International recognition of the State of Palestine
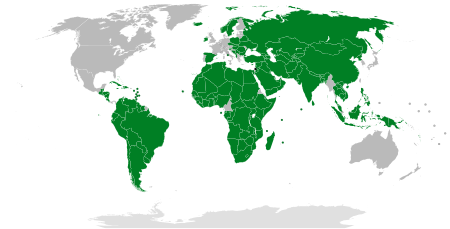
The State of Palestine has been accepted as an observer state of the United Nations General Assembly in November 2012.[1][2] As of April 2024, 140 of the 193 United Nations (UN) member states have recognized the State of Palestine.
The State of Palestine had been officially declared by the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) on 15 November 1988, claiming sovereignty over the internationally recognized Palestinian territories: the West Bank, which includes East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip. By the end of 1988, the Palestinian state was recognized by 78 countries.[3][4]
In an attempt to solve the decades-long Israeli–Palestinian conflict, the Oslo Accords were signed between Israel and the PLO in 1993 and 1995, creating the Palestinian Authority (PA) as a self-governing interim administration in the Gaza Strip and around 40% of the West Bank.[5] After the assassination of Yitzhak Rabin and Benjamin Netanyahu's ascension to power, negotiations between Israel and the PA stalled, which led the Palestinians to pursue international recognition of the State of Palestine without Israeli acquiescence.
In 2011, the State of Palestine was admitted into UNESCO; in 2012, after it was accepted as an observer state of the United Nations General Assembly with the votes of 138 member states of the United Nations, the PA began to officially use the name "State of Palestine" for all purposes.
Among the G20, nine countries (Argentina, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Turkey) have recognized Palestine as a state (Indonesia and Saudi Arabia recognize Palestine but not Israel), while ten countries (Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and the United States) have not.[note 1] Although these countries generally support some form of a two-state solution to the conflict, they take the position that their recognition of a Palestinian state is conditioned to direct negotiations between Israel and the PA.
History
Background
On 22 November 1974, United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3236 recognised the right of the Palestinian people to self-determination, national independence and sovereignty in Palestine. It also recognised the PLO as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people, and accorded it observer status in the United Nations. The designation "Palestine" for the PLO was adopted by the United Nations in 1988 in acknowledgment of the Palestinian declaration of independence, but the proclaimed state still has no formal status within the system.
Shortly after the 1988 declaration, the State of Palestine was recognised by many developing states in Africa and Asia, and from communist and non-aligned states.[6][7] At the time, however, the United States was using its Foreign Assistance Act and other measures to discourage other countries and international organisations from extending recognition.[8] Although these measures were successful in many cases,[9] the Arab League and the Organisation of the Islamic Conference (OIC) immediately published statements of recognition of, support for, and solidarity with Palestine, which was accepted as a member state in both forums.[10][11][12]
In February 1989 at the United Nations Security Council, the PLO representative acknowledged that 94 states had recognised the new Palestinian state.[13][14] It subsequently attempted to gain membership as a state in several agencies connected to the United Nations, but its efforts were thwarted by U.S. threats to withhold funding from any organisation that admitted Palestine.[15][failed verification] For example, in April of the same year, the PLO applied for membership as a state in the World Health Organization, an application that failed to produce a result after the U.S. informed the organisation that it would withdraw funding if Palestine were admitted.[16] In May, a group of OIC members submitted to UNESCO an application for membership on behalf of Palestine, and listed a total of 91 states that had recognised the State of Palestine.[17]
In June 1989, the PLO submitted to the government of Switzerland letters of accession to the Geneva Conventions of 1949. However, Switzerland, as the depositary state, determined that because the question of Palestinian statehood had not been settled within the international community, it was therefore incapable of determining whether the letter constituted a valid instrument of accession.[16]
Due to the [uncertainty] within the international community as to the existence or the non-existence of a State of Palestine and as long as the issue has not been settled in an appropriate framework, the Swiss Government, in its capacity as depositary of the Geneva Conventions and their additional Protocols, is not in a position to decide whether this communication can be considered as an instrument of accession in the sense of the relevant provisions of the Conventions and their additional Protocols.[18]
Consequently, in November 1989, the Arab League proposed a General Assembly resolution to formally recognise the PLO as the government of an independent Palestinian state. The draft, however, was abandoned when the U.S. again threatened to cut off its financing for the United Nations should the vote go ahead. The Arab states agreed not to press the resolution, but demanded that the U.S. promise not to threaten the United Nations with financial sanctions again.[19]
Many of the early statements of recognition of the State of Palestine were termed ambiguously.[20] In addition, hesitation from others did not necessarily mean that these nations did not regard Palestine as a state.[16] This has seemingly resulted in confusion regarding the number of states that have officially recognized the state declared in 1988. Numbers reported in the past are often conflicting,[21] with figures as high as 130 being seen frequently.[9][22] In July 2011, in an interview with Haaretz, Palestinian ambassador to the United Nations, Riyad Mansour claimed that 122 states had so far extended formal recognition.[23] At the end of the month, the PLO published a paper on why the world's governments should recognize the State of Palestine and listed the 122 countries that had already done so.[24] By the end of September the same year, Mansour claimed the figure had reached 139.[25]
Israeli position
Between the end of the Six-Day War and the Oslo Accords, no Israeli government proposed a Palestinian state. During Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu's government of 1996–1999, he accused the two previous governments of Rabin and Peres of bringing closer to realisation what he claimed to be the "danger" of a Palestinian state, and stated that his main policy goal was to ensure that the Palestinian Authority did not evolve beyond an autonomy.[26]
In June 2003, Ariel Sharon was the first Israeli Prime Minister to proclaim that a Palestinian state was a possibility. Sharon addressed "the possibility of the establishment of a Palestinian state with temporary borders, if conditions permit" and claimed that interim Palestinian state would be "completely demilitarised, and this nation will be the home of the Palestinian diaspora and Palestinian refugees will not be allowed into Israeli territory."[27]
The government headed by Ehud Olmert repeated the same objective. Following the inauguration of the Netanyahu government in 2009, the government again claimed that a Palestinian state posed a danger for Israel.[28] The government position changed, however, following American pressure from the Obama administration, and on 14 June 2009, Netanyahu for the first time made a speech in which he supported the notion of a demilitarized and territorially reduced Palestinian state.[29] This position met some criticism for its lack of commitment on the territories to be ceded to the Palestinian state in the future. Netanyahu in February 2023 said "I'm certainly willing to have them have all the powers that they need to govern themselves, but none of the powers that can threaten us, and this means that Israel should have the overriding security responsibility."[30]
Israel has refused to accept the 1967 borders, which Israeli military experts have argued are strategically indefensible.[31] It also opposes the Palestinian plan of approaching the UN General Assembly on the matter of statehood, as it claims it does not honor the Oslo Accords agreement in which both sides agreed not to pursue unilateral moves.[32]
Timeline of Palestine in the United Nations
- On 14 October 1974, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) was recognized by the UN General Assembly as the representative of the Palestinian people and granted the right to participate in the deliberations of the General Assembly on the question of Palestine in plenary meetings.[33][34]
- On 22 November 1974, the PLO was granted non-state observer status, allowing the PLO to participate in all Assembly sessions, as well as in other UN platforms.[35]
- On 15 December 1988, UN General Assembly Resolution 43/177 acknowledged the Palestinian Declaration of Independence of November 1988 and replaced the designation "Palestine Liberation Organization" with "Palestine" in the United Nations system.[36]
- On 23 September 2011, Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas submitted an application for membership of Palestine in the United Nations.
- On 29 November 2012, the General Assembly granted Palestine non-member observer state status in United Nations General Assembly resolution 67/19.
- On 17 December 2012, UN Chief of Protocol Yeocheol Yoon decided that the constitutional name 'State of Palestine' shall be used by the Secretariat in all official United Nations documents.[37]
Application for UN membership
After a two-year impasse in negotiations with Israel, the Palestinian Authority began a diplomatic campaign to gain recognition for the State of Palestine on the borders prior to the Six-Day War, with East Jerusalem as its capital.[38] The efforts, which began in late 2009, gained widespread attention in September 2011, when President Mahmoud Abbas submitted an application to the United Nations to accept Palestine as a member state. This would have constituted collective recognition of the State of Palestine, which would have allowed its government to pursue legal claims against other states in international courts.[39][40]
In order for a state to gain membership in the General Assembly, its application must have the support of two-thirds of member states with a prior recommendation for admission from the Security Council. This requires the absence of a veto from any of the Security Council's five permanent members.[39] At the prospect of a veto from the United States, Palestinian leaders signalled that they might opt instead for a more limited upgrade to "non-member state" status, which requires only a simple majority in the General Assembly but provides the Palestinians with the recognition they desired.
The campaign, dubbed "Palestine 194",[41] was supported by the Arab League in May,[42] and was officially confirmed by the PLO on 26 June.[43] The decision was labelled by the Israeli government as a unilateral step, while the Palestinian government countered that it was essential to overcoming the current impasse. Several other countries—such as Germany and Canada—also denounced the decision and called for a prompt return to negotiations. However, many others—such as Norway and Russia—endorsed the plan, as did Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon, who stated: "UN members are entitled whether to vote for or against the Palestinian statehood recognition at the UN."[44]

Diplomatic efforts to gain support for the bid gained momentum following a succession of endorsements from South America in early 2011.[45][46][failed verification] High-level delegations led by Yasser Abed Rabbo, Riyad al-Maliki, Saeb Erekat, Nabil Shaath and Riyad Mansour paid visits to many states. Palestinian ambassadors, assisted by those of other Arab states, were charged with enlisting the support of the governments to which they were accredited.[46] During the lead-up to the vote, Russia, China, and Spain publicly pledged their support for the Palestinian bid,[47][48] as did inter-governmental organisations such as the African Union,[49] and the Non-Aligned Movement.[50]
Israel took steps to counter the initiative,[51] and Germany, Italy, Canada and the U.S. announced publicly that they would vote against the resolution.[46] Israeli and U.S. diplomats began a campaign pressuring many countries to oppose or abstain from the vote.[46] However, because of the "automatic majority" enjoyed by the Palestinians in the General Assembly,[52] the Netanyahu administration stated that it did not expect to prevent a resolution from passing should it go ahead.[51][53] In August, Haaretz quoted the Israeli ambassador to the United Nations, Ron Prosor, as stating that Israel would be unable to block a resolution at the General Assembly by September. "The maximum that we can hope to gain is for a group of states who will abstain or be absent during the vote", wrote Prosor. "Only a few countries will vote against the Palestinian initiative."[54]
Instead, the Israeli government focused on obtaining a "moral majority" of major democratic powers, in an attempt to diminish the weight of the vote.[55][56] Considerable weight was placed on the position of the European Union,[57] which had not yet been announced. EU foreign policy chief Catherine Ashton stated that it was likely to depend on the wording of the resolution.[58] At the end of August, Israel's defence minister Ehud Barak said that "it is very important that all the players come up with a text that will emphasize the quick return to negotiations, without an effort to impose pre-conditions on the sides."[59]
Efforts from both Israel and the U.S. also focused on pressuring the Palestinian leadership to abandon its plans and return to negotiations.[57] In the U.S., Congress passed a bill denouncing the initiative and calling on the Obama administration to veto any resolution that would recognize a Palestinian state declared outside of an agreement negotiated by the two parties.[60] A similar bill was passed in the Senate, which also threatened a withdrawal of aid to the West Bank.[61][62] In late August, another congressional bill was introduced which proposes to block U.S. government funding for United Nations entities that support Palestinian membership in the UN.[63] Several top U.S. officials, including ambassador to the United Nations Susan Rice and consul-general in Jerusalem Daniel Rubinstein, made similar threats.[64][65] In the same month, it was reported that the Israeli Ministry of Finance was withholding its monthly payments to the PNA.[66] Foreign Minister Avigdor Lieberman warned that if Palestine took unilateral action, Israel would consider the Oslo Accords null and void,[57] and would break off relations with the PA.[59]

On 11 July 2011, the Quartet met to discuss a return to negotiations, but the meeting produced no result.[68] President Mahmoud Abbas claimed that he would suspend the bid and return to negotiations if the Israelis agreed to the 1967 borders and ceased the expansion of settlements in the West Bank.
