement in American landscape painting related to the Hudson River School.

The leading Barbizon School painter Camille Corot painted in both a romantic and a realistic vein; his work prefigures Impressionism, as does the paintings of Eugène Boudin who was one of the first French landscape painters to paint outdoors. Boudin was also an important influence on the young Claude Monet, whom in 1857 he introduced to Plein air painting. A major force in the turn towards Realism at mid-century was Gustave Courbet. In the latter third of the century Impressionists like Édouard Manet, Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Camille Pissarro, Alfred Sisley, Berthe Morisot, Mary Cassatt, and Edgar Degas worked in a more direct approach than had previously been exhibited publicly. They eschewed allegory and narrative in favor of individualized responses to the modern world, sometimes painted with little or no preparatory study, relying on deftness of drawing and a highly chromatic pallette. Manet, Degas, Renoir, Morisot, and Cassatt concentrated primarily on the human subject. Both Manet and Degas reinterpreted classical figurative canons within contemporary situations; in Manet's case the re-imaginings met with hostile public reception. Renoir, Morisot, and Cassatt turned to domestic life for inspiration, with Renoir focusing on the female nude. Monet, Pissarro, and Sisley used the landscape as their primary motif, the transience of light and weather playing a major role in their work. While Sisley most closely adhered to the original principals of the Impressionist perception of the landscape, Monet sought challenges in increasingly chromatic and changeable conditions, culminating in his series of monumental works of Water Lilies painted in Giverny.

Pissarro adopted some of the experiments of Post-Impressionism. Slightly younger Post-Impressionists like Vincent van Gogh, Paul Gauguin, and Georges Seurat, along with Paul Cézanne led art to the edge of modernism; for Gauguin Impressionism gave way to a personal symbolism; Seurat transformed Impressionism's broken color into a scientific optical study, structured on frieze-like compositions; Van Gogh's turbulent method of paint application, coupled with a sonorous use of color, predicted Expressionism and Fauvism, and Cézanne, desiring to unite classical composition with a revolutionary abstraction of natural forms, would come to be seen as a precursor of 20th-century art. The spell of Impressionism was felt throughout the world, including in the United States, where it became integral to the painting of American Impressionists such as Childe Hassam, John Twachtman, and Theodore Robinson; and in Australia where painters of the Heidelberg School such as Arthur Streeton, Frederick McCubbin and Charles Conder painted en plein air and were particularly interested in the Australian landscape and light. It also exerted influence on painters who were not primarily Impressionistic in theory, like the portrait and landscape painter John Singer Sargent. At the same time in America at the turn of the 20th century there existed a native and nearly insular realism, as richly embodied in the figurative work of Thomas Eakins, the Ashcan School, and the landscapes and seascapes of Winslow Homer, all of whose paintings were deeply invested in the solidity of natural forms. The visionary landscape, a motive largely dependent on the ambiguity of the nocturne, found its advocates in Albert Pinkham Ryder and Ralph Albert Blakelock.
In the late 19th century there also were several, rather dissimilar, groups of Symbolist painters whose works resonated with younger artists of the 20th century, especially with the Fauvists and the Surrealists. Among them were Gustave Moreau, Odilon Redon, Pierre Puvis de Chavannes, Henri Fantin-Latour, Arnold Böcklin, Edvard Munch, Félicien Rops, and Jan Toorop, and Gustav Klimt amongst others including the Russian Symbolists like Mikhail Vrubel.
Symbolist painters mined mythology and dream imagery for a visual language of the soul, seeking evocative paintings that brought to mind a static world of silence. The symbols used in Symbolism are not the familiar emblems of mainstream iconography but intensely personal, private, obscure and ambiguous references. More a philosophy than an actual style of art, the Symbolist painters influenced the contemporary Art Nouveau movement and Les Nabis. In their exploration of dreamlike subjects, symbolist painters are found across centuries and cultures, as they are still today; Bernard Delvaille has described René Magritte's surrealism as "Symbolism plus Freud".[47]
20th-century modern and contemporary[edit]
The heritage of painters like Van Gogh, Cézanne, Gauguin, and Seurat was essential for the development of modern art. At the beginning of the 20th century Henri Matisse and several other young artists revolutionized the Paris art world with "wild", multi-colored, expressive, landscapes and figure paintings that the critics called Fauvism. Pablo Picasso made his first cubist paintings based on Cézanne's idea that all depiction of nature can be reduced to three solids: cube, sphere and cone.
Pioneers of the 20th century[edit]
- Henri Matisse 1905, Fauvism
- Pablo Picasso 1907, Proto-Cubism