The PNA's campaign saw an increasing level of support in grass-roots activism. Avaaz began an online petition urging all United Nations members to endorse the bid to admit Palestine; it reportedly attained 500,000 e-signatures in its first four days.[69] OneVoice Palestine launched a domestic campaign in partnership with local news agencies, with the aim of getting the involvement and support of Palestinian citizens.[70] Overseas, campaigns were launched in several nations, calling on their governments to vote "yes" in the resolution.[71][72] On 7 September, a group of Palestinian activists under the banner "Palestine: State No. 194" staged a demonstration outside the United Nations' office in Ramallah.[73] During the demonstration, they submitted to the office a letter addressed to Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon, urging him to "exert all possible efforts toward the achievement of the Palestinian people's just demands". The following day, Ban told reporters: "I support ... the statehood of Palestinians; an independent, sovereign state of Palestine. It has been long overdue", but he also stated that "recognition of a state is something to be determined by the member states."[74]
Other United Nations organs had previously expressed readiness to see a Palestinian state. In April 2011, the UN's co-ordinator for the Middle East peace process issued a report on the Palestinian Authority's state-building progress, describing "aspects of its administration as sufficient for an independent state".[75] It echoed a similar assessment published the week prior by the International Monetary Fund.[76] The World Bank released a report in September 2010 that found the Palestinian Authority "well-positioned to establish a state" at any point in the near future. However, the report highlighted that, unless private-sector growth in the Palestinian economy was stimulated, a Palestinian state would remain donor dependent.[77]
The effort to secure full UN membership was renewed in 2024 during the Israel–Hamas war,[78] with the United Nations Security Council holding a vote on the topic in April.[79] The vote was 12 in favor, two abstentions, and one vote against, with the United States vetoing the measure.[80]
United Nations Security Council Resolution Vote on Recommendation to the United Nations General Assembly that Membership Admission in the United Nations for Palestine (State of Palestine)[80][81][82]  Date: 18 April 2024 | ||
|---|---|---|
| In favour (12) | Abstentions (2) | Against (1) |
- Note
Bold: Denotes the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.
P: Denotes the president of the United Nations Security Council at that time.
D: Denotes the resolution draft submitter.[82]
V: United States as the permanent member uses their veto power to prevent the adoption of said proposal.
Non-member observer state status

In favour Against Abstentions Absent Non-members
During September 2012, Palestine decided to pursue an upgrade in status from "observer entity" to "non-member observer state". On 27 November of the same year, it was announced that the appeal had been made officially and would be put to a vote in the General Assembly on 29 November, where the status upgrade was expected to be supported by a majority of states. In addition to granting Palestine "non-member observer state status", the draft resolution "expresses the hope that the Security Council will consider favorably the application submitted on 23 September 2011 by the State of Palestine for admission to full membership in the United Nations, endorses the two state solution based on the pre-1967 borders, and stresses the need for an immediate resumption of negotiations between the two parties."
On 29 November 2012, in a 138–9 vote (with 41 abstaining) General Assembly resolution 67/19 passed, upgrading Palestine to "non-member observer state" status in the United Nations.[83][84] The new status equated Palestine's with that of the Holy See. The change in status was described by The Independent as "de facto recognition of the sovereign state of Palestine".[85] Voting "no" were Israel, Canada, the Czech Republic, the Marshall Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, Palau, Panama and the United States.
The vote was an important benchmark for the partially recognized State of Palestine and its citizens, while it was a diplomatic setback for Israel and the United States. Status as an observer state in the UN allows the State of Palestine to join treaties and specialized UN agencies,[86] the Law of the Seas treaty, and the International Criminal Court. It permits Palestine to pursue legal rights over its territorial waters and air space as a sovereign state recognized by the UN, and allows the Palestinian people the right to sue for sovereignty over their territory in the International Court of Justice and to bring "crimes against humanity" and war-crimes charges, including that of unlawfully occupying the territory of State of Palestine, against Israel in the International Criminal Court.[87][88]
The UN has, after the resolution was passed, permitted Palestine to title its representative office to the UN as "The Permanent Observer Mission of the State of Palestine to the United Nations",[89] seen by many as a reflection of the UN's de facto position of recognizing the State of Palestine's sovereignty under international law,[83] and Palestine started to re-title its name accordingly on postal stamps, official documents and passports.[84][90] The Palestinian authorities also instructed its diplomats to officially represent the "State of Palestine", as opposed to the "Palestine National Authority".[84] Additionally, on 17 December 2012, UN Chief of Protocol Yeocheol Yoon decided that "the designation of "State of Palestine" shall be used by the Secretariat in all official United Nations documents",[37] recognizing the "State of Palestine" as the official name of the Palestinian nation.
On 26 September 2013 at the United Nations, Mahmoud Abbas was given the right to sit in the General Assembly's beige chair which is reserved for heads of state waiting to take the podium and address the General Assembly.[91]
Other positions
Diplomatic recognitions
UN member states
Of the 193 member states of the United Nations, 140 of the 193 United Nations (UN) member states have recognized the State of Palestine. [92] The list below is based on the list maintained by the Palestine Liberation Organization during the campaign for United Nations recognition in 2011,[24] and maintained by the Permanent Observer Mission to the UN.[93]
Some states, marked with an asterisk (*) below, expressly recognized the State of Palestine on the borders of 4 June 1967 (i.e., the West Bank, Gaza and East Jerusalem), which constituted Arab territory prior to the Six-Day War.
| States that maintain diplomatic relations with the State of Palestine |
| # | Name[94] | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations [note 2] | Relevant membership, further details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes[95] | Arab League, African Union (AU), OIC; Algeria–Palestine relations | |
| 2 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes[96] | Arab League, GCC, OIC; Bahrain–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the State of Bahrain. | |
| 3 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, OIC; Iraq–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the Ba'athist Iraqi Republic. | |
| 4 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes[97] | Arab League, GCC, OIC[98] | |
| 5 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC; Libya–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya. | |
| 6 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | ASEAN, OIC; Malaysia–Palestine relations | |
| 7 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 8 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC;[99][100] Morocco–Palestine relations | |
| 9 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League,AU, OIC Further details Recognition extended by the Somali Democratic Republic. | |
| 10 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes[101] | Arab League, AU, OIC; Palestine–Tunisia relations | |
| 11 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes[102] | NATO, OIC, OTS; Palestine–Turkey relations | |
| 12 | 15 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, OIC; Palestine–Yemen relations Further details Recognition extended by both Democratic Yemen and the Yemen Arab Republic, prior to Yemeni unification. In a joint letter to the UN Secretary-General sent just prior to unification, the Ministers of Foreign affairs of North and South Yemen stated that "All treaties and agreements concluded between either the Yemen Arab Republic or the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen and other States and international organizations in accordance with international law which are in force on 22 May 1990 will remain in effect, and international relations existing on 22 May 1990 between the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen and the Yemen Arab Republic and other States will continue."[103] | |
| 13 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes[104] | OIC, SAARC Further details Recognition extended by the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. | |
| 14 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | OIC, SAARC; Bangladesh–Palestine relations | |
| 15 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | Cuba–Palestine relations | |
| 16 | 16 November 1988[105] | Yes[105] | ASEAN, OIC; Indonesia–Palestine relations | |
| 17 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, OIC; Jordan–Palestine relations | |
| 18 | 16 November 1988[17] | No | AU Further details Recognition extended by the Democratic Republic of Madagascar. | |
| 19 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | EU; Malta–Palestine relations | |
| 20 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | — | |
| 21 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | OIC, SAARC; Pakistan–Palestine relations | |
| 22 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 23 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC; Palestine–Saudi Arabia relations | |
| 24 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC; Palestine–United Arab Emirates relations | |
| 25 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes[106] | —, Palestine–Serbia relations Further details Recognition extended by the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). Although the UN did not recognise the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (later renamed Serbia and Montenegro, itself to be succeeded by Serbia in 2006) as its successor, it claims to be such and pledges to adhere to all ratifications, signatures and recognitions conducted by SFRY. | |
| 26 | 16 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU | |
| 27 | 17 November 1988[17] | Yes[107] | NATO, OIC; Albania–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the People's Socialist Republic of Albania. | |
| 28 | 17 November 1988[17] | Yes | ASEAN, OIC[108] | |
| 29 | 17 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 30 | 17 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU Further details Recognition extended by Mauritius as a Commonwealth realm. | |
| 31 | 17 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC[109] | |
| 32 | 18 November 1988*[17] | Yes | EU; Cyprus–Palestine relations Further details In January 2011, the Cypriot government reaffirmed its recognition of the Palestinian state in 1988. The government also added that any modifications to the borders from 1967 onwards would not be acknoweldged until both countries reached a consensus.[110] | |
| 33 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes | EU, NATO Further details Recognition extended by the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic.[17] Following its dissolution, both the Czech Republic and Slovakia retained ties. | |
| 34 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes | EU, NATO; Palestine–Slovakia relations Further details Recognition extended by the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic.[17] Following its dissolution, both the Czech Republic and Slovakia retained ties. | |
| 35 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC; Egypt–Palestine relations | |
| 36 | 18 November 1988[93] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 37 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes[111] | SAARC; India–Palestine relations | |
| 38 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 39 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU | |
| 40 | 18 November 1988[17] | Yes | SAARC; Palestine–Sri Lanka relations | |
| 41 | 19 November 1988[17] | Yes | CSTO; Belarus–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended as the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. Belarus is the legal successor of the Byelorussian SSR and in the Constitution it states, "Laws, decrees and other acts which were applied in the territory of the Republic of Belarus prior to the entry into force of the present Constitution shall apply in the particular parts thereof that are not contrary to the Constitution of the Republic of Belarus."[112] | |
| 42 | 19 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 43 | 19 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU Further details Namibia was established by the South West Africa People's Organization (SWAPO), which recognised the State of Palestine during its time as a UN observer entity.[113] | |
| 44 | 19 November 1988[17] | Yes[114] | CSTO, UNSC (permanent); Palestine–Russia relations Further details Recognition extended as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. President Dmitry Medvedev reconfirmed the position in January 2011.[115] | |
| 45 | 19 November 1988[17] | Yes | —; Palestine–Ukraine relations Further details Recognition extended as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, of which Ukraine is the legal successor. The modern republic continues all "rights and duties pursuant to international agreements of Union SSR which do not contradict the Constitution of Ukraine and interests of the Republic".[116] | |
| 46 | 19 November 1988[17] | Yes[117] | ASEAN; Palestine–Vietnam relations | |
| 47 | 20 November 1988[17] | Yes | UNSC (permanent); China–Palestine relations | |
| 48 | 21 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC; Burkina Faso–Palestine relations | |
| 49 | 21 November 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC Further details Recognition extended by the Federal Islamic Republic of the Comoros. | |
| 50 | 21 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 51 | 21 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 52 | 21 November 1988[17] | Yes | ASEAN Further details Recognition extended by the People's Republic of Kampuchea, the predecessor to modern Cambodia. Its civil-war rival, internationally recognized Democratic Kampuchea, announced its recognition three days prior. | |
| 53 | 22 November 1988[17] | Yes[118] | — Further details Recognition extended by the Mongolian People's Republic. | |
| 54 | 22 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 55 | 23 November 1988[17] | Yes | EU, NATO; Hungary–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the Hungarian People's Republic. | |
| 56 | 24 November 1988[17] | Yes[119] | AU | |
| 57 | 24 November 1988[17] | Yes | —, North Korea–Palestine relations | |
| 58 | 24 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 59 | 24 November 1988[17] | Yes | EU, NATO; Palestine–Romania relations Further details Recognition extended by the Socialist Republic of Romania. | |
| 60 | 24 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU; Palestine–Tanzania relations | |
| 61 | 25 November 1988[17] | Yes | EU, NATO; Bulgaria–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the People's Republic of Bulgaria. | |
| 62 | 28 November 1988[17] | Yes | OIC, SAARC; Maldives–Palestine relations | |
| 63 | 29 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU | |
| 64 | 29 November 1988[17] | Yes[120] | AU, OIC | |
| 65 | 29 November 1988[17] | Yes | AU | |
| 66 | 1 December 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 67 | 2 December 1988[17] | Yes[121] | ASEAN | |
| 68 | 3 December 1988[17] | Yes[122] | AU, OIC | |
| 69 | 3 December 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 70 | 5 December 1988[17] | Yes | AU Further details Recognition extended by the People's Republic of the Congo. | |
| 71 | 6 December 1988[17] | Yes[123] | AU Further details Recognition extended by the People's Republic of Angola. | |
| 72 | 8 December 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC Further details Recognition extended by the People's Republic of Mozambique. | |
| 73 | 10 December 1988[17] | No | AU | |
| 74 | 10 December 1988[17] | No | AU Further details Recognition extended by the Republic of Zaire, which was ruled by Mobutu Sese Seko until his removal in 1997 when the state was succeeded by the Democratic Republic of the Congo during the First Congo War. | |
| 75 | 12 December 1988[17] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 76 | 13 December 1988[17] | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC; Oman–Palestine relations | |
| 77 | 14 December 1988[17] | Yes | EU, NATO; Palestine–Poland relations Further details Recognition extended by the Polish People's Republic. | |
| 78 | 19 December 1988[17] | Yes[124] | AU | |
| 79 | 19 December 1988[17] | No | SAARC Further details Recognition extended by the Kingdom of Nepal. | |
| 80 | 22 December 1988[17] | No | AU | |
| 81 | 23 December 1988[17] | No | AU | |
| 82 | 25 December 1988[17] | No | SAARC | |
| 83 | 2 January 1989[17] | No | AU | |
| 84 | 4 February 1989[17] | Yes | AU Further details Recognition extended by the People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. | |
| 85 | 4 February 1989[17] | Yes | OIC; Iran–Palestine relations | |
| 86 | May 1989 or before[17][13] [when?] | Yes | AU, OIC Further details Recognition extended by the People's Republic of Benin. | |
| 87 | May 1989 or before[17][13][when?] | No | AU | |
| 88 | May 1989 or before[17][13][125][when?] | Yes | AU | |
| 89 | 21 August 1989[126] | Yes | MSG, PIF | |
| 90 | September 1989[130] | Yes[130] | ASEAN; Palestine–Philippines relations | |
| 91 | 1 July 1991[132] | Yes[133] | AU Further details Recognition extended as Swaziland. | |
| 92 | 6 April 1992[134] | Yes[134] | CSTO, OIC, OTS; Kazakhstan–Palestine relations | |
| 93 | 15 April 1992[135] | Yes[135] | OIC, OTS; Azerbaijan–Palestine relations | |
| 94 | 17 April 1992[136] | Yes[137][138] | OIC[139] | |
| 95 | 25 April 1992[140] | Yes[141] | —; Georgia–Palestine relations | |
| 96 | 27 May 1992[142] | Yes[142] | Bosnia and Herzegovina–Palestine relations Further details Recognition extended by the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. | |
| 97 | 6 September 1992[143] | Yes[143][144] | CSTO, OIC | |
| 98 | 25 September 1994[145] | Yes[145] | OIC, OTS | |
| 99 | 4 October 1994[146] | Yes[146][147] | MSG, PIF | |
| 100 | 15 February 1995 | Yes[148] | AU; Palestine–South Africa relations | |
| 101 | 12 September 1995 | Yes[149][150] | CSTO, OIC, OTS | |
| 102 | 23 October 1998*[151][152] | Yes[153] | AU | |
| 103 | 1 March 2004[154] | Yes[147][154] | — | |
| 104 | 25 March 2005*[155] | Yes[155] | OAS Further details On 28 January 2011, Paraguay's Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a written reaffirmation of its government's recognition of the State of Palestine. The statement noted that the establishment of diplomatic relations between the two governments in 2005 had implied mutual recognition.[155] | |
| 105 | 24 July 2006[156] | Yes[156] | NATO; Montenegro–Palestine relations | |
| 106 | 5 February 2008[157] | Yes[158] | OAS | |
| 107 | 30 November 2008 | Yes[159] | Arab League, OIC; Lebanon–Palestine relations Further details Date given is that of first official recognition. In Palestine's application to UNESCO in May 1989, Lebanon was listed as having recognised the State of Palestine, but without a date.[17] The list was submitted without objection from Lebanon, but later sources have shown that official recognition was not accorded until 2008.[160] At that time, the Lebanese cabinet approved the establishment of full diplomatic relations with the State of Palestine, but did not set a date for when this was to occur. On 11 August 2011, the cabinet agreed to implement its earlier decision and Abbas formally inaugurated his government's embassy in Beirut on 16 August.[161] | |
| 108 | 1 December 2008[162] | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 109 | 27 April 2009[163] | Yes | —, Palestine–Venezuela relations | |
| 110 | 14 July 2009[164] | Yes[165] | OAS | |
| 111 | 1 December 2010*[166][167] | Yes[168] | OAS; Brazil–Palestine relations | |
| 112 | 6 December 2010*[169] | Yes[170][171][172] | OAS; Argentina–Palestine relations[45] | |
| 113 | 17 December 2010*[173][174] | Yes[175] | OAS | |
| 114 | 24 December 2010*[176] | Yes[177] | OAS | |
| 115 | 7 January 2011[178] | Yes[179] | OAS; Chile–Palestine relations | |
| 116 | 13 January 2011*[180] | Yes | CARICOM, OAS, OIC[177] | |
| 117 | 24 January 2011[181] | Yes[177] | OAS; Palestine–Peru relations | |
| 118 | 1 February 2011*[182] | No | CARICOM, OAS, OIC | |
| 119 | 15 March 2011[183] | Yes[184] | OAS; Palestine–Uruguay relations | |
| 120 | 6 June 2011*[151] | Yes[186] | AU | |
| 121 | 9 July 2011[187] | Yes[188] | AU | |
| 122 | 18 July 2011*[189] | Yes[190] | Arab League, OIC; | |
| 123 | 19 July 2011[162] | No | AU[39] | |
| 124 | 25 August 2011[191] | Yes[192] | OAS; El Salvador–Palestine relations | |
| 125 | 26 August 2011*[193] | Yes[194] | OAS;[195] Honduras–Palestine relations | |
| 126 | 29 August 2011*[196][197] | Yes[198] | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 127 | 9 September 2011*[199] | Yes | CARICOM, OAS[200] | |
| 128 | 19 September 2011[201][202][203] | Yes[204] | CARICOM, OAS[207] | |
| 129 | 22 September 2011*[208] | No | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 130 | 15 December 2011*[209] | Yes | EFTA, NATO; Iceland–Palestine relations | |
| 131 | 18 January 2012*[210] | Yes[211] | ASEAN; Palestine–Thailand relations | |
| 132 | 9 April 2013[212] | No | OAS | |
| 133 | 29 September 2013[213][214] | Yes[213][214] | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 134 | 29 September 2013[213][214] | Yes[213][214] | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 135 | 30 October 2014[215][216] | Yes | EU, NATO; Palestine–Sweden relations | |
| 136 | 14 September 2015[217] | Yes[217] | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 137 | 3 August 2018[218] | Yes | OAS | |
| 138 | 30 July 2019[219] | Yes[220] | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 139 | 19 April 2024[221] | No | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 140 | 23 April 2024[222] | No | CARICOM, OAS |
Not members of the UN
| # | Name | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations [note 2] | Relevant membership, further details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 141 | 15 November 1988[223] | No | AU | |
| 142 | February 2015[224] | Yes[225] | —; Holy See–Palestine relations |
No diplomatic recognition
UN member states
| # | Name | Official position | Relations [note 2] | Relevant memberships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | In January 2011, Andorra co-sponsored a draft resolution guaranteeing the Palestinian people's right to self-determination.[226] In September, it argued for a proposed resolution to give the State of Palestine observer status in the United Nations.[227] | No | ||
| 2 | On 20 June 2011, Fatah representative Nabil Shaath met with Foreign Minister Eduard Nalbandyan to enlist the support of Armenia in the upcoming resolution.[228] Afterwards, Shaath announced that he had been informed by a number of countries that they would recognize Palestine in the following weeks, and that he expected Armenia to be the first of these.[229] However, the Armenian government did not release any statement regarding the meeting. The situation in Palestine is seen as analogous by the Armenian government to the conflict in Nagorno-Karabakh, and that any recognition of a Palestinian state by Armenia would set a precedent for the right to self-determination in that region.[230] On similar situations, President Serzh Sargsyan previously stated, "Having the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, Armenia can not recognize another entity in the same situation as long as it has not recognized the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic".[231] | No | Armenia–Palestine relations | |