The heritage of painters like Van Gogh, Cézanne, Gauguin, and Seurat was essential for the development of modern art. At the beginning of the 20th century Henri Matisse and several other young artists including the pre-cubist Georges Braque, André Derain, Raoul Dufy and Maurice de Vlaminck revolutionized the Paris art world with "wild", multi-colored, expressive, landscapes and figure paintings that the critics called Fauvism. Henri Matisse's second version of The Dance signifies a key point in his career and in the development of modern painting.[48] It reflects Matisse's incipient fascination with primitive art: the intense warm colors against the cool blue-green background and the rhythmical succession of dancing nudes convey the feelings of emotional liberation and hedonism. Pablo Picasso made his first cubist paintings based on Cézanne's idea that all depiction of nature can be reduced to three solids: cube, sphere and cone. With the painting Les Demoiselles d'Avignon 1907, Picasso dramatically created a new and radical picture depicting a raw and primitive brothel scene with five prostitutes, violently painted women, reminiscent of African tribal masks and his own new Cubist inventions. analytic Cubism was jointly developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, exemplified by Violin and Candlestick, Paris, from about 1908 through 1912. Analytic cubism, the first clear manifestation of cubism, was followed by synthetic cubism, practised by Braque, Picasso, Fernand Léger, Juan Gris, Albert Gleizes, Marcel Duchamp and countless other artists into the 1920s. Synthetic cubism is characterized by the introduction of different textures, surfaces, collage elements, papier collé and a large variety of merged subject matter.

Les Fauves (French for The Wild Beasts) were early-20th-century painters, experimenting with freedom of expression through color. The name was given, humorously and not as a compliment, to the group by art critic Louis Vauxcelles. Fauvism was a short-lived and loose grouping of early-20th-century artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities, and the imaginative use of deep color over the representational values. Fauvists made the subject of the painting easy to read, exaggerated perspectives and an interesting prescient prediction of the Fauves was expressed in 1888 by Paul Gauguin to Paul Sérusier,
How do you see these trees? They are yellow. So, put in yellow; this shadow, rather blue, paint it with pure ultramarine; these red leaves? Put in vermilion.
The leaders of the movement were Henri Matisse and André Derain – friendly rivals of a sort, each with his own followers. Ultimately Matisse became the yang to Picasso's yin in the 20th century. Fauvist painters included Albert Marquet, Charles Camoin, Maurice de Vlaminck, Raoul Dufy, Othon Friesz, the Dutch painter Kees van Dongen, and Picasso's partner in Cubism, Georges Braque amongst others.[49]