| 3 | Australian policy calls for a two-state solution, but it has not supported calls toward Palestinian statehood in the past, insisting instead on a negotiated settlement. In regards to a resolution to admit Palestine as a UN non-member observer state, a division in positions emerged: Former Foreign Minister Kevin Rudd recommended abstaining from the vote, whilst former Prime Minister Julia Gillard declared strong support for Israel.[232] In response, Gillard noted: "There isn't a resolution available for people to read or respond to. If such a resolution does hit the deck, then in deciding how Australia will vote, we will bring our very long-standing principles about questions in the Middle East. That is, we are long-standing supporters of a two-state solution."[233] In 2014, Australia voted against a United Nations Security Council draft resolution proposing the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Gaza and the West Bank by 2017.[234] In April 2021, the Australian Labor Party (Rudd and Gillard's party) passed an amendment to its policy platform recognising Palestine as a state.[235] | Yes | ||
| 4 | Austria conferred full diplomatic status on the PLO representation in Vienna on 13 December 1978, under then-chancellor Bruno Kreisky.[236] In June 2011, Foreign Minister Michael Spindelegger said that Austria "had not yet made up its mind whether to support a UN recognition of a Palestinian state", adding that he preferred to wait for a joint EU approach to the issue. "We will decide at the last moment because it might still give [the two parties] the opportunity to bring the Middle East peace process back on track."[237] Spindelegger also suggested that the EU draft its own version of the resolution.[238] Further details In Annex II of the State of Palestine's UNESCO application, Austria was initially listed as having extended recognition on 14 December 1988. However, the submitting states (Algeria, Indonesia, Mauritania, Nigeria, Senegal and Yemen) later requested that Austria be removed from the list.[17] | Yes[239] | EU | |
| 5 | On the issue of Palestinian statehood, Belgium supports the declarations of the European Union.[240] Prime Minister Yves Leterme called for the creation of a European consensus before September,[241] and the Senate urged the government on 15 July 2011 to recognize a Palestinian state with the pre-1967 borders.[242] The parties of the new centre right government agreed to recognize Palestine. The Chamber of Representatives has already adopted a resolution in favour on 5 February 2015. The left-wing opposition called for an unconditional recognition of Palestine.[243][244] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 6 | Cameroon officially supports a two-state solution.[245] Although a member of the OIC, President Paul Biya has developed strong ties with Israel since the mid-1980s.[246] This perceived friendship has soured the country's traditionally close ties with Arab states, many of whom have withdrawn longstanding economic development assistance and pressed Biya to support Palestinian interests.[247] Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu asked Biya to oppose the United Nations resolution that would admit Palestine as a member state.[248] | Yes[245] | AU, OIC[39] | |
| 7 | Canada supports the creation of a sovereign Palestinian state, but only as part of a "comprehensive, just and lasting peace settlement".[249] The Harper government (2006–2015) was regarded as a staunch supporter of Israel. In July 2011, the spokesman for Foreign Minister John Baird stated, "Our government's long-standing position has not changed. The only solution to this conflict is one negotiated between and agreed to by the two parties. ... One of the states must be a Jewish state and recognized as such, while the Palestinian state is to be a non-militarized one".[250] | Yes | NATO | |
| 8 | Croatia formalized relations with the PLO on 31 March 2011. Former Croatian Prime Minister Jadranka Kosor stated in 2011 that her government supported the co-existence of Israel and Palestine as two independent states,[251] however Croatia abstained during voting on upgrading Palestine to non-member observer state status in the United Nations and on admission of Palestine to UNESCO. Former Croatian Foreign Minister Vesna Pusić stated on 24 October 2014 that "Croatia will most likely recognize Palestine soon".[252] The Croatian government tends to favour Israel over Palestine as a commitment to the United States, to whom Croatia is aligned, and the central quarters of the European Union of which Croatia has been a member since 2013. Croatia believes that if it were to recognize Palestine, this would frustrate its position with the EU and ties to the US, and also because the situation in the Middle East is complicated it feels there is no guarantee that there would be peace and further existence of the Jewish state if Israel eventually decides to withdraw from the occupied territories.[253] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 9 | Danish Foreign Minister Lene Espersen met Abbas on 9 March 2011 to persuade him to return to negotiating with Israel. Espersen also extended Danish support to Palestinian national development.[254] During the campaign for the 2011 elections, the largest opposition party argued that Denmark should recognize the State of Palestine. Foreign Minister Lene Espersen, however, warned that such a unilateral decision could have "more negative than beneficial" consequences, and stressed the need to co-ordinate policy with the EU.[255] In December 2014, a bill that called on Denmark to recognize Palestine as a state was rejected in the Danish parliament.[256] | Yes | EU, NATO; Denmark–Palestine relations | |
| 10 | Eritrea is one of only two African countries that does not recognise Palestine, the other being Cameroon.[39][257] In October 2010, President Isaias Afewerki stated, "Israel needs a government, we must respect this. The Palestinians also need to have a dignified life, but it can not be the West Bank or Gaza. A two-state solution will not work. It's just to fool people. Israelis and Palestinians living in the same nation will never happen for many reasons. One option that may work is a Transjordan. Israel may be left in peace and the Palestinian and Jordanian peoples are brought together and can create their own nation".[258] In his address to the UN General Assembly in 2011, Afewerki stated that "Eritrea reaffirms its long-standing support to the right of the Palestinian people to self-determination and an independent, sovereign state. It also upholds the right of Israel to live in peace and security within internationally recognized boundaries."[259] On 29 November 2012, Eritrea voted in favour of a resolution to make Palestine non-member observer state at the UN. | Yes[260] | AU | |
| 11 | During a meeting with Riyad al-Malki in June 2010, Minister Urmas Paet said the country approved an agreement between the two countries and a Palestine independence.[261] Officials stated that the government would not adopt a position regarding the United Nations bid until the final wording of the resolution was published.[262] | Yes[263] | EU, NATO | |
| 12 | Fijian policy on the Israeli–Palestinian conflict is largely based on United Nations resolutions.[264] | No | ||
| 13 | Finland supports a two-state solution to the conflict.[265] In October 2014, president Sauli Niinistö said that Finland would not follow Swedish decision in recognizing the State of Palestine.[266] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 14 | According to President Nicolas Sarkozy, "France supports the solution of two nation states living side-by-side in peace and security, within safe and recognized borders."[267] In May 2011, Sarkozy said that if peace talks with Israel had not resumed by September, he would recognize the State of Palestine as part of its bid at the United Nations.[268] This echoed statements made in March by Nabil Shaath, who claimed to have received a promise from France that it would recognize in September a Palestinian state on the 1967 borders.[269] According to Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, however, Sarkozy had said that France's support would require the Palestinians to recognize Israel as the state of the Jewish people.[267] This was confirmed in July, when Foreign Minister Alain Juppé stated that any solution to the conflict would require the recognition of "the nation-state of Israel for the Jewish people, and the nation-state of Palestine for the Palestinian people."[270] This broke with the European Union's traditional position, which adamantly opposes any mention of Israel as a Jewish state.[271] Sarkozy later turned around on this policy, reportedly saying that the idea of a Jewish state was "silly".[272] In August, Sarkozy stressed the importance of a united EU position on the September initiative, and proposed a compromise where the State of Palestine would be given observer status instead of full membership. The proposal, which was to prevent a split among members of the EU, included a promise from Paris and other members that they would vote for the resolution.[273] In October 2014, France's foreign minister said France would recognize a Palestinian state even if peace talks with Israel fails.[274] On 2 December 2014 the French National Assembly approved a non-binding motion calling on the government to recognise Palestine.[275] | Yes | EU, NATO, UNSC (permanent) | |
| 15 | In April 2011, Chancellor Angela Merkel labelled the Palestinian bid for recognition a "unilateral step",[276] and stated unequivocally that Germany will not recognize a Palestinian state without its prior acceptance by Israel. "Unilateral recognitions therefore definitely do not contribute to achieving this aim ... This is our stance now and it will be our stance in September. There needs to be mutual recognition, otherwise it is not a two-state solution".[277] She also reaffirmed her government's commitment to see an agreement reached as soon as possible. "We want a two-state solution. We want to recognize a Palestinian state. Let us ensure that negotiations begin. It is urgent".[278] Further details The German Democratic Republic recognised the State of Palestine on 18 November 1988,[17] but it later unified with the Federal Republic of Germany and the current government does not recognise it. | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 16 | President Karolos Papoulias has stated that Greece ultimately supports the creation of a Palestinian state alongside Israel.[279] Under previous governments, Greece garnered a reputation as a staunch supporter of the Palestinian cause.[280] Within the wider Arab–Israeli conflict, Andreas Papandreou maintained a stronger stand against Israel than any other government in the European Community. Diplomatic relations were founded with the PLO in 1981, while relations with Israel were maintained only at the consular level until Greece's formal recognition of Israel in 1990 under Mitsotakis.[281] Since the formation of current foreign policy under George Papandreou, Greece has seen a rapid improvement in relations with Israel,[282] leading the media to mark the conclusion of Greece's pro-Palestinian era.[283] However, in December 2015, Greece's parliament voted in favour of a motion requesting that the government recognize Palestine.[284] | Yes | EU, NATO; Greece–Palestine relations | |
| 17 | In January 2011, Ireland accorded the Palestinian delegation in Dublin diplomatic status.[285] A few months later, their Foreign Affairs Minister stated that Ireland would "lead the charge" in recognizing Palestinian statehood, but that it would not come until the PNA was in full and sole control over its territories.[286] In October 2014, the Upper House of the Irish Parliament unanimously passed a motion calling on the Government to recognize the State of Palestine.[287] In December 2014, the Lower House of Ireland's Parliament followed suit.[288] Although the motion passed through both houses, the government wishes to recognise Palestine as part of a wider EU movement and as such does not officially recognise the state of Palestine.[289] On 26 May 2021, following the escalation of violence in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, the lower house of Ireland's parliament, the Dáil, passed a resolution condemning Israel's "de facto annexation" of Palestine in contravention of international law.[290] | Yes | EU; Ireland–Palestine relations | |
| 18 | See above | Yes | ||
| 19 | In May 2011, at an event in Rome celebrating Israel's independence, then Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi pledged his country's support to Israel.[291] In June, he reiterated Italy's position against unilateral actions on either side of the conflict, stressing that "peace can only be reached with a common initiative through negotiations".[292] This position was shared by parliamentarians, who drafted a letter to the United Nations stating that "a premature, unilateral declaration of Palestinian statehood would [...] undermine rather than resolve the Israeli–Palestinian peace process".[293] Nevertheless, at the same time, Italy upgraded the diplomatic status of the Palestinian delegation in Rome to a mission, similarly to what other EU countries were doing, giving the head of the delegation ambassadorial status.[294] Moreover, on 31 October 2011, Italy did not oppose Palestine's UNESCO membership bid[295] and, on 29 November 2012, Italy voted in favour of UN Resolution 67/19, giving Palestine a non-member observer state status at the United Nations.[296] Italy's opposition to unilateral actions was reiterated on 21 December 2017, when it voted in favour of a UN draft resolution calling on all countries to comply with Security Council resolutions regarding the status of Jerusalem,[297] following the decision by the U.S. to move its embassy to Israel from Tel Aviv to the city.[298] | Yes | EU, NATO; Italy–Palestine relations | |
| 20 | Japan supports a two-state solution to the conflict,[299] and supports the establishment of a Palestinian state.[300] In October 2007, a Japanese Justice Ministry official said "Given that the Palestinian Authority has improved itself to almost a full-fledged state and issues its own passports, we have decided to accept the Palestinian nationality".[301] The Japanese government declared that it would not recognize any act that would jeopardize a Palestianian state with the pre-1967 borders nor the annexation of East Jerusalem by Israel.[302][303] Japan voted favorably for the United Nations General Assembly resolution to accord Palestine Non-member Observer State status in the United Nations in November 2012, and since then, refers to the country as "Palestine".[304] | Yes | ||
| 21 | During the summit of the Pacific Islands Forum in early September 2011, the foreign minister of Kiribati reportedly expressed support for the Palestinian position.[305] | No | ||
| 22 | Latvia supports a two-state solution to the conflict and provides development assistance to the Palestinian National Authority.[306][307] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 23 | Liechtenstein relies on Switzerland to carry out most of its foreign affairs.[308] In January 2011, it co-sponsored a draft resolution guaranteeing the Palestinian people's right to self-determination,[226] and stated that this right must be exercised with a view to achieving a viable and fully sovereign Palestinian state.[309] | No | EFTA | |
| 24 | Like the rest of the European Union, Lithuania supports a two-state solution including an independent Palestinian state.[310] Foreign Minister Audronius Ažubalis called for a strong, unanimous European position that encouraged both parties to resume peace talks.[311] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 25 | In an interview with Foreign Minister Jean Asselborn in March 2011, The Jerusalem Post stated that Luxembourg was considered among the "least friendly" countries to Israel in the EU.[312][313] In response to divisions within the EU regarding the Palestinians' September bid for UN membership, Asselborn reportedly urged the PNA to accept an upgrade in its observer status and not ask for membership. He insisted, "We cannot let the Palestinians leave New York at the end of the month with nothing",[314] He referred to the positions of four members in particular that stood as an obstacle to the achievement of a common position,[305] but that he "cannot agree to say no" to the Palestinian endeavour.[315] He noted that securing the support of all EU nations would have been a great moral advantage for Palestine.[314] In December 2019, Asselborn wrote to Josep Borrell, the head of EU foreign policy, urging a debate on recognising Palestinian statehood.[316] | Yes | EU, NATO; Luxembourg–Palestine relations | |
| 26 | The Marshall Islands has, like the US, long been a close voting ally of Israel at the United Nations. In December 2017, the Marshall Islands was one of just nine countries (including the US and Israel) to vote against a motion adopted by the UN General Assembly condemning the United States' recognition of Jerusalem as Israel's capital city.[317] Additionally, it was one of only five countries (the others being Israel, the US, Micronesia and Nauru) to oppose a UN draft resolution in November 2020 on the creation of a Palestinian state.[318] | |||
| 27 | Mexico maintains a policy of supporting a two-state solution.[319] Palestinian and Israeli officials expected Mexico to follow South American countries in recognizing the State of Palestine in early 2011.[320][321] Its position on the matter is seen as influential in Latin America, and therefore critical to both proponents and opponents.[322] Opposition parties have urged the government to recognize a Palestinian state as part of the September initiative, putting down its hesitance to U.S. pressure.[323] | Yes | Mexico–Palestine relations | |
| 28 | The Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) is a consistent supporter of Israel, especially in international resolutions,[324] though this is due in part to its association with the United States.[308] Former FSM President Manny Mori said that the relationship goes back to 1986, when Israel made "[an] early decision to support Micronesia's membership in the UN".[325] During the summit of the Pacific Islands Forum in September 2011, the leader of the Micronesian delegation reportedly stated his country's solidarity with the Palestinian people's suffering and support for their right to self-determination. Regarding the PNA's endeavour to gain admission to the United Nations, however, the official stated that the agreements signed with the U.S. prevented the FSM from voting according to its government's wishes in cases where they conflicted with those of the U.S.[305] In reference to Israel's continued development assistance to Micronesians, another diplomat noted, "We need Israeli expertise, so I don't see a change in our policy anytime soon."[324] | No | ||
| 29 | Moldova maintains a policy of neutrality in international affairs. It has expressed full support for the Quartet principles for the settlement of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, which call for an independent Palestinian state. | Yes | ||
| 30 | No | |||
| 31 | Myanmar is one of only two Asian members of the Non-Aligned Movement that has not recognized the State of Palestine, alongside Singapore.[210][326] Former foreign affairs minister Win Aung stated in 2000 that Myanmar supports a two-state solution within internationally recognized borders.[327] | No | ASEAN | |
| 32 | During the Pacific Islands Forum in early September 2011, Foreign Affairs Minister Kieren Keke confirmed his nation's solidarity with the Palestinian people and their right to self-determination.[328] The PNA's foreign ministry published a statement prior to the summit claiming that most Pacific island nations would vote against a United Nations resolution regarding the Palestinian state.[329] | No | ||
| 33 | In June 2011, Foreign Minister Uri Rosenthal stated that the request to admit Palestine at the United Nations would "not be supported by the Netherlands". He called instead for a resumption of negotiations: "We will continue to stress for a restart to direct negotiations."[330] He insisted that a peace deal must be based "on an agreement between all parties",[238] and that the Netherlands was opposed to anything done without the consent of both parties.[331] Abbas highlighted the importance of the Dutch role in the peace process, precisely because it maintained close ties with Israel: "It doesn't disturb us at all. They play a very important role and the Palestinian people are very appreciative of their help."[330] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 34 | New Zealand supports a two-state solution to the peace process.[332] It also maintains a policy of tacit rather than explicit recognition of new states. For Palestine, this would mean upgrading its accredited delegation to a diplomatic status.[333] In early September 2011, Foreign Minister Murray McCully said that the government would not make a decision until the wording of the resolution was released. "We've got a reputation for being fair minded and even handed on this matter and all we can do is wait to see the words.[332] He also told Riyad al-Malki that he had refused to give any pledges Israel to oppose to vote.[305] Since 2017, Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern has reiterated her support for a two-state solution and opposition to settler expansions.[334][335] | Yes[147] | ||
| 35 | North Macedonia is one of the few countries with no political or diplomatic relations with Palestine, of any kind. Whilst he was Macedonian Foreign Minister, Nikola Poposki stated that the Macedonian position will be built in accordance with the views of the European Union and its strategic partners.[336] | No | NATO | |
| 37 | The Norwegian government upgraded the Palestinian mission in Oslo to an embassy in December 2010 and called for the creation of a Palestinian state within the following year.[337] In January 2011, Støre stated that, should negotiations with Israel fail to make progress by September, his country would recognize Palestine within the United Nations framework.[338][339] Following a meeting with Abbas in July 2011, Støre claimed that it was "perfectly legitimate" for the Palestinians to seek a vote on recognition of statehood.[340] "The fundamental Norwegian view is that a people have the right to use UN institutions to clarify questions about the legitimacy of their status in the world. We are opposed to denying this to the Palestinians". The minister withheld full commitment until the request was officially announced,[341][342] after which, on 18 September, he confirmed that Norway would lend recognition to Palestine.[343] | Yes | EFTA, NATO | |
| 38 | Palau is one of four countries (alongside the Marshall Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia and Nauru) that has almost always voted with the U.S. in bills at the UN. Palau, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia and the U.S. make up the Compact of Free Association,[344] which some observers have suggested amounts to "checkbook diplomacy", whereby the U.S. bought the tiny island states' votes for cash.[345] When the UN overwhelmingly voted to condemn Donald Trump's decision to recognise Jerusalem as Israel's capital and relocate the U.S. embassy there, Palau was one of only nine countries to support the move.[346][347] | No | ||
| 39 | Panama has not indicated its position regarding a vote on statehood,[348] and is reported to be undecided on the matter.[349] President Ricardo Martinelli has a record of supporting Israel in UN resolutions,[350] and has reportedly resisted pressure from other Latin American governments to recognize Palestine.[351] The Central American Integration System (SICA) was expected to adopt a joint position on the issue at its summit on 18 August,[352] but Panama insisted that discussion should retain a regional focus and the matter was not included on the final agenda.[353] In early September, Foreign Minister Roberto Henriquez said that the government's decision would not be made public until its vote is cast, but added, "It is very important that the birth of this country and its recognition in the international forum is previously accompanied by a full peace agreement with its neighbour, Israel."[354] On 4 July 2015, Panama's Vice President and Foreign Minister Isabel De Saint Malo de Alvarado said that her government is looking at ways to recognize the State of Palestine without affecting their "close relationship" with Israel.[355] | No | ||
| 40 | In February 2011, several parliamentary factions proposed resolutions calling on the government to recognize the State of Palestine.[356] However, these were dismissed by the two majority parties, which insisted on a prior settlement acceptable to both Palestinians and Israelis.[357] Foreign Minister Paulo Portas stated that Portugal supports the initiative to recognize Palestine, but that it must not forget the security of Israel: "We will do everything for Palestine, which deserves to have its state, and do nothing against Israel, which deserves to have its security."[358] In December 2014, the Portuguese Parliament passed a resolution that is non-binding calling on the government to recognize Palestine as an independent state with 9 of 230 members opposing the measure.[359] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 41 | Prime Minister Tuila'epa Sailele Malielegaoi has expressed support for a two-state solution to the conflict.[360] | No | ||