Fauvism, as a movement, had no concrete theories, and was short lived, beginning in 1905 and ending in 1907, they only had three exhibitions. Matisse was seen as the leader of the movement, due to his seniority in age and prior self-establishment in the academic art world. His 1905 portrait of Mme. Matisse The Green Line, (above), caused a sensation in Paris when it was first exhibited. He said he wanted to create art to delight; art as a decoration was his purpose and it can be said that his use of bright colors tries to maintain serenity of composition. In 1906 at the suggestion of his dealer Ambroise Vollard, André Derain went to London and produced a series of paintings like Charing Cross Bridge, London (above) in the Fauvist style, paraphrasing the famous series by the Impressionist painter Claude Monet. Masters like Henri Matisse and Pierre Bonnard continued developing their narrative styles independent of any movement throughout the 20th century.
By 1907 Fauvism no longer was a shocking new movement, soon it was replaced by Cubism on the critics' radar screen as the latest new development in Contemporary Art of the time. In 1907 Appolinaire, commenting about Matisse in an article published in La Falange, said, "We are not here in the presence of an extravagant or an extremist undertaking: Matisse's art is eminently reasonable."[50] Analytic cubism was jointly developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque from about 1908 through 1912. Analytic cubism, the first clear manifestation of cubism, was followed by Synthetic cubism, practised by Braque, Picasso, Fernand Léger, Juan Gris, Albert Gleizes, Marcel Duchamp and countless other artists into the 1920s. Synthetic cubism is characterized by the introduction of different textures, surfaces, collage elements, papier collé and a large variety of merged subject matter.
During the years between 1910 and the end of World War I and after the heyday of cubism, several movements emerged in Paris. Giorgio de Chirico moved to Paris in July 1911, where he joined his brother Andrea (the poet and painter known as Alberto Savinio). Through his brother he met Pierre Laprade a member of the jury at the Salon d'Automne, where he exhibited three of his dreamlike works: Enigma of the Oracle, Enigma of an Afternoon and Self-Portrait. During 1913 he exhibited his work at the Salon des Indépendants and Salon d'Automne, his work was noticed by Pablo Picasso and Guillaume Apollinaire and several others. His compelling and mysterious paintings are considered instrumental to the early beginnings of Surrealism. During the first half of the 20th century in Europe masters like Georges Braque, André Derain, and Giorgio de Chirico continued painting independent of any movement.
Pioneers of Modern art[edit]
- André Derain, 1905, Le séchage des voiles (The Drying Sails), Fauvism
- Henri Matisse, 1905, Woman with a Hat, Fauvism
- Edvard Munch, Death of Marat I (1907), an example of Expressionism
- Gustav Klimt, expressionism, 1907–1908
- Pablo Picasso, 1908, Dryad, Proto-Cubism
- Franz Marc 1912, Der Blaue Reiter
- Robert Delaunay, 1911, Orphism
- Wassily Kandinsky 1913, birth of abstract art
In the first two decades of the 20th century and after Cubism, several other important movements emerged; futurism (Balla), abstract art (Kandinsky), Der Blaue Reiter), Bauhaus, (Kandinsky) and (Klee), Orphism, (Robert Delaunay and František Kupka), Synchromism (Morgan Russell), De Stijl (Mondrian), Suprematism (Malevich), Constructivism (Tatlin), Dadaism (Duchamp, Picabia, Arp) and Surrealism (De Chirico, André Breton, Miró, Magritte, Dalí, Ernst). Modern painting influenced all the visual arts, from Modernist architecture and design, to avant-garde film, theatre and modern dance and became an experimental laboratory for the expression of visual experience, from photography and concrete poetry to advertising art and fashion. Van Gogh's painting exerted great influence upon 20th-century Expressionism, as can be seen in the work of the Fauves, Die Brücke (a group led by German painter Ernst Kirchner), and the Expressionism of Edvard Munch, Egon Schiele, Marc Chagall, Amedeo Modigliani, Chaïm Soutine and others..
Wassily Kandinsky a Russian painter, printmaker and art theorist, one of the most famous 20th-century artists is generally considered the first important painter of modern abstract art. As an early Modernist, in search of new modes of visual expression, and spiritual expression, he theorized as did contemporary occultists and theosophists, that pure visual abstraction had corollary vibrations with sound and music. They posited that pure abstraction could express pure spirituality. His earliest abstractions were generally titled as the example in the (above gallery) Composition VII, making connection to the work of the composers of music. Kandinsky included many of his theories about abstract art in his book Concerning the Spiritual in Art. Robert Delaunay was a French artist who is associated with Orphism, (reminiscent of a link between pure abstraction and cubism). His later works were more abstract, reminiscent of Paul Klee. His key contributions to abstract painting refer to his bold use of color, and a clear love of experimentation of both depth and tone. At the invitation of Wassily Kandinsky, Delaunay and his wife the artist Sonia Delaunay, joined The Blue Rider (Der Blaue Reiter), a Munich-based group of abstract artists, in 1911, and his art took a turn to the abstract.[51]
Other major pioneers of early abstraction include Russian painter Kasimir Malevich, who after the Russian Revolution in 1917, and after pressure from the Stalinist regime in 1924 returned to painting imagery and Peasants and Workers in the field, and Swiss painter Paul Klee whose masterful color experiments made him an important pioneer of abstract painting at the Bauhaus. Still other important pioneers of abstract painting include the Swedish artist Hilma af Klint, Czech painter František Kupka as well as American artists Stanton Macdonald-Wright and Morgan Russell who, in 1912, founded Synchromism, an art movement that closely resembles Orphism.
Expressionism and Symbolism are broad rubrics that involve several important and related movements in 20th-century painting that dominated much of the avant-garde art being made in Western, Eastern and Northern Europe. Expressionist works were painted largely between World War I and World War II, mostly in France, Germany, Norway, Russia, Belgium, and Austria. Expressionist artists are related to both Surrealism and Symbolism and are each uniquely and somewhat eccentrically personal. Fauvism, Die Brücke, and Der Blaue Reiter are three of the best known groups of Expressionist and Symbolist painters.
Artists as interesting and diverse as Marc Chagall, whose painting I and the Village, (above) tells an autobiographical story that examines the relationship between the artist and his origins, with a lexicon of artistic Symbolism. Gustav Klimt, Egon Schiele, Edvard Munch, Emil Nolde, Chaïm Soutine, James Ensor, Oskar Kokoschka, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, Max Beckmann, Franz Marc, Käthe Schmidt Kollwitz, Georges Rouault, Amedeo Modigliani and some of the Americans abroad like Marsden Hartley, and Stuart Davis, were considered influential expressionist painters. Although Alberto Giacometti is primarily thought of as an intense Surrealist sculptor, he made intense expressionist paintings as well.
Pioneers of abstraction[edit]
- Piet Mondrian, 1912, early De Stijl
- Kasimir Malevich 1916, Suprematism
Piet Mondrian's art was also related to his spiritual and philosophical studies. In 1908 he became interested in the theosophical movement launched by Helena Petrovna Blavatsky in the late 19th century. Blavatsky believed that it was possible to attain a knowledge of nature more profound than that provided by empirical means, and much of Mondrian's work for the rest of his life was inspired by his search for that spiritual knowledge.
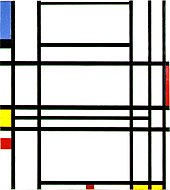
De Stijl also known as neoplasticism, was a Dutch artistic movement founded in 1917. The term De Stijl is used to refer to a body of work from 1917 to 1931 founded in the Netherlands.[52][53]
De Stijl is also the name of a journal that was published by the Dutch painter, designer, writer, and critic Theo van Doesburg propagating the group's theories. Next to van Doesburg, the group's principal members were the painters Piet Mondrian, Vilmos Huszár, and Bart van der Leck, and the architects Gerrit Rietveld, Robert van 't Hoff, and J. J. P. Oud. The artistic philosophy that formed a basis for the group's work is known as neoplasticism – the new plastic art (or Nieuwe Beelding in Dutch).