| 42 | No | |||
| 43 | Singapore has not recognized the State of Palestine and has not announced a position regarding a resolution.[361] The island state has a strong relationship with Israel.[362] However, Singapore established a representative office in Ramallah as a move to improve coordination of capacity-building initiatives and fortify relations with the Palestinian National Authority.[363][364] | Yes | ASEAN | |
| 44 | On 28 November 2014, the Foreign Policy Committee rejected a motion to immediately recognize Palestine, but approved an alternative motion requiring the government to submit a proposal to recognize Palestine to the National Assembly.[365] | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 45 | Foreign Minister Peter Shannel Agovaka met Riyad al-Malki in early September at the summit of the Pacific Islands Forum in Wellington. Agovaka reportedly confirmed his government's support of Palestinian efforts at the United Nations, and that possible recognition of the State of Palestine would be considered in the next cabinet meeting.[305] | No | ||
| 46 | The government of South Korea does not recognize the State of Palestine.[366] However, South Korea established a representative office in Ramallah. | Yes | ||
| 47 | On 1 July 2011, the Spanish parliament passed a resolution urging its government to recognize the State of Palestine on the 1967 borders.[citation needed] Prior to this, Nabil Shaath had claimed in May that Spain intended to recognize the Palestinian state before September.[367] In late July, Foreign Minister Trinidad Jiménez said that Spain supports the bid, but that it would not determine its position until the proposal is made official.[368] In an interview with El País in August, Jiménez confirmed Spain's support: "We are working with the idea that there is a majority in the EU that will support moving forward with the recognition of Palestine." She added that it was the right time to do this, since it would give Palestinians much needed hope about their future state.[369] On 20 November 2014, the Spanish parliament approved a non-binding motion calling on the government to recognize Palestine by a vote of 319–2.[370] In November 2023, following his reelection as Prime Minister, Pedro Sánchez announced the intention of his government to recognize "any second now" the State of Palestine, and told so to the Israel PM Benjamin Netanyahu.[371][372] | Yes | EU, NATO; Palestine–Spain relations | |
| 48 | Switzerland does not recognize Palestine as an independent state but voted in favor of granting it a non-member observer status at the UN in November 2014. Swiss President Simonetta Sommaruga voiced her support for a two-state solution, saying "Switzerland has worked for years for a solution to the conflict between Israel and Palestine. Our aim is to achieve peace."[373] | Yes | EFTA | |
| 49 | The Bahamas has not publicized an official position of its own regarding the State of Palestine.[349] As a member of the Caribbean Community, it supports a two-state solution along internationally recognized borders.[205] | No | ||
| 50 | In September 2011, following the summit of the Pacific Islands Forum in Wellington, the PNA's foreign ministry noted that it had made significant strides in its efforts to attain recognition from Tonga.[328] | No | ||
| 51 | In December 2017, Foreign Affairs Minister Dennis Moses said, "Trinidad and Tobago's policy has always been to support the two states policy which means steadfast recognition of the State of Israel with secure territorial borders as well as the establishment of a Palestinian State."[374] | No | ||
| 52 | On 10 September 2015, the United Nations General Assembly passed a Palestinian resolution to allow its flag to fly in front of the United Nations headquarters in New York. The vote was passed with 119 votes in support, 8 opposing, and 45 abstentions. Tuvalu was one of the eight opposing votes.[375] | No | ||
| 53 | In September 2011, the UK said it would recognize Palestine as a state, but only with non-member observer status, rather than full membership, at the United Nations.[citation needed] In October 2014, the UK House of Commons passed a symbolic non-binding Motion by a vote of 274 in favour to 12 against which called on the Government to recognize Palestine.[376][377] Also in October 2014, the devolved government of Scotland called for recognition of Palestine as an independent state and for the UK to open an Embassy.[378] Shortly before the 47th G7 summit in June 2021, Labour Party leader Keir Starmer called on Prime Minister Boris Johnson to "press for renewed agreement to finally recognise a state of Palestine and to stop expansion of illegal settlements and to get a meaningful peace process back and running."[379] | Yes | NATO, UNSC (permanent); Palestine–United Kingdom relations. | |
| 54 | In September 2011, President Barack Obama declared U.S. opposition to the bid in his speech to the General Assembly, saying that "genuine peace can only be realized between Israelis and Palestinians themselves" and that "[u]ltimately, it is Israelis and Palestinians – not us – who must reach an agreement on the issues that divide them".[380] Obama told Abbas that they would veto any United Nations Security Council move to recognize Palestinian statehood.[381] Presidents Donald Trump and Joe Biden have maintained that UNSC veto policy.[382][383] | Yes | NATO, UNSC (permanent); Palestine–United States relations |
Not members of the UN
| # | Name | Official position | Relations [note 2] | Relevant memberships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Yes [384][385] |
Multilateral treaties
The State of Palestine is a party to several multilateral treaties, registered with five depositaries: the United Kingdom, UNESCO, United Nations, the Netherlands and Switzerland. The ratification of the UNESCO conventions took place in 2011/2012 and followed Palestine becoming a member of UNESCO, while the ratification of the other conventions were performed in 2014 while negotiations with Israel were in an impasse.
| Depositary Country/organization | Depositary organ | Number of treaties | Examples | Date of first ratification/accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Netherlands | Ministry of Foreign Affairs | 1[386] | Convention respecting the laws and customs of war on land | 2 April 2014 |
| Russia | 1[387] | Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons | 10 February 2015 | |
| Switzerland | Federal Council | 7[388][389] | Geneva Conventions and Protocols | 2 April 2014 |
| UNESCO | Director-General | 8[390] | Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage | 8 December 2011 |
| United Nations | Secretary-General | >50[391] | Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations Statute of the International Criminal Court | 9 April 2014 |
| United Kingdom | Foreign and Commonwealth Office | 2[392][393] | UNESCO Constitution Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons | 23 November 2011 |
In an objection of 16 May 2014, Israel informed the Secretary General of the United Nations that it did not consider that 'Palestine' (single quotation marks in original) met the definition of statehood and that its requested accession to the United Nations Convention against Torture as being "without legal validity and without effect upon Israel's treaty relations under the Convention".[394] The United States and Canada lodged similar objections.[395][396]
Palestine participated in the negotiation of the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons and voted in favour of its adoption on 7 July 2017.[397]
See also
- List of states with limited recognition
- List of positions on Jerusalem
- International recognition of Israel
- Palestinian nationalism
- Proposals for a Palestinian state
- Palestine–European Union relations
- Right to exist
Notes
References
- ^ United Nations A/67/L.28 General Assembly Archived 1 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine. 26 November 2012.
- ^ "Palestinians win implicit U.N. recognition of sovereign state". Reuters. 29 November 2012. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- ^ United Nations Educational, Scientific; Cultural Organization, Executive Board (12 May 1989). "Hundred and thirty-first Session: Item 9.4 of the provisional agenda, Request for the Admission of the State of Palestine to UNESCO as a Member State" (PDF). United Nations. pp. 18, Annex II. Retrieved 15 November 2010. The list contains 92 entries, including a number of states which no longer exist.
- ^ Tessler, Mark (1994). A History of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict (2nd, illustrated ed.). Indiana University Press. p. 722. ISBN 978-0-253-20873-6. "Within two weeks of the PNC meeting, at least fifty-five nations, including states as diverse as the Soviet Union, China, India, Greece, Yugoslavia, Sri Lanka, Malta, and Zambia, had recognised the Palestinian state."
- ^ "Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements (Oslo Accords) | UN Peacemaker". peacemaker.un.org. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ Hillier, Tim (1998). Sourcebook on Public International Law. Routledge. pp. 128, 218. ISBN 978-1-85941-050-9.
- ^ "Q&A: Palestinian bid for full membership at the UN". BBC News. 30 November 2012.
- ^ Sabasteanski, Anna (2005). Patterns of Global Terrorism 1985–2005: U.S. Department of State Reports with Supplementary Documents and Statistics. Vol. 1. Berkshire. p. 47. ISBN 0-9743091-3-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Boyle, Francis A. (1 September 2009). Palestine, Palestinians and International Law. Clarity Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-932863-37-9. "As I had predicted to the PLO, the creation of [a] Palestinian State was an instantaneous success. Palestine would eventually achieve de jure diplomatic recognition from about 130 states. The only regional hold-out was Europe and this was because of massive political pressure applied by the United States Government."
- ^ Shashaa, Esam. "The state of Palestine". Palestine History. Archived from the original on 27 November 2010. Retrieved 28 December 2010.
- ^ Charter of the League of Arab States (22 March 1945): Annex regarding Palestine; available at University of the Basque Country. Retrieved 21 January 2011. Archived 14 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ See the following:
- Organisation of the Islamic Conference (13–16 March 1989). "Resolutions on Political, Legal and Information Affairs". The Eighteenth Islamic Conference of Foreign Ministers (Session of Islamic Fraternity and Solidarity). Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- Organisation of the Islamic Conference (13–16 March 1989). "Final Communique". The Eighteenth Islamic Conference of Foreign Ministers (Session of Islamic Fraternity and Solidarity). Archived from the original on 20 February 2009. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- Organisation of the Islamic Conference (28–30 May 2003). "Resolutions on Palestine Affairs". The Thirtieth Session of the Islamic Conference of Foreign Ministers (Session of Unity and Dignity). United Nations Information System on the Question of Palestine. Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- ^ a b c d United Nations Security Council; United Nations Department of Political and Security Council Affairs (2008). Repertoire of the practice of the Security Council. United Nations Publications. p. 759. ISBN 9789211370300.
- ^ Reut Institute (14 August 2004). "Act of Recognition of Statehood". Structure of the Political Process. Archived from the original on 1 October 2022. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ Quigley, John (1990). Palestine and Israel: A Challenge to Justice. Duke University Press. p. 231.
- ^ a b c Quigley, John (2009). "The Palestine Declaration to the International Criminal Court: The Statehood Issue" (PDF). Rutgers Law Record. 35. Newark: Rutgers School of Law. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn United Nations Educational, Scientific; Cultural Organization, Executive Board (12 May 1989). "Hundred and thirty-first Session: Item 9.4 of the provisional agenda, Request for the Admission of the State of Palestine to UNESCO as a Member State" (PDF). United Nations. pp. 18, Annex II. Retrieved 15 November 2010. The list contains 92 entries, including a number of states which no longer exist.