Proponents of De Stijl sought to express a new utopian ideal of spiritual harmony and order. They advocated pure abstraction and universality by a reduction to the essentials of form and colour; they simplified visual compositions to the vertical and horizontal directions, and used only primary colors along with black and white. Indeed, according to the Tate Gallery's online article on neoplasticism, Mondrian himself sets forth these delimitations in his essay "Neo-Plasticism in Pictorial Art". He writes, "... this new plastic idea will ignore the particulars of appearance, that is to say, natural form and colour. On the contrary, it should find its expression in the abstraction of form and colour, that is to say, in the straight line and the clearly defined primary colour." The Tate article further summarizes that this art allows "only primary colours and non-colours, only squares and rectangles, only straight and horizontal or vertical line."[54] The Guggenheim Museum's online article on De Stijl summarizes these traits in similar terms: "It [De Stijl] was posited on the fundamental principle of the geometry of the straight line, the square, and the rectangle, combined with a strong asymmetricality; the predominant use of pure primary colors with black and white; and the relationship between positive and negative elements in an arrangement of non-objective forms and lines."[55]
De Stijl movement was influenced by Cubist painting as well as by the mysticism and the ideas about "ideal" geometric forms (such as the "perfect straight line") in the neoplatonic philosophy of mathematician M. H. J. Schoenmaekers. The works of De Stijl would influence the Bauhaus style and the international style of architecture as well as clothing and interior design. However, it did not follow the general guidelines of an "ism" (Cubism, Futurism, Surrealism), nor did it adhere to the principles of art schools like Bauhaus; it was a collective project, a joint enterprise.
Dada and Surrealism[edit]
- Francis Picabia 1916, Dada
- Max Ernst, 1921, Surrealism
- André Masson, 1922, early Surrealism



 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch










![Gwion Gwion rock paintings found in the north-west Kimberley region of Western Australia c. 15,000 BC[17]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/43/Bradshaw_rock_paintings.jpg/140px-Bradshaw_rock_paintings.jpg)


















































































































































































































































