- ^ "Note of Information" (Press release). Government of Switzerland. 13 September 1989.
- ^ Lewis, Paul (6 December 1989). "Arabs at U.N. Relax Stand on P.L.O." The New York Times. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ Crawford, James (1999), "Israel (1948–1949) and Palestine (1998–1999): Two Studies in the Creation of States", in Goodwin-Gil, G.S.; Talmon, S. (eds.), The Reality of International Law: Essays in Honour of Ian Brownlie, New York: Fitzroy Dearborn, Oxford University Press, pp. 95–100, 110–115 "...Declaration was quite widely recognized by states, although often in equivocal terms."
- ^ Boyle, Francis A. (1990). "Creation of the State of Palestine". European Journal of International Law. 1 (301): 301–306. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.ejil.a035773. Archived from the original on 9 December 2014. "Over 114 states have already recognized the newly proclaimed state of Palestine".
- Kurz, Anat N. (2005). Fatah and the Politics of Violence: the institutionalization of a popular struggle. Brighton: Sussex Academic Press. p. 123. ISBN 978-1-84519-032-3. "117 UN member states recognized the declared State of Palestine ..."
- Quigley, John B. (30 December 2010). "Recognize Palestine now". McClatchy-Tribune. Youngstown News. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 31 December 2010. "With recognitions in recent weeks by Brazil and Argentina, some 105 states now formally recognize Palestine at the diplomatic level."
- ^ Boyle, Francis A. (30 September 2010). "The Impending Collapse of Israel in Palestine". MWC News. Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- Staff writers (25 December 2010). "Ecuador latest Latin country to recognize Palestine". RFI. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- Mercier, Gilbert (26 December 2010). "Ecuador Joins Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay And Bolivia To Recognize Palestine". News Junkie Post. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ Ravid, B. (13 July 2011). "Palestinian envoy to UN: European states will recognize Palestine before September". Haaretz. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ^ a b Negotiations Affairs Department (July 2011). "Recognizing the Palestinian State on the 1967 border & Admission of Palestine as a Full Member of the United Nations" (PDF). Palestinian National Authority. p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ Flower, K; Roth, R; Vaccarello, J; Sweeney, F (26 September 2011). "U.N. Security Council to send Palestinian state bid to admissions committee". CNN. Retrieved 10 October 2011.
- ^ Ziv, Guy (2 November 2017). "Fight the Right-wingers Rewriting History: Rabin Wanted a Palestinian State". Haaretz. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ "Sharon statement boosts road map for peace". The Guardian. 4 June 2003. Retrieved 18 January 2024.
- ^ Chen, Joanna (28 August 2010). "Can Netanyahu Make Peace With the Palestinians?". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on 22 March 2013.
- ^ McCarthy, Rory (14 June 2009). "Netanyahu backs an independent Palestinian state for first time". The Guardian.
- ^ Gold, Hadas (1 February 2023). "Netanyahu outlines vision for two-state solution -- without Palestinian sovereignty". CNN. Retrieved 3 November 2023.
- ^ Pearce, David D. (12 February 1978). "Mideast Stakes Touch All Parts of the Globe". The Milwaukee Journal.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Prusher, Ilene R. (15 November 2009). "Israel rejects Palestinian statehood bid via the UN". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ UNGA, 14 October 1974; Resolution 3210 (XXIX). Invitation to the Palestine Liberation Organization (doc.nr.A/RES/3210 (XXIX)) Archived 3 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3236
- ^ UNGA, 22 November 1974; Resolution 3237 (XXIX). Observer status for the Palestine Liberation Organization (doc.nr. A/RES/3237 (XXIX)) Archived 27 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ UNGA, 15 December 1988; Resolution 43/177. Question of Palestine (doc.nr. A/RES/43/177) Archived 1 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Gharib, Ali (20 December 2012). "U.N. Adds New Name: "State of Palestine"". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on 1 January 2013. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ Phillips, Leigh (17 November 2009). "EU rejects request to recognise independent Palestine". EU Observer. Retrieved 30 August 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Erekat, Saeb. The Eminence of September. Group 194.
- ^ Vick, Karl (1 September 2011). "The Palestinians' Statehood Dilemma: Full U.N. Membership or Observer Status?". Time. Archived from the original on 2 September 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Schell, Bernhard (31 July 2011). "UN will count 194 members if Palestine gets in". InDepthNews. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ Sawafta, A. (14 July 2011). "Arabs to seek full Palestinian upgrade at UN". Reuters. Retrieved 19 July 2011.
- ^ Staff writers (6 July 2011). "Arab League Requests Palestinian Statehood from U.N." Palestine News Network. Retrieved 19 July 2011.
- ^ Ashkar, Alaa; Bannoura, Saed (9 September 2011). "UN Secretary-General Supports Full Palestinian Membership". International Middle East Media Center. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ a b c Waked, Ali (7 December 2010). "Argentina, Uruguay recognize Palestinian state". Israel News. Yedioth Internet. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- ^ a b c d Ravid, Barak (4 July 2011). "Palestinians set up diplomatic 'war room' ahead of September vote on statehood". Haaretz. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Sherwood, Harriet (18 January 2011). "Dmitry Medvedev restates Russian support for Palestinian state". The Guardian. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Media agencies (26 August 2011). "China announces support for Palestinian UN statehood bid". Haaretz. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
- ^ Staff writers (31 January 2011). "African Union declares support for Palestine". Ma'an News Agency. Archived from the original on 27 October 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ "Non-Aligned movement confirms support for Palestinian statehood bid". Al Arabiya. Agence France-Presse. 6 September 2011. Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ a b Staff writers (18 July 2011). "Israeli minister says Palestinians losing UN bid". Almasry Alyoum. Archived from the original on 10 December 2012. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Gruen, G.E. (1982). The Palestinians in perspective: implications for Mideast peace and U.S. policy. Institute of Human Relations Press, American Jewish Committee. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-87495-042-7.
- ^ Medzini, Ronen (26 May 2011). "Palestinian UN bid: Israel's battle for Europe". Ynetnews. Yedioth Internet. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- ^ Ravid, Barak (28 August 2011). "UN envoy Prosor: Israel has no chance of stopping recognition of Palestinian state". Haaretz. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
- ^ Somfalvi, Attila (17 August 2011). "PA to soften UN statehood bid?". Ynetnews. Yedioth Internet. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Keinon, Herb (24 April 2011). "EU split over UN recognition of Palestinian state". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ a b c Susser, Leslie (21 June 2011). "Pressure mounts on Palestinians to abandon U.N. statehood gambit". Jewish Telegraph Agency. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ "Palestinians see progress in EU stance on UN bid". France 24. Agence France-Presse. 28 August 2011. Archived from the original on 29 August 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ a b Keinon, Herb (28 August 2011). "Israel looks to influence text of PA statehood resolution". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 31 August 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ United States Congress (15 December 2010). "H.Res. 1765 - Supporting a negotiated solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and condemning unilateral measures to declare or recognize a Palestinian state, and for other purposes". 111th Congress. Library of Congress.
- ^ United States Senate (28 June 2011). "S.Res. 185 - A resolution reaffirming the commitment of the United States to a negotiated settlement of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict through direct Israeli-Palestinian negotiations, reaffirming opposition to the inclusion of Hamas in a unity government unless it is willing to accept peace with Israel and renounce violence, and declaring that Palestinian efforts to gain recognition of a state outside direct negotiations demonstrates absence of a good faith commitment to peace negotiations, and will have implications for continued United States aid. 112th Congress. Library of Congress.
- ^ Mozgovaya, N. (29 June 2011). "U.S. Senate passes resolution threatening to suspend aid to Palestinians". Haaretz. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ Mozgovaya, Natasha (31 August 2011). "U.S. bill aims to cut funds to pro-Palestinian UN groups". Haaretz. Associated Press. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Swaine, J. (24 June 2011). "US 'could withdraw funding from UN if Palestine state is recognised'". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ "U.S.: We will stop aid to Palestinians if UN bid proceeds". Haaretz. 26 August 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Lapide, Joshua (31 August 2011). "Israel's increasingly bitter war against Palestinian seat in UN". AsiaNews. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ Staff writers (19 January 2011). "Russia recognizes Palestine". United Press International. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ Ravid, Barak (12 July 2011). "Officials: Mideast Quartet talks failed due to disagreement over Israel as Jewish state". Haaretz. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ "Palestine: the world's next nation". Avaaz.org.
- ^ OneVoice Movement (8 September 2011). "OneVoice youth activists unveil campaign backing Palestinian UN bid". Archived from the original on 26 October 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Concerned Citizens. "UNRECOGNISED". Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Sadaka. "Join Ireland's call to support UN membership for Palestine!". Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 9 September 2011.: "...to be printed in the Irish Times on 17th September 2011".
- ^ "The National Campaign". Palestine: State No. 194. Archived from the original on 23 September 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Staff writers (9 September 2011). "UN Secretary General: Palestinian statehood is 'long overdue'". Haaretz. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Office of the United Nations Special Co-ordinator for the Middle East Peace Process (13 April 2011). "Palestinian State-Building: A Decisive Period" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ^ Kershner, Isabel (12 April 2011). "U.N. Praises Palestinians' Progress Toward a State". New York Times. Retrieved 2 July 2011.
- ^ "Palestinians able to establish a state". Alertnet.org. Reuters. 17 September 2010. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ Lederer, Edith M. (3 April 2024). "Palestinians will seek full UN membership again, but U.S. is almost certain to block the request". PBS NewsHour. PBS. Associated Press. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ Sullivan, Becky; Keleman, Michele (18 April 2024). "What to know about the U.N. vote on whether to admit Palestinians as full members". Middle East. NPR. Retrieved 19 April 2024.
- ^ a b Lederer, Edith M. (19 April 2024). "US vetoes widely supported resolution backing full UN membership for Palestine". World News. Associated Press. Retrieved 19 April 2024.
- ^ "Security Council - Veto List". Dag Hammarskjöld Library Research Guide. Archived from the original on 24 April 2024. Retrieved 24 April 2024.
- ^ a b "S/2024/312" (PDF). UNdocs.org. United Nations Security Council. Retrieved 24 April 2024.
- ^ a b "A/67/L.28 of 26 November 2012 and A/RES/67/19 of 29 November 2012". Unispal.un.org. Archived from the original on 10 December 2012. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ^ a b c "Palestine: What is in a name (change)?". Al Jazeera. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ "Israel defies UN after vote on Palestine with plans for 3,000 new homes in the West Bank". The Independent. 1 December 2012.
- ^ Laub, Karin; Daraghmeh, Mohammed (7 January 2013). "State Of Palestine: Palestinians Change Name, Won't Rush To Issue New Passports". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 11 October 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ "Palestine threatens to sue Israel at ICC". 30 January 2013. Archived from the original on 18 April 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ "Palestinians' UN upgrade to nonmember observer state: Struggles ahead over possible powers". Washington Post. 30 November 2012. Archived from the original on 12 November 2018.
- ^ "Permanent Observer Mission of the State of Palestine to the United Nations". Archived from the original on 31 January 2013.
- ^ "Palestinian Authority officially changes name to 'State of Palestine'". Haaretz. 5 January 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ "UN allow Palestine leader Abbas to use heads-of-state chair". The Sydney Morning Herald. 26 September 2013. Retrieved 4 October 2014.
- ^ "Countries That Recognize Palestine 2021". worldpopulationreview.com. Retrieved 23 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Diplomatic Relations" Archived 27 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Permanent Observer of the State of Palestine to the United Nations. Accessed March 2016
- ^ "Diplomatic Relations". Permanent Observer Mission of The State of Palestine to the United Nations New York. Archived from the original on 27 September 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- ^ Government of Algeria (28 December 2010). "Algerie-Palestine-Diplomatie" (in French). Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2011. "Ambassadeur extraordinaire et plénipotentiaire de l'État de Palestine".
- ^ Government of Bahrain. "Bilateral Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 1 February 2011.
- ^ Government of Kuwait. "The nature of the work of the Department of the Arab world". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 23 June 2011. Retrieved 20 February 2011. "دولة فلسطين".
- ^ Government of Kuwait. "The Arab Economic Summit 2009". Al-Diwan Al-Amiri, official website, State of Kuwait. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011. "Mr. Mahmoud Abbas is the President of the Palestinian National Authority (PNA) and the President of the State of Palestine."
- ^ Government of Morocco. "Conventions, Treaties, Agreements and Protocols". Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 20 February 2011. "État de Palestine".
- ^ Government of Morocco. "Protocole de coopération entre le Ministère des Affaires Culturelles du Maroc et le Ministère de la Culture et de l'Information de l'Etat Palestinien". Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- ^ Government of Tunisia. "Les Relations Tuniso–Palestiniennes". Retrieved 20 February 2011.[permanent dead link] "Les deux pays ont établi des relations diplomatiques en 1994. chacune des deux parties étant représentée par un bureau de liaison."
- ^ Government of Turkey. "Turkey´s Political Relations with the Palestinian National Authority". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 29 January 2011. "Turkey established official relations with the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) in 1975 and was one of the first countries that recognized the Palestinian State established in exile on 15 November 1988."
- ^ Bühler, Konrad (2001). State Succession and Membership in International Organizations. Martinus Nijhoff Publisher. ISBN 9041115536.
- ^ Government of Afghanistan. "Afghan Diplomatic Missions". Embassy of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, Canberra. Archived from the original on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 5 August 2011. "Embassy of Afghanistan in Damascus ... non-resident envoy to: Jordan, Lebanon and Palestine".
- ^ a b Government of Indonesia. "Bilateral Cooperation – Palestine". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 1 February 2011. "Indonesia's formal recognition towards the recently established State of Palestine the very next day, on 16 November 1988 ... One year later, Indonesia and Palestine agreed to advance their bilateral relations through the signing of a Joint Communique on the Commencement of Indonesia-Palestine Diplomatic Relations at Ambassadorial Level, on 19 October 1988 ... Indonesia assigned its Head of Mission to the Republic of Tunisia as the Ambassador non-resident for Palestine until 1 June 2004, when the assignment was relegated to the Indonesia's Ambassador for the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan in Amman."
- ^ Government of Serbia. "Bilateral political relations Serbia-Palestine". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 19 May 2011. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ Government of Albania (January 2011). "Diplomatic list" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 6 August 2011. "Embassy of the State of Palestina".
- ^ Government of Brunei Darusalam (23 October 2007). "Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade Welcomes the Palestinian President". Ministry of Foreign Affairs & Trade. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 10 March 2011. "His Excellency Mahmoud Abbas, President of the State of the Palestine".
- ^ President of Sudan. "Speech elected President Omar al-Bashir during his inauguration ceremony in Parliament". Archived from the original on 26 May 2011. Retrieved 10 March 2011. "... representative of His Excellency the President of the State of Palestine".
- ^ Kype (31 January 2011). "Cyprus will not recognize any changes to the pre-1967 borders". Famagusta Gazette. Archived from the original on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "India-Palestine Relations" (PDF). Ministry of External Affairs – India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 November 2010. Retrieved 7 December 2010. "In 1947, India voted against the partition of Palestine at the UN GA. India was first Non-Arab State to recognize PLO ... in 1974. India was one of the first countries to recognize the State of Palestine in 1988. In 1996, India opened its Representative Office to the Palestine Authority in Gaza, which later was shifted to Ramamllah in 2003".
- ^ Constitution of Belarus, Art. 142.
- ^ United Nations General Assembly (9 December 1988). "Resolution 43/160: Observer status of national liberation movements" (PDF). United Nations Documentation Centre. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2012. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ^ Посольство (in Russian). Palestine.ru. Archived from the original on 16 June 2010. Retrieved 22 January 2011. "Первое представительство ООП (Организации Освобождения Палестины) в Москве было открыто в 1974 г., и первым Главой Представительства стал Бригадный Генерал Мухаммад Аль-Шаер. В 1981г. Представительство было преобразовано в дипломатическую миссию. А 18 ноября 1988 г. СССР официально признал Палестинское Государство. В январе 1990г. Представительство было преобразовано в Посольство Государство Палестина."
- ^ Sherwood, Harriet (18 January 2011). "Dmitry Medvedev restates Russian support for Palestinian state". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ The Law of Ukraine on Succession of Ukraine, Verkhovna Rada (5 October 1991).
- ^ "Vietnam-Palestine Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs – Vietnam. Retrieved 18 July 2009. "1968: Viet Nam established ties with the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO)... 19 November 1988: Viet Nam recognized the State of Palestine and officially transformed the PLO's resident Representative Office into the Embassy of the State of Palestine."
- ^ Government of Mongolia. "List of states with diplomatic relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 10 March 2011. "State of Palestine". Relations established with the PLO prior to the 1988 declaration of independence.
- ^ "لقاء السفير عبد الرحيم الفرا برئيس جمهورية الرأس الأخضر..شاهد الصور" (in Arabic). 4 December 2009. Retrieved 23 January 2024.
- ^ "سفارة دولة فلسطين – جمهورية توغو" (in Arabic). Archived from the original on 5 August 2018. Retrieved 23 January 2024.
- ^ Government of Lao DPR. "List of states whom Lao D.P.R. has established diplomatic relation since 1950". Lao Embassy in Hanoi. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2010. "Palestine".
- ^ "السفير أبوبكر يلتقي وزير الخارجية السيراليون" (in Arabic). 6 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2024.
- ^ Permanent Observer Mission of Palestine to the United Nations (10 December 2010). "Palestine Embassies, Missions, Delegations Abroad". United Nations. Archived from the original on 25 February 2011. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ "Palestine, Botswana establish full diplomatic relations". وكالة الأنباء والمعلومات الفلسطينية – وفا.
- ^ Peters, Joel (1992). Israel and Africa: the problematic friendship. I.B.Tauris. p. 141. ISBN 978-1-870915-10-6.
- ^ Government of Vanuatu (21 August 1989). Letter to ambassador Ali Kazak (Ref: 8/3/3/nv-mf, 10/417/2). Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Accessed 30 May 2011.
- ^ Embassy of the Philippines in Amman (6 December 2009). "Amb. Julius D. Torres presents credentials to Palestinian president". Government of the Philippines. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2010. "...as non-resident Ambassador to Palestine to Palestinian National Authority President Mahmoud Abbas".
- ^ Department of Budget and Management. "Embassies and Diplomatic Missions" (PDF). Government of the Philippines. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2010. "Consulate General of the State of Palestine".
- ^ Budianto, Lilian (8 December 2010). "Palestine issue still low on ASEAN agenda". The Jakarta Post. PT Bina Media Tenggara. Retrieved 11 December 2010.
- ^ a b Embassies & consulates in the Philippines. Best of the Philippines. 1995. ISBN 9789719151609., p219: "The State of Palestine is recognized by over one hundred states including the Republic of the Philippines. In September 1989, diplomatic relations were established between the two governments leading to the opening of the Embassy of the State of Palestine in Manila, May 1990."
- ^ "PNN" السفير عبد الجواد يقدم نسخة من أوراق اعتماده لوزير خارجية مملكة سوازيلاند (in Arabic). Palestine News Network. 3 November 2010. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "These are all the countries that recognise Palestine as a state". Archived from the original on 9 June 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ^ Palestinian National Authority. السفير عبد الجواد يقدم نسخة من أوراق اعتماده لوزير خارجية مملكة سوازيلاند (in Arabic). Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 4 August 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2011.
- ^ a b Government of Kazakhstan. "Cooperation of the Republic of Kazakhstan with the State of Palestine". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2010. Relations established on 6 April 1992. Palestinian Embassy in Kazakhstan was opened in 1993.
- ^ a b Government of Azerbaijan. "Politics" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2013. Retrieved 30 October 2014. "The Republic of Azerbaijan has diplomatic relations with Palestine since 15.04.1992".
- ^ "States with which Turkmenistan established diplomatic ties". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Turkmenistan. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Palestinian Ambassador accredited in Turkmenistan". Turkmenistan.ru. 6 April 2012. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "Ambassador of Palestine accredited to Turkmenistan". Turkmenistan: The Golden Age. State News Agency of Turkmenistan. 6 April 2012. Archived from the original on 24 September 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Staff writers (11 November 2004). "Niyazov offers condolences to leadership and people of Palestine over demise of Yasser Arafat". Turkmenistan.ru. Archived from the original on 23 March 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2011. "Niyazov sent a message of condolences to the government of the State of Palestine".
- ^ Ismail, Mohamed. "Interview of Minister of Foreign Affairs of Georgia Gela Bezhuashvili to the newspaper Egyptian Gazette". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2011. "[Bezhuashvili] added that Georgia recognised the Palestinian state in 1992 and has official ties with it."
- ^ Government of Georgia. "Bilateral Relations between Georgia and Palestine". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 20 November 2010. Relations established 25 April 1992.
- ^ a b Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina. "Dates of Recognition and Establishment of Diplomatic Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2010. "Lista zemalja koje su priznale Bosnu i Hercegovinu i datumi uspostavljanja diplomatskih odnosa – Palestine – 27.05.1992, 30.10.1992".


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch