List of sovereign states by date of formation
This article possibly contains original research. (July 2019) |
Below is a list of sovereign states with the dates of their formation (date of their independence or of their constitution), sorted by continent.
This list includes the 195 states which are currently member states of the United Nations or non-member observer states with the United Nations General Assembly. This does not include extinct states, but does include several states with limited recognition.[note 1]
For proposed states or various indigenous nations which consider themselves still under occupation, see list of active autonomist and secessionist movements.
Nation-building is a long evolutionary process, and in most cases the date of a country's "formation" cannot be objectively determined; e.g., the fact that England and France were sovereign kingdoms on equal footing in the medieval period does not prejudice the fact that England is not now a sovereign state (having passed sovereignty to Great Britain in 1707), while France is a Republic founded in 1870 (though the term France generally refers to the current French Fifth Republic government, formed in 1958).
An unambiguous measure is the date of national constitutions; but as constitutions are an almost entirely modern concept, all formation dates by that criterion are modern or early modern (the oldest extant constitution being that of San Marino, dating to 1600).
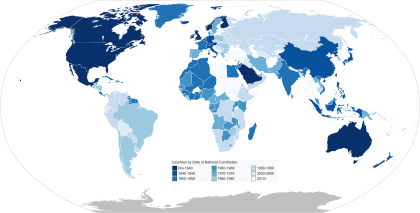
| Pre-1940 1940–1949 1950–1959 | 1960–1969 1970–1979 1980–1989 | 1990–1999 2000–2009 2010–present |
Independence dates for widely recognized states earlier than 1919 should be treated with caution, since prior to the founding of the League of Nations, there was no international body to recognize nationhood, and independence had no meaning beyond mutual recognition of de facto sovereigns (the role of the League of Nations was effectively taken over by the United Nations after the Second World War). See also: disputed territories.
Many countries have some remote (or fantastically remote) symbolic foundation date as part of their national mythology, sometimes artificially inflating a country's "age" for reasons of nationalism, sometimes merely gesturing at a long and gradual process of the formalizing national identity. Such dates do not reflect the formation of a state (an independent political entity).[citation needed]
The following list contains the formation dates of countries with a short description of formation events. For a more detailed description of a country's formation and history, please see the main article for that country.
Africa[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 September 1958 | Provisional Government of the Algerian Republic proclaimed | 202 BC | Massinissa unifies Numidia which extended from the Moulouya river in the west to Cyrenaica in the east | 18 March 1845 | Lalla Maghnia treaty between French administration in Algeria and the Sherifian empire, the treaty confirms the Sherifian acquisitions in 1813, the Moulouya river is no longer the border between the two territories and is relocated to Oued Kiss. Algerian territory no longer comprises Oujda and Figuig | |
| 5 July 1962 | Algeria reclaims sovereignty over the entire Algerian territory upon independence from France | |||||
| 1975 | 11 November 1975 | Independence from Portugal | ||||
| 1 March 1960 | 1 August 1960 | Independence from France | 15 January 1894 | Borders of French Protectorate of Dahomey set at conclusion of Second Franco-Dahomean War | ||
| 30 September 1966 | 30 September 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 31 December 1999 | Sedudu ruled to belong to Botswana rather than Namibia by the International Court of Justice. | ||
| 30 September 2022 | Coup d'état | 5 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||
| 28 November 1966 | Monarchy replaced by republic | 1 July 1962 | Independence from Belgium | |||
| 5 July 1975 | 5 July 1975 | Independence from Portugal | ||||
| 20 May 1972 | 1 January 1960 | Independence from France | 1 October 1961 | Merger of part of British Cameroons with Cameroon | ||
| 21 September 1979 | Monarchy replaced by republic | 13 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||
| 10 October 2022 | National Transitional Council established | 11 August 1960 | Independence from France | 3 February 1997 | Aouzou Strip awarded to Chad | |
| 6 July 1975 | Independence from France declared | |||||
| 17 May 1997 | 30 June 1960 | Independence from Belgium | ||||
| 15 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 27 June 1977 | Independence from France | |||||
| 18 June 1953 | Egyptian revolution of 1952, Egyptian monarchy overthrown in a military coup, republic declared | 28 February 1922 | The UK ends its protectorate, granting independence to Egypt | 1925 | The eastern borders of Libya and British Egypt are changed to their present boundaries. | |
| 12 October 1968 | Independence from Spain | |||||
| 27 April 1993 | Independence from Ethiopia declared | 1 April 2002 | Badme ruled to be Eritrean by the Eritrea–Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC after the Eritrean–Ethiopian War). Contested by Ethiopia | |||
| 8 February 2006 | Constitution of Eswatini | 6 September 1968 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||
| 21 August 1995 | 1995 Constitution of Ethiopia | 900 | Zagwe dynasty | 1 April 2002 | Badme ruled to be Eritrean by the Eritrea–Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC after the Eritrean–Ethiopian War). Contested by Ethiopia | |
| 17 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 18 February 1965 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 6 March 1957 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 13 December 1956 | Union of British Togoland with Gold Coast | |||
| 2 October 1958 | Independence from France | |||||
| 24 September 1973 | Independence from Portugal declared | |||||
| 10 September 1974 | Independence from Portugal recognized | |||||
| 4 December 1958 | Autonomous republic within French Community | |||||
| 7 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 12 December 1963 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 4 October 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 12 March 1868 | Area that is now Lesotho placed under British rule | |||
| 26 July 1847 | Independence from American Colonization Society | 6 January 1986 | Current constitution came into effect | |||
| 4 August 2014 | House of Representatives takes power.[note 2] | 24 December 1951 | Independence from UN Trusteeship (British and French administration after Italian governance ends in 1947) | 13 February 1984 | Aouzou Strip awarded to Chad. | |
| 14 October 1958 | The Malagasy Republic was created as autonomous state within French Community | |||||
| 26 June 1960 | France recognizes Madagascar's independence | |||||
| 6 July 1964 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 25 November 1958 | French Sudan gains autonomy | 8 April 1960 | Senegal secedes from Mali Federation | |||
| 22 September 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 28 November 1960 | Independence from France | 11 August 1979 | Mauritania withdraws from Tiris al-Gharbiyya (part of Western Sahara) | |||
| 12 March 1968 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 1965 | Separation of Chagos Archipelago | |||
| 18 November 1955 | Protectorate Abolished | 788, AD | Enthronement of Idris I in Volubilis | 6 November 1975 | Green March | |
| 27 October 1994 | Mozambique holds its first multiparty election since the Civil War | 25 June 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |||
| 21 March 1990 | Independence from South African rule | 1 March 1997 | Walvis Bay integrated into Namibia | |||
| 4 December 1958 | Autonomy within French Community | |||||
| 3 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 1 October 1960 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 15 January 1970 | Biafra re-integrated into Nigeria | |||
| 1 June 1961 | Northern Cameroons integrated in Nigeria | |||||
| 1 July 1962 | Independence from Belgium | |||||
| 12 July 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |||||
| 20 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 29 June 1976 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 27 April 1961 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 20 August 2012 | Federal Government of Somalia established.[note 3] | 1 July 1960 | Union of Trust Territory of Somalia (former Italian Somaliland) and State of Somaliland (formerly British Somaliland) | 18 May 1991 (disputed) | Somaliland declares independence, but is not recognized by any UN state. | |
| 31 May 1961 | Republic declared | 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster, which establishes a status of legislative equality between the self-governing dominion of the Union of South Africa and the UK | 21 March 1990 | De facto: South West Africa declares independence, forming Namibia | |
| 4 February 1997 | The post-Apartheid Constitution of South Africa comes into effect | 31 May 1910 | Creation of the autonomous Union of South Africa from the previously separate colonies of the Cape, Natal, Transvaal and Orange River | 27 April 1994 | De jure: Reincorporation of the nominally independent but unrecognised bantustans into post-apartheid South Africa | |
| 9 July 2011 | 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum | 9 July 2011 | Separation of Southern Sudan from Sudan | |||
| 15 April 2010 | First democratic election since the Second Sudanese Civil War | 1 January 1956 | Independence from Egyptian and British joint rule | 9 July 2011 | South Sudan secedes from Sudan | |
| 1 July 1991 | Amendment to Constitution of Tanzania ends status as one-party state | 9 December 1961 | Independence of Tanganyika from the United Kingdom | 26 April 1964 | Merger of Zanzibar with Tanganyika to form Tanzania | |
| 30 August 1958 | Autonomy within French Union | |||||
| 27 April 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 25 July 2022 | 2022 Constitution of Tunisia | 20 March 1956 | Independence from France | |||
| 1 March 1962 | Self-government granted | |||||
| 9 October 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 24 October 1964 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 22 December 1987 | Robert Mugabe revises the Constitution of Zimbabwe to create an executive presidency.[note 4] | 11 November 1965 | Unilateral declaration of independence by Southern Rhodesia | 1901 | BSAC separates North-Eastern Rhodesia from Southern Rhodesia | |
| 18 April 1980 | Recognized independence from the United Kingdom as Zimbabwe |
Americas[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 November 1981 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 10 December 1983 | The current Constitution of Argentina enters in force | 25 May 1810 | May Revolution installs first local government | 18 October 1884 | Conquest of the Desert | |
| 9 July 1816 | Argentine Declaration of Independence from Spain. | |||||
| 7 January 1964 | Internal self-governance granted | |||||
| 10 July 1973 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 30 November 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 1 January 1964 | Self-governing colony | 1859 | Treaty establishes border between British Honduras and Guatemala | |||
| 21 September 1981 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 25 January 2009 | Constitution of Bolivia | 6 August 1825 | Bolivian War of Independence from Spain. | 11 November 1903 | Treaty of Petrópolis with Brazil whereby Bolivia gained lands in Mato Grosso in exchange for the territory of Acre | |
| 21 July 1844 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 5 October 1988 | Constitution of Brazil established as the third Federative Republic | 7 September 1822 | Independence from the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves declared | 11 November 1903 | Signing of the Treaty of Petrópolis with Bolivia whereby Brazil was given the territory of Acre in exchange for lands in Mato Grosso | |
| 29 August 1825 | Independence recognized by Portugal | |||||
| 15 November 1889 | Proclamation of the Federal Republic | |||||
| 1 July 1867 | Granted nominal independence (Dominion status), establishing as a federation | 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster | 1 April 1999 | Nunavut Territory created as per native land claims act from two thirds of the area of Northwest Territories. | |
| 17 April 1982 | Constitution Act, 1982 established | |||||
| 17 August 1989 | Amendment to the Constitution of Chile ends the military dictatorship | 18 September 1810 | First Government Junta | 3 July 1929 | Chile awarded Arica district in Treaty of Lima | |
| 12 February 1818 | Chilean Declaration of Independence from Spain | |||||
| 25 April 1844 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 4 July 1991 | Colombian Constitution of 1991 established as a presidential republic. | 20 July 1810 | Colombia declares independence from Spain. | 4 July 1991 | The Sovereign territory was organized under the National Constituent Assembly. | |
| 17 December 1819 | Colombia merged with Venezuela, Panama, and Ecuador. | |||||
| 19 November 1831 | Gran Colombia dissolved creating a pact with Panama as the Republic of New Granada. | |||||
| 22 May 1858 | The Republic of New Granada was replaced to the Granadine Confederation under the 1858 constitution. | |||||
| 8 May 1863 | The Granadine Confederation was replaced to the United States of Colombia under the constitutional change of 1864. | |||||
| 30 January 1881 | Declaration of Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 8 August 1886 | Establishment of the current sovereignty of Colombia as a republic. | |||||
| 7 November 1949 | Constitution of Costa Rica | 15 September 1821 | Costa Rica declared independence from Spain | 25 July 1824 | Partido de Nicoya | |
| 15 November 1838 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America | |||||
| 10 May 1850 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 1 January 1959 | Cuban Revolution | 10 October 1898 | Several wars were declared against Spain from 1868 to 1898, ending with the military support of USA to the Cuban Revolution. | |||
| 10 December 1898 | Spain loses the war against the United States and the military occupation of Cuba by the U.S. begins. | |||||
| 20 May 1902 | United States military occupation ends[2] | |||||
| 3 November 1978 | Constitution of Dominica | 27 February 1967 | Became an associated state of the United Kingdom | |||
| 3 November 1978 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 28 November 1966 | Civilian constitution of the Dominican Republic following the Dominican Civil War.[note 5] | 27 February 1844 | The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti | 9 May 1936 | Haiti and the Dominican Republic sign a treaty setting a definitive border. | |
| 14 October 1874 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 28 September 2008 | Constitution of Ecuador established. | 10 August 1809 | First declaration of Independence from Spain | 26 February 1946 | Rio Protocol ends border dispute with Peru | |
| 24 May 1822 | Second declaration of independence from Spain of Gran Colombia, of which Ecuador is a part of | |||||
| 13 May 1830 | Dissolution of Gran Colombia | |||||
| 16 February 1840 | Declaration of Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 16 December 1983 | Constitution of El Salvador established as the third Unitary presidential republic | 15 September 1821 | El Salvador becomes independent from Spain, and 4 months later becomes province in First Mexican Empire | |||
| 1 July 1823 | El Salvador becomes a state of Federal Republic of Central America from the First Mexican Empire | |||||
| 2 February 1841 | Dissolution of the Federal Republic of Central America, El Salvador becomes independent nation | |||||
| 18 February 1841 | El Salvador was internationally recognized. | |||||
| 24 June 1865 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 30 September 1978 | Paul Scoon Takes power after the US Invasion Which Ousted the PRG | 27 February 1967 | Associated state of the United Kingdom | |||
| 7 February 1974 | Full independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 31 May 1985 | Constitution of Guatemala established | 15 September 1821 | Guatemala becomes state in Federal Republic of Central America, which declared independence from Spain | |||
| 17 April 1839 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America declared | |||||
| 29 May 1863 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 26 May 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| March 1987 | Constitution of 1987 (superseded) | 1 January 1804 | The French colony Saint-Domingue gains independence as Haiti | 27 February 1844 | The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti | |
| 9 May 1936 | Haiti and the Dominican Republic sign a treaty setting a definitive border. | |||||
| 11 January 1982 | Constitution of Honduras. | 15 September 1821 | Honduras becomes state in Federal Republic of Central America, which declared independence from Spain | 1 September 1972 | Swan Islands returned to Honduras from United States occupation | |
| 26 October 1838 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America | |||||
| 17 November 1894 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 6 August 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 7 February 1917 | Constitution of Mexico | 16 September 1810 | Independence from Spain declared | 30 December 1853 | Gadsden Purchase | |
| 27 September 1821 | Declaration of Independence of the Mexican Empire | |||||
| 28 December 1836 | Declaration of Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 9 January 1987 | Constitution of Nicaragua established | 15 September 1821 | Nicaragua becomes state in Federal Republic of Central America, which declared independence from Spain | |||
| 5 November 1838 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America | |||||
| 24 July 1850 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 11 October 1972 | Constitution of Panama established | 3 November 1903 | Independence from Colombia | 31 December 1999 | Sovereignty of Panama Canal Zone transferred to Panama from the United States | |
| 10 May 1904 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 20 June 1992 | Democratic Constitution of Paraguay | 14 May 1811 | Independence from Spain declared | 1938 | Paraguay awarded a large portion of the Gran Chaco as a result of the Chaco War | |
| 10 September 1880 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 31 December 1993 | Constitution of Peru established | 28 July 1821 | Independence from Spain declared | 26 February 1942 | Rio Protocol ends border dispute with Ecuador | |
| 14 August 1879 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 27 February 1967 | Associated state of the United Kingdom | 19 December 1980 | Anguilla separated from Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla | |||
| 19 September 1983 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 27 February 1967 | Associated statehood | |||||
| 22 February 1979 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 27 October 1969 | Associated statehood | |||||
| 27 October 1979 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 15 December 1954 | Self-government granted | |||||
| 25 November 1975 | Independence from Netherlands | |||||
| 31 August 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 4 March 1789 | United States Constitution enters into force, replacing the previous Articles of Confederation and creating a new system of government | 4 July 1776 | Declaration of Independence from Great Britain is adopted by the United States Congress | 21 August 1959 | United States Territory: Territory of Hawaii joins the United States as the State of Hawaii | |
| 3 September 1783 | Independence from Great Britain recognized | 7 September 1981 | Insular area: The United States cedes Serrana Bank and Roncador Bank to the Republic of Colombia as a result of a treaty signed in 1972 | |||
| 8 December 1996 | 1996 Uruguayan constitutional referendum | 25 August 1825 | Independence from Empire of Brazil declared, joined in union with United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (current Argentina). | |||
| 27 August 1828 | Treaty of Montevideo signed, recognizing Uruguay's independence by Brazil | |||||
| 19 July 1870 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 20 December 1999 | New Constitution of Venezuela establishes the Bolivarian Fifth Republic | 19 April 1810[3] | Independence from Spain declared | 3 October 1899 | Tribunal of Arbitration awards most of disputed territory to British Guyana. | |
| 13 January 1830 | Dissolution of Gran Colombia | |||||
| 30 March 1845 | Independence recognized by Spain |
Asia[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 August 2021 | Fall of Kabul reestablished the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. | 1747 | Durrani Empire | |||
| 21 September 1991 | 2015 Armenian constitutional referendum creates a parliamentary republic | 189 BC | Kingdom of Armenia under Artaxiad dynasty[4] | 5 December 1936 | Establishment of the Armenian SSR | |
| 880 | Evolving as a feudal kingdom in the ninth century, Armenia experienced a brief cultural, political and economic renewal under the Bagratuni dynasty. | |||||
| 21 September 1991 | Independence recognized by the Soviet Union | |||||
| 14 February 2002 | 2002 Constitution of Bahrain | 15 August 1971 | End of treaties with the United Kingdom | 1 July 1521 | Portuguese conquest of current territory | |
| 4 November 1972 | De jure: Constitution of Bangladesh | 26 March 1971 | Independence from Pakistan declared | 31 July 2015 | India and Bangladesh exchange enclaves | |
| February 27, 1991 | De facto: First general election since restoration of parliamentary democracy. | |||||
| 24 March 2008 | First elections to the National Assembly | 1885 | Ugyen Wangchuck ends period of civil war and unites Bhutan | 11 November 1865 | Treaty of Sinchula | |
| 29 September 1959 | De jure: Constitution of Brunei | 1 January 1984 | Brunei regains its independence after an agreement with the British on 4 January 1979 | 18 August 1841 | Kingdom of Sarawak founded | |
| 12 December 1962 | De facto: Martial law declared during the Brunei Revolt, suspending democratic elections indefinitely. | |||||
| 21 September 1993 | Constitution of Cambodia | 802 | Khmer Empire[5] | |||
| 9 November 1953 | France grants Cambodia independence | |||||
| 26 September 1989 | Becomes free from Vietnamese occupation; it gets back its name instead of the People's Republic of Kampuchea | |||||
| 1 January 1912 | A republic was formally established following the Xinhai Revolution, | 1600 BC | The Shang dynasty is the earliest dynasty of traditional Chinese history firmly supported by archaeological evidence | 20 January 1955 | Loss of Yijiangshan Islands, resulting in the current free area of the Republic of China | |
| 25 December 1947 | The Republic of China adopted its constitution during the National Assembly on 25 December 1947, with further revisions and amendments since 1991 | |||||
| 1 October 1949 | Proclamation of the People's Republic of China in Beijing | 6 October 2011 | Tajikistan ceded 1158 square kilometers of land to China | |||
| 4 December 1982 | The People's Republic of China adopted its constitution during the 5th National People's Congress on 4 December 1982, with further revisions about every five years | |||||
| 26 January 1950 | De jure: Constitution of India | 15 August 1947 | Independence from the British Empire | 31 July 2015 | India and Bangladesh exchange exclaves | |
| 2500 BC | Indus Valley Civilisation was the earliest settlement in India | |||||
| 11 February 1979 | Iranian Revolution ended the monarchy and establishes the Islamic Republic on 11 February 1979 | 2600 BC | Founded by the Elamite | 10 February 1828 | Signing of the Treaty of Turkmenchay, whereby the territories that now constitute Armenia, Azerbaijan (the remaining part which hadn't been lost by the Treaty of Gulistan (1813)), and Iğdır are ceded to Russia | |
| 14 August 1971 | Bahrain's independence from Iran | |||||
| 30 November 1971 | Recapture of Abu Musa and the Greater and Lesser Tunbs | |||||
| 3 December 1979 | the new constitution was approved according to the results of the constitutional referendum of 2 and 3 December 1979 | |||||
| 15 October 2005 | Constitution of Iraq following the Iraq War[note 6] | 762 | The Abbasid Caliphate built the city of Baghdad along the Tigris in the 8th century as its capital, and the city became the leading metropolis of the Arab and Muslim world for five centuries | 28 February 1991 | Kuwait liberated.[note 6] | |
| 3 October 1932 | Kingdom of Iraq | |||||
| 14 May 1948 | Democratic state of Israel. Reading of the Declaration of Independence of Israel | 14 May 1948 | Democratic state of Israel. Reading of the Declaration of Independence of Israel | 14 December 1981 | The Golan Heights Law annexes the Golan Heights, conquered from Syria in the Six-day war to Israel proper; they were administered as a militarily-occupied territory until that point. | |
| 12 September 2005 | The Completion of Israel's unilateral disengagement from the Gaza Strip | |||||
| 22 December 1885 | On December 22, 1885, "Daijo-kan No. 69" were established, and the Cabinet system was established in place of the Daijo-kan system. | 11 February 660 BC | Traditional founding date of the imperial dynasty by Emperor Jimmu. | 15 May 1972 | Return of the Ryukyu Islands to Japan and abolition of the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands | |
| 1 January 1952 | Constitution of Jordan | 25 May 1946 | End of the British Mandate for Palestine | 26 October 1997 | Signing of the Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace, whereby most of the disputed 400 square-kilometer area in the Arabah was handed back to Jordan | |
| 12 June 2011 | The Cabinet of Jordan is made an elected body[6] | |||||
| 9 September 1948 | Kim Il-sung declared Premier of North Korea, establishing the still-ruling Kim dynasty. Independence declared from the Soviet Union. | 918 | The Goryeo Dynasty unified the Korean states, the exonym Korea originated from the word Goryeo. | 12 October 1962 | Signing of the Sino–Korean Border Agreement with the People's Republic of China | |
| 25 December 1972 | The Constitution of North Korea replaced Communism with Juche as North Korea's governing philosophy.[note 7] | |||||
| 15 August 1948 | First Republic of Korea established, Independence declared from the United States | 27 July 1953 | Cease-fire in the Korean War creates the northern border along the Military Demarcation Line | |||
| 29 October 1987 | Current Sixth Republic of South Korea founded, ending military rule | |||||
| 11 November 1962 | Constitution of Kuwait | 1752 | Establishment of the Sheikhdom of Kuwait | 18 December 1969 | Formal division of Saudi-Kuwaiti neutral zone | |
| 10 June 2010 | Constitution of Kyrgyzstan introduces parliamentary system. | 31 August 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union[7] | 5 December 1936 | Establishment of the Kirghiz SSR | |
| 2 December 1975 | Lao PDR formed | 22 October 1953 | Independence from France | |||
| 23 May 1926 | Lebanese Republic formed | 26 November 1941 | Independence from France declared | 1 September 1920 | France establishes State of Greater Lebanon with current boundaries | |
| 22 November 1943 | Independence from France recognized | |||||
| 16 September 1963 | Formation of Malaysia[8][9] | 31 August 1957 | Malayan Independence[10] from the United Kingdom was declared in Dataran Merdeka (Independence Square) | 9 August 1965 | Singapore expelled from the Federation of Malaysia[11][12][13] | |
| 16 September 1963 | Malaysia was formed by the federation of North Borneo, Sarawak and Singapore with the existing States of the Federation of Malaya.[8][14] | |||||
| 11 November 1968 | Declaration of Republic | 26 July 1965 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||
| 12 February 1992 | Constitution of Mongolia declares the country a parliamentary democracy. | 1206 | Mongol Empire formed | |||
| 29 December 1911 | Proclamation of Mongolian independence from Manchu's Qing dynasty | |||||
| 1 February 2021 | The SAC with help from the Tatmadaw overthrows the elected government | 849 | Early Pagan Kingdom formed[15] | |||
| 4 January 1948 | Myanmar (Burma) declares independence from the British Empire | 1956 | Signing of border treaty with the People's Republic of China | |||
| 28 May 2008 | Formation of Republic | 25 September 1768 | Nepali unification | 2 December 1815 | Sugauli Treaty ends the Gurkha War | |
| 10 June 1749 | Beginning of the Al Said dynasty, current absolute monarchical line of Oman. | 26 January 1650 | Expulsion of the Portuguese | 8 December 1958 | Gwadar sold to Pakistan | |
| 1996 | Basic Law of Oman | |||||
| 14 August 1973 | Constitution of Pakistan | 14 August 1947 | Establishment from the Indian Empire after Independence from the British Empire and Partition of India | |||
| 4 May 1994 | Agreement on the Gaza Strip and the Jericho Area | 15 November 1988 | Palestinian Declaration of Independence | 15 June 2007 | Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip | |
| 2 February 1987 | The current form of government was established in 1987, as a compromise between different versions of the previous constitutions and patterned after the 1935 Commonwealth constitution | 12 June 1898 | The evolving revolutionary movement in the Philippines declares itself independent from the Spanish Empire.[16][17][18] Spain regarded this as an expression of continued rebellion.[note 8] This difference in viewpoints was not resolved. | 2012[19][20] | In 2012, the United Nations approved a 2009 claim by the Philippines to the Benham Rise.[20] | |
| 10 December 1898 | Spain, still sovereign,[note 9] cedes the Philippines to the United States via the Treaty of Paris (1898).[21] | |||||
| 4 July 1946 | The United States recognizes Philippine independence under the provisions of the Treaty of Manila (1946). The 1935 Constitution remained in effect until 1973, when the Marcos regime promulgated a newer one, in turn replaced by the present 1987 Constitution. | |||||
| 8 September 1971 | Influence from Britain concluded | 18 December 1878 | Independence from the Ottoman Empire | 4 November 2021 | Acquisition of the rest of Khawr al Udayd[citation needed] | |
| 23 September 1932 | Regions of al-Hasa, Qatif, Nejd and Hejaz unified to become Saudi Arabia | 13 January 1902 | Establishment of the Third Saudi State | 4 November 2021 | Fixed border territory with Qatar | |
| 9 August 1965[11] | Singapore ceased to be a state of Malaysia | 3 June 1959 | Self-government under the United Kingdom | 9 August 1965 | Establishment of Singapore as an independent sovereign state[13] | |
| 9 August 1965 | separate from and independent of Malaysia[11][12] | |||||
| 22 May 1972 | Constitution of Sri Lanka | 4 February 1948 | Independence from United Kingdom | 14 February 1815 | De jure: The Kandyan Kingdom is annexed by British Ceylon | |
| 18 May 2009 | De facto: The Sri Lankan government regains control of the whole island following the end of the Sri Lankan Civil War. | |||||
| 27 February 2012 | Constitution of Syria[note 10] | 28 September 1961 | End of the United Arab Republic | 8 November 1941 | De jure: Lebanon declares independence from the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon[note 10] | |
| 10 June 1967 | De facto: Israel conquers the Golan Heights from Syria during the Six-day War | |||||
| 9 September 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union[7] | 5 December 1929 | Establishment of the Tajik SSR | |||
| 6 April 2017 | Constitution of the Kingdom of Thailand 2017 | 6 November 1767 | Salvage Independence by King Taksin the Great consist of expulsion of Burmese out of former capital (Through Taksin's reunification of Siam on October-6 November 1767) and Establish a New kingdom together with reunification of Thailand | 10 March 1909 | Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909 | |
| 20 May 2002 | Constitution of East Timor | 20 May 2002 | Independence was recognized by the international community following the UN-sponsored act of self-determination of 1999 | 1914 | The borders of Portuguese Timor are agreed.[22] | |
| 28 September 2008 | Constitution of Turkmenistan | 27 October 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union[7] | 7 August 1921 | Establishment of the Turkmen SSR | |
| 2 December 1971 | End of treaty relationship with the United Kingdom | 11 February 1972 | Ras al-Khaimah joins the UAE | |||
| 31 August 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union declared[7] | 24 October 1924 | Establishment of the Uzbek SSR | |||
| 31 December 1959 | North Vietnam declared a socialist republic | 2 September 1945 | Withdrawal of the Japanese after World War II | 2 July 1976 | Reunification of North Vietnam and South Vietnam as Socialist Republic of Vietnam | |
| 1 January 2014 | Current Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam | |||||
| 22 May 1990 | Unification of North Yemen and South Yemen | 1597 | Qasimid State/Zaidi Imamate[23] | |||
| 1 November 1918 | North Yemen independence from the Ottoman Empire | 21 September 2014 | Houthis seized control of the bulk of the former North Yemen territory and its capital Sana'a | |||
| 30 November 1967 | South Yemen independence from the United Kingdom | 26 April 2020 | Southern Transitional Council declares self-governance of Socotra and some areas controlled by the former PDR Yemen. |
- Table notes
- ^ Taiwan: For some clarification and more detail including the sovereignty status of the Republic of China, see the following articles: Cross-Strait relations, One-China policy and Political status of Taiwan.
- ^ Palestinian National Authority: For some clarification and more detail, see History of the State of Palestine.
- ^ Philippines: For some clarification and more detail, see Timeline of Philippine Sovereignty and Sovereignty of the Philippines.
Europe[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 November 1989 | People's Republic of Bulgaria was replaced by the Republic of Bulgaria | 681 on territories of the Eastern Roman Empire | (Danubian) Bulgaria | 28 October 1944 | Under the 1944 Armistice with the Allies, Bulgaria renounces the 1941 annexation of Vardar Macedonia from Yugoslavia and Eastern Macedonia and Western Thrace from Greece. Formally confirmed on 10 February 1947 by Paris Peace Treaties. | |
| 1185 | Second Bulgarian Empire formed | |||||
| 13 July 1878 | Autonomy within Ottoman Empire recognized internationally by the Treaty of Berlin | |||||
| 22 September 1908 | Independence from Ottoman Empire | |||||
| 28 April 1993 | Current Constitution of Andorra entered force | 1278 | Independence from Aragon | 28 August 2001 | The Andorra–France border is adjusted to allow Andorra to construct the Envalira Tunnel access bridge | |
| 12 November 1918 | Declaration of the Republic of German-Austria | 17 September 1156 | Privilegium Minus: Sovereignty from Duchy of Bavaria as a Duchy of the Holy Roman Empire | 14 December 1921 | City of Sopron, and 8 other towns moved to Hungary after plebiscite | |
| 11 August 1804 | Proclamation of the Austrian Empire | |||||
| 27 April 1945 | Restoration of the Republic of Austria | |||||
| 28 November 1996 | Constitutional amendment abolishes the Supreme Soviet and establishes the National Assembly | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | |||
| 27 July 1990 | Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1945 | Western border with Poland: modification of the Curzon Line determined at the 1945 Yalta Conference | |||
| 25 August 1991 | Independence recognized by Soviet Union[7] | |||||
| 21 July 1831 | King Leopold I of Belgium swears allegiance to the constitution making the country a constitutional monarchy | 4 October 1830 | Independence was proclaimed by the provisonial government | 28 June 1919 | Belgian proper: Treaty of Versailles and annexation of the East Cantons | |
| 1 July 1962 | Belgian colonial empire: Ruanda-Urundi declares independence and split within two countries: Rwanda and Burundi. | |||||
| 3 March 1992 | 3 March 1992 | Independence declared from the SFR Yugoslavia[note 11] | 25 November 1943 | Establishment of SR Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia | ||
| 29 April 1991 | Socialist People's Republic of Albania was replaced by the Republic of Albania. | 1190 c. | Principality of Arbër was established by archon Progon. | 1945 | Occupied Kosovo, west Macedonia and border region of Montenegro returned to Yugoslavia | |
| 28 November 1912 | Declaration of independence from Ottoman Empire | |||||
| 28 November 1944 | Albanian state re-established after Italian/German occupation | |||||
| 8 October 1991 | Independence from SFR Yugoslavia[note 11] | 879 | Duke Branimir was recognized as an independent ruler of the Duchy of Croatia by Pope John VIII.[24][25][26][27][28] | 10 February 1947 | Annexation of most of Istria to SR Croatia as a result of signing the 1947 Paris Peace Treaties | |
| 925 | Formation of Kingdom of Croatia by King Tomislav | |||||
| 1 January 1993 | Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, creating Czech Republic and Slovakia | October 1918 | Creation of Czechoslovakia | |||
| 5 June 1953 | Constitutional Act of Denmark | 965 | Harald Bluetooth unifies Denmark | 15 June 1920 | Denmark proper: Sønderjylland was recovered from Germany.[note 12] | |
| 24 February 1918 | Estonian Declaration of Independence, whereby a republic was declared[Europe 1] | 20 August 1991 | Independence (from the Soviet Union) reasserted, end of occupation[note 13] | 1 January 1945 | De facto: Eastern coast of Narva river and most of Petseri County were transferred to Russian SFSR | |
| 29 March 1809 | Diet of Porvoo, birth of Finland as an autonomous state entity within Russian Empire | 6 December 1917 | Independence from Russian Empire declared | 26 January 1956 | Porkkala returned from Soviet control | |
| 3 January 1918 | Independence from Russia recognized by the highest Soviet executive body, VTsIK | |||||
| 4 October 1958 | Establishment of the current semi-presidential system known as the Fifth Republic | 481 then 843 | First creation with (Clovis), king of the Franks. Then creation of the Kingdom of France (West Francia), Treaty of Verdun | 10 February 1947 | Metropolitan France: Annexation of Tende, La Brigue and other villages formerly in Italy.[note 14][note 15] | |
| 22 September 1792 | French Republic founded. | 30 July 1980 | Overseas France: The New Hebrides Condominium declares independence and becomes Vanuatu. | |||
| 23 May 1949 | The Basic Law of Germany comes into effect. | 843 then 962 | Creation of East Francia East Francia becomes the Holy Roman Empire (with the Kingdom of Germany as a main part of the empire) | 3 October 1990 | Reunification of West Germany and East Germany | |
| 1815 | German Confederation founded | |||||
| 18 January 1871 | German Empire founded | |||||
| 1954 | German Democratic Republic (commonly referred to at the time as East Germany) declared fully sovereign | |||||
| 5 May 1955 | Federal Republic of Germany (commonly referred to at the time as West Germany) declared fully sovereign | |||||
| 15 May 1991 | Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany ends the Four Power occupation. | |||||
| 11 June 1975 | Third Hellenic Republic | 600 BC | Peloponnesian League / Spartan Alliance[30] | 10 February 1947 | Peace treaty with Italy awards the Dodecanese to Greece | |
| 478 BC | Delian League / Athenian Empire[31] | |||||
| 338 BC | League of Corinth / | |||||
| 3 February 1830 | Modern Greece Independence recognized by the London Protocol as Kingdom of Greece.[33] | |||||
| 23 October 1989 | People's Republic of Hungary was replaced by the Republic of Hungary. | 895 | Principality of Hungary formed | 10 February 1947 | With the Paris Peace Treaty, Hungary loses all territories that were regained with the First and Second Vienna Awards and during World War II, thus it returns to the 1937 borders (except for three villages in the northwest given to Czechoslovakia). | |
| 1 January 2012 | The Basic Law of Hungary comes into effect. | 1000 | Formation of the Kingdom of Hungary by Stephen I of Hungary. | |||
| 930 | The Icelandic Commonwealth established and first meeting held of the Althingi (Parliament). | 1 December 1918 | Iceland becomes sovereign and independent from Denmark as the Kingdom of Iceland but retains a personal union with the King of Denmark. | 1 September 1972 | No territorial changes on land have taken place, however the expansion of the Exclusive Economic Zone was such an important change in territory for Iceland that it merits a special inclusion here. | |
| 1 July 1845 | The Althingi resumes meeting after hiatus since 1799. | 17 June 1944 | Kingdom of Iceland becomes a Republic. | |||
| 21 January 1919 | Elected Irish Parliament Dáil Éireann unilaterally declares Ireland's independence from the United Kingdom | 1542 | Foundation of the Kingdom of Ireland | |||
| 6 December 1922 | Irish Free State secedes from United Kingdom by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty but remains a dominion of the British Empire | 8 December 1922 | De facto: Northern Ireland secedes from the Irish Free State and rejoins the United Kingdom in accordance with the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922 | |||
| 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster confers legislative independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 29 December 1937 | Constitution of Ireland establishes the roles of Taoiseach and President, and replaces the Irish Free State (or Saorstat Eireann in Irish language) with a new state named Ireland (or Éire in Irish language). | 18 April 1949 | Republic of Ireland Act 1948 terminates the functions of the British King in Ireland's diplomatic relations; domestic United Kingdom law purports that Ireland was one of the King's dominions until this date; Irish law does not accept this interpretation. | 2 December 1999 | De jure: Amendment to the Irish constitution removes irredentist claims to Northern Ireland.[note 16] | |
| 2 June 1946 | Italian Republic founded. | 1720 | Sovereignty of the Kingdom of Sardinia, existing since 1324 as part of the Spanish Empire first and subsequently of the Holy Roman Empire. | 1 January 1948 | The Peace treaty with Italy officially determines the boundaries of the Republic of Italy. The Italian Constitution of 1948 implements it at articles 10 and 117. | |
| 17 March 1861 | Italian unification | |||||
| 25 April 1945 | Disestablishment of the German-backed Italian Social Republic, whereby the unity and independence of the Italian state was restored | |||||
| 17 February 2008 | Kosovo Republic founded | 2008 | Kosovan-Serbian War | 2008 | Kosovo War | |
| 7 November 1922 | Constitution of Latvia enforced[Europe 1] | 4 May 1990 | Independence (from Soviet Union) reasserted[note 13] | 1944 | Abrene district ceded to Russian SFSR (modern Russia) | |
| 16 March 2003 | The 2003 Liechtenstein constitutional referendum increases the Prince's powers and makes the country an absolute monarchy[34] | 19 October 1813 | Dissolution of the Confederation of the Rhine | 23 January 1719 | Purchase of Vaduz | |
| 11 March 1990 | Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania independence (from the Soviet Union) reasserted, end of occupation[note 13][Europe 1] | 16 February 1918 | Independence declared from Germany and Russia | 27 October 1939 and 3 August 1940 | Western part (approximately half) of Vilnius Region ceded to Lithuania | |
| 23 November 1890 | Separates from union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, becomes Grand Duchy in its own right | 1945 | End of German occupation during World War II | 19 April 1839 | Partition of Luxembourg under the Treaty of London | |
| 13 December 1974 | The State of Malta became a republic | 21 September 1964 | Independence from United Kingdom | 20 August 1801 | Gozo rejoined Malta | |
| 27 August 1997 | Constitution of Moldova (1997) | 27 August 1991 | Independence from Soviet Union[7] | 2 August 1940 | De jure: Moldavian SSR formed | |
| 2 September 1990 | De facto: Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic declares independence. The government is not recognized by any UN member, but has de facto control over the Transnistria region. | |||||
| 17 December 1962 | Amendment to Constitution of Monaco curtails the power of the prince and establishes the modern National Council | 1297 | François Grimaldi captures the fortress atop the Rock of Monaco. | 1848 | Secession of Menton and Roquebrune-Cap-Martin. | |
| 22 October 2007 | Constitution of Montenegro | 3 June 2006 | Declaration of independence from Serbia and Montenegro. | |||
| 24 August 1815 | Adoption of the constitution of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. | 26 July 1581 | Plakkaat van Verlatinghe signed, independence from Spain | 16 March 1839 | European Netherlands: The United Kingdom of the Netherlands divided under the Treaty of London (1839). | |
| 15 December 1954 | Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands signed | 5 May 1945 | Surrender of Nazi forces occupying the Netherlands | 25 November 1975 | Kingdom of the Netherlands: Suriname declares independence. | |
(until 2019 Republic of Macedonia) | 17 November 1991 | Constitution of North Macedonia | 8 September 1991 | After a referendum, the Socialist Republic of Macedonia declared independence from Yugoslavia[note 11] | 2 August 1944 | Establishment of SR Macedonia |
| 1814 | Constitution of Norway | 872 | King Harald I of Norway unifies the Petty kingdoms of Norway. | 27 February 1930 | Jan Mayen was made part of the Kingdom of Norway. | |
| 1814 | Dissolution of the union between Norway and Denmark. | |||||
| 7 June 1905 | Dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden. | |||||
| 8 May 1945 | German occupying forces surrender. | |||||
| 4 June 1989 | The first partially free Parliament's vote after 45-year-long Soviet domination | 966 | Adoption of Christianity by the first historically documented Polish ruler Mieszko I. | 15 February 1951 | Polish-Soviet border adjustment treaty | |
| 11 November 1918 | Poland regains its independence. | |||||
| 2 April 1976 | Constitution of Portugal | 5 October 1143 | Formation of Kingdom of Portugal by Treaty of Zamora signing. | 6 June 1801 | Continental Portugal: Spain occupies the present day border town of Olivença since the War of the Oranges. | |
| 20 December 1999 | Portuguese Overseas: De facto: Portuguese Macau transferred to the People's Republic of China | |||||
| 20 May 2002 | Portuguese Overseas: De jure: Portuguese Timor, occupied by Indonesia since 1975, officially dissolved to form the independent state of East Timor.[note 17] | |||||
| 22 December 1989 | Romanian Revolution of 1989 | 24 January 1859 | Autonomous Principality of Romania founded; becomes kingdom in 1866 and achieved independence 1878 Ottoman Empire | 10 February 1947 | Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina | |
| 13 July 1878 | International recognition by the Treaty of Berlin. | |||||
| 1600 | Constitution of San Marino | 3 September 301 | Independence from Roman Empire | 1463 | Added Fiorentino, Montegiardino, Serravalle, and Faetano | |
| 27 April 1992 | Independence from SFR Yugoslavia, forming the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.[note 11] | 780 | 8th century-Creation of the Principality of Serbia in the Southeastern Europe. | 17 February 2008 (disputed)[35] | The region of Kosovo declared independence unilaterally on 17 February 2008, and is recognized by 97 UN states. Serbia recognizes the government of Kosovo but claims its territory as an Autonomous Province. | |
| 8 June 2006 | Republic of Serbia declared legal successor to Serbia and Montenegro, ending the process of the dissolution of Yugoslavia. | 13 July 1878 | International recognition by the Treaty of Berlin. | |||
| 1 January 1993 | Dissolution of Czechoslovakia | October 1918 | Creation of Czechoslovakia | |||
| 13 December 1991 | Constitution of Slovenia | 25 June 1991 | Declaration of independence from Yugoslavia[note 11] | 19 February 1945 | Formation of SR Slovenia | |
| 6 December 1978 | Spanish Constitution | 1479 | Dinastical unification of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon by the Catholic Monarchs. The governments, institutions, and legal traditions of each kingdom remained independent of each other; alien laws (Leyes de extranjeria) determined that the national of one kingdom was a foreigner in the other Crowns/States.[36] | 26 February 1976 | Spanish Sahara is lost following the Madrid Accords. | |
| 1707~1716 | De jure by the Nueva Planta decrees | |||||
| 1831 | Dissolution of crowns and kingdoms and creation de jure, of the unified Kingdom of Spain. | |||||
| 1 January 1974 | Instrument of Government | 970 (Or prior) | Eric the Victorious, the first king of Sweden about whom anything definite is known, becomes king. | 29 March 1809 | Loss of Finland to Imperial Russia. | |
| 6 June 1523 | Gustav Vasa elected King of Sweden and marking a definite secession from the Kalmar Union. | |||||
| 12 November 1848 | Foundation of the federal state after Sonderbund war | 1291 | Traditional founding | 1815 | The cantons of Valais, Neuchâtel and Geneva join the Swiss Confederation. | |
| 7 August 1815 | Restoration of the Ancien Régime (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte. | |||||
| 24 August 1991 | Independence of former Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic from Soviet Union declared.[7] | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | Annexation of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts by Russia | |
| 22 January 1918 | Ukraine declares independence as the Ukrainian People's Republic. | |||||
| 8 December 1922 | The Irish Free State seceded from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922, however Northern Ireland opted to exclude itself from the Irish Free State two days later creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. | 927 | Kingdom of England | 1603 | The Kingdoms of Scotland, England and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots inherited the crowns of England and Ireland; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal and religious institutions.[37][38] | |
| 843 | Kingdom of Scotland (Devolved Parliament since 1999) | |||||
| 1057[39] then 1165[40] | Kingdom of Wales then Principality of Wales (Annexed by England in 1542) | |||||
| 1171 then 1542 | Lordship of Ireland then Kingdom of Ireland | |||||
| 1 May 1707 | Kingdom of Great Britain (United the parliaments of Scotland and England) | |||||
| 1 January 1801 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland[41][42][43] (United the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland) | 6 December 1922 then 8 December 1922 | Irish Free State secedes from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922. | |||
| 1 July 1997 | British Overseas Territories: Hong Kong was transferred to the People's Republic of China in 1997.[note 14] | |||||
| 1274 | Birth of current form of government the Papal conclave in 1274 | 7 June 1929 | Ratification of the Lateran Treaty, making the Vatican City a sovereign state | 11 February 1929 | Signing of the Lateran Treaty |
- Table notes
- ^ a b c The date of formation of the current states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania is subject to an international dispute. Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania all maintain that they were illegally occupied by the Soviet Union, and that the current states are direct continuations of the pre-WWII states, which continued to exist through governments-in-exile. Russia maintains that the current three states are legally distinct entities newly created after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. All three states were admitted the UN as independent nations, not successor states of the USSR. For more information, see State continuity of the Baltic states.
Australia/Oceania[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January 1901 | Commonwealth of Australia established as federation. | 1 January 1901 | Independence from United Kingdom. | 16 September 1975 | Papua New Guinea becomes formally independent of Australia | |
| 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster | |||||
| 3 March 1986 | Australia Act 1986 | |||||
| State in free association with New Zealand with a local prime minister | 4 August 1965 | 1962 autonomy of New Zealand | ||||
| 10 October 1970 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 12 July 1979 | Independence from United Kingdom | 1 October 1975 | Separation of the Gilbert Islands (later Kiribati) and the Ellice Islands (later Tuvalu) | |||
| 1 May 1979 | Constitution and local government established | 21 October 1986 | Compact of Free Association with the United States | |||
| 10 May 1979 | Constitution ratified | 3 November 1986 | Compact of Free Association with the United States | 10 May 1979 | Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei, and Kosrae unite to form the Federated States of Micronesia | |
| 31 January 1968 | Independence from UN Trusteeship (Australian, British and New Zealand administration ends) | |||||
| 6 February 1840 | Treaty of Waitangi where the British Crown established a right to govern from indigenous Māori tribes[44] | 17 January 1853 | Self-Government | 1 June 1962 | Samoa becomes fully independent from New Zealand. It is also the first small-island country in the Pacific to become independent. | |
| 18 April 1856 | Responsible Government | |||||
| 26 September 1907 | Granted nominal independence (Dominion status). | |||||
| 25 October 1926 | Balfour Declaration of 1926 — Great Britain and the Dominions are "autonomous Communities within the British Empire, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs" | |||||
| 27 July 1938 | Governor-General ceases to represent the British Government and becomes the personal representative of the King. | |||||
| 25 November 1947 | Statute of Westminster adopted — Britain loses the power to legislate for New Zealand except by request | |||||
| 10 December 1947 | Full power to amend own constitution | |||||
| 1 December 1967 | Governor-General becomes a New Zealand appointment | |||||
| 1 January 1981 | Republic of Palau created upon adoption of constitution | 1 October 1994 | Emerged from United Nations trusteeship (administered by the United States). | |||
| 1 December 1973 | Self-governing territory | |||||
| 16 September 1975 | Independence from Australia | |||||
| 1 June 1962 | Independence from New Zealand | |||||
| 2 January 1976 | Self-government granted by United Kingdom | |||||
| 7 July 1978 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 4 July 1970 | Independence from United Kingdom | 4 December 1845 | Unification of what is now the islands of Tonga by George Tupou I of Tonga | |||
| 1 October 1975 | Separation of Gilbert Islands (later Kiribati) and Ellice Islands (later Tuvalu) | 1 October 1978 | Independence from United Kingdom | 7 February 1979 | Treaty with United States recognizing Tuvaluan control over Funafuti, Nukufetau, Nukulaelae, and Niulakita atolls | |
| 30 July 1980 | Independence from joint British-French condominium[45] |
Transcontinental states[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 October 1991 | Declaration of independence from the Soviet Union | 28 May 1918 | Establishment of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic.[7] | 28 April 1920 | Establishment of the Azerbaijan SSR | |
| 4 August 1886 | Creation of the Republic of Colombia | 20 July 1810 | Independence declared from Spain | 3 November 1903 | Separation of Panama from Colombia | |
| 7 August 1819 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 1830 | Dissolution of Gran Colombia | |||||
| 16 August 1960 | Constitution of Cyprus establishes consocial government. Consociationalism de facto suspended in 1963.[46][47][48] | 16 August 1960 | Independence from United Kingdom | 23 July 1974 | Establishment of the United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus | |
| 15 November 1983 (disputed) | Northern Cyprus declares independence. The government has de facto control of the northern part of the island, but is only recognized by Turkey | |||||
| 18 June 1953 | Egyptian revolution of 1952, Egyptian monarchy overthrown in a military coup, republic declared | 28 February 1922 | The UK ends its protectorate, granting independence to Egypt | 1925 | The eastern borders of Libya and British Egypt are changed to their present boundaries. | |
| 22 September 1792 | French Republic founded. | 481 then 843 | First creation with (Clovis), king of the Franks. Then creation of the Kingdom of France (West Francia), Treaty of Verdun | 10 February 1947 | Metropolitan France: Annexation of Tende, La Brigue and other villages formerly in Italy.[note 18][note 19] | |
| 4 October 1958 | Establishment of the current semi-presidential system known as the Fifth Republic | 30 July 1980 | Overseas France: The New Hebrides Condominium declares independence and becomes Vanuatu. | |||
| 9 April 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union declared | 1008 | Establishment of the Kingdom of Georgia | 23 July 1992 | Abkhazia unilaterally declared independence | |
| 26 May 1918 | Establishment of Democratic Republic of Georgia[7] | 28 November 1991 | South Ossetia unilaterally declared independence | |||
| 18 August 1945 | Ratification of the Constitution of Indonesia by the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence | 17 August 1945 | Indonesian Declaration of Independence from Netherlands | 20 May 2002 | Independence of East Timor, formerly administered as a province of Indonesia | |
| 27 December 1949 | Independence from the Netherlands recognized | |||||
| 30 August 1995 | Constitution of Kazakhstan | 16 December 1991 | Independence declared from the Soviet Union[7] | 5 December 1936 | Establishment of the Kazakh SSR | |
| 30 March 1993 (disputed) | Baikonur Cosmodrome and surrounding areas leased to Russia.[note 20] | |||||
| 3 November 1903 | Separation of Panama from Colombia, independence from Spain | 1 October 1979 | Panama Canal Zone | |||
| 25 December 1993 | 1993 Russian constitutional referendum replaces the Supreme Soviet with the Federal Assembly and increases presidential power. | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | Annexation of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts by Russia | |
| 25 December 1991 | After the USSR ceased to exist, the Russian Federation became an independent state and was recognized by the international community as the successor state of the USSR. | |||||
| 6 December 1978 | Spanish Constitution | 1479 | Dinastical unification of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon by the Catholic Monarchs. The governments, institutions, and legal traditions of each kingdom remained independent of each other; alien laws (Leyes de extranjeria) determined that the national of one kingdom was a foreigner in the other Crowns/States.[36] | 26 February 1976 | Spanish Sahara is lost following the Madrid Accords. | |
| 1707~1716 | De jure by the Nueva Planta decrees | |||||
| 1831 | Dissolution of crowns and kingdoms and creation de jure, of the unified Kingdom of Spain. | |||||
| 24 June 2018 | 2017 Turkish constitutional referendum comes into effect; Turkey transitions from a parliamentary republic to a presidential republic. | 1299 | Formation of the Ottoman Empire | 29 June 1939 | Turkey annexes the once Syrian province of Hatay. | |
| 29 October 1923 | The provincial government, formed in 1920, declares the foundation of the Republic of Turkey, as the legal successor state to the Ottoman Empire. | |||||
| 8 December 1922 | The Irish Free State seceded from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922, however Northern Ireland opted to exclude itself from the Irish Free State two days later creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. | 927 | Kingdom of England | 1603 | The Kingdoms of Scotland, England and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots inherited the crowns of England and Ireland; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal and religious institutions.[37][38] | |
| 843 | Kingdom of Scotland (Devolved Parliament since 1999) | |||||
| 1057[39] then 1165[40] | Kingdom of Wales then Principality of Wales (Annexed by England in 1542) | |||||
| 1171 then 1542 | Lordship of Ireland then Kingdom of Ireland | |||||
| 1 May 1707 | Kingdom of Great Britain (United the parliaments of Scotland and England) | 6 December 1922 then 8 December 1922 | Irish Free State secedes from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922. | |||
| 1 January 1801 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland[41][42][43] (United the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland) | |||||
| 1 July 1997 | British Overseas Territories: Hong Kong was transferred to the People's Republic of China in 1997.[note 14] |
Sortable list[edit]
In this list, "date of last subordination" refers to the last date of control by an external government. The list shows large groupings associated with the dates of independence from decolonization (e.g. 41 current states gained control of sovereignty from the United Kingdom and France between 1956 and 1966) or dissolution of a political union (e.g. 18 current states gained control of sovereignty from the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia between 1990 and 1992). In other cases, a sovereign state submitted to foreign military occupation or political subjugation for a period of time and later regained its independence (e.g. 6 current states gained control of sovereignty from Nazi Germany between 1944 and 1945).
Dates refer to de facto rule or occupation of the major territory, whether or not legitimized by international recognition.
In a union such as Czechoslovakia, the Soviet Union, or the Kalmar Union, one of the constituents can be considered the dominant power – generally where the seat of government was located. The United Kingdom is a particularly complicated case. If England is viewed as the dominant member, then history can be traced from Roman conquest, Saxon invasions, 10th-century unification, and the 1066 Norman Conquest before the union of England and Scotland in 1707. However, if viewed from a Scottish perspective, an unbroken history of sovereignty can be traced from unification in 843 through the 1707 union with England (with a brief annexation by England from 1657 to 1660). Some Scots view the 1707 union as a ceding of sovereignty to England.[50]
There are cases where a state is completely extinguished or abolished without having any successor states. Cases like this occur when, for example, one state is annexed or conquered by another and ceases to exist even in nominal form (i.e. not even a "government in exile" is established). The most recent case in human history is the German Democratic Republic (East Germany), which was completely abolished after the German reunification. Modern Germany is a continuation of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany), it is not a successor state.
The Holy Roman Empire is not considered a state by modern historians, but a political entity bringing together several sovereign states in a confederation.
The concept of sovereign state should not be confused with that of nation (for example there are even stateless nations). This list has the date of creation of current sovereign states but not of nations. The historiography of some nations, such as the Bulgarians, even separates the different states founded by these nations (for example First, Second and Third Bulgarian State)
| Country | Continent | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of last subordination | Previous governing power | Historical Notes | Description of Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | July 1747 (Durrani Empire) | 1796 | 2021–present: 2004–2021: 2002–2004: 1996–2001: 1987–1992: | Afghanistan is a theocratic unitary Islamic autocracy, considered by many a dictatorship, the Taliban group does not respect human rights and is therefore criticized by the international community, Afghanistan has gone through reigns, empires and republics,The Taliban's opposition is made up of the West and NATO the Taliban are natively of Pashto ethnicity so they are supported by Pashto groups in the region of Afghanistan and Pakistan as: Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan The following countries also recognize the Taliban as Afghanistan: Qatar Pakistan Saudi Arabia Afghanistan was invaded by the United States after allegedly planned the 2001 Twin Towers attack. | ||
| Europe | 28 Nov 1912 | Nov 1944[51] | 1992–present: 1946–92: 1944–46: 1943–44: 1939–43: | Albania is a unitary parliamentary republic, which is mostly Islamic, for a long time Albania was a colony of the Ottoman Turkish Empire and then inherited the religion of the empire, Albanian nationalists believe in the idea of "Greater Albania" where Albania would encompass lands of Kosovo and Montenegro with a Muslim majority, this idea has existed since the Ottoman Turkish empire. Albania and Kosovo are close countries, Albania helped Kosovo in the war, but Kosovo continued to be the poorest region in the Balkans. | ||
| Africa | 3 July 1962[53] | 3 July 1962[54] | 1962–present: 1830–1962: Part of 1659–1830: De facto Independence of | Algeria is a Semi-Presidential Republic. during the Algerian war against France Pierre Lagaillard founded the secret armee. Nowadays Algeria is at peace with any other nation in the world | ||
| Europe | 7 Sep 1278[56][57] | Nov 1944[58] | 1278–present: Principality of Andorra (via Paréage of Andorra; occupied by France 1812–13, 1870, 1914, 1936, 1939, 1944) 987–1278: Part of France | Andorra is a co-principality that has a parliamentarism, with a co-prince of Andorra, a representative, a prime minister and a general syndic. The estate of Andorra was founded in 1278 respectively from the Crown of aragon Andorra was often invaded by France in its history because Andorra is a buffer state for Spain and France | ||
| Africa | 11 Nov 1975[59] | 11 Nov 1975 | 1992–present: Republic of Angola 1975–1992: People's Republic of Angola (via the Alvor Agreement) 1972–1975: State of Angola (part of the Portuguese Empire) 1951–1972: Overseas Province of Angola (part of the Portuguese Empire) 1575–1951: State of West Africa (part of the Portuguese Empire) The territory of Angola has been inhabited since the Paleolithic Era, hosting a wide variety of ethnic groups, tribes and kingdoms (like the kingdoms of Kongo, Ndongo and Matamba). | Angola is the only socialist country in its region, which is why the country has a very different policy from the others in the Angolan civil war , AMPLA Angola's socialist party , | ||
| The Americas | 1 Nov 1981[60] | 1 Nov 1981 | 1981–present: 1632–1981: Part of the | Antigua and Barbuda is a constitutional monarchy forming part of the Commonwealth of Nations community. The only notable event in the history of Antigua was the Caribbean Liberation Movement of Antigua from 1968 to 1992 | ||
| The Americas | 25 May 1810 | 9 July 1816[61] | 1861–present: 1831–1861: | The Argentine Republic took a very radical step when Argentina elected Javier Milei as president of the country in 2023. Argentina has claimed Falkland Island from the UK, the Argentina says the island is called Islas Malvinas. There is great controversy about its discovery and subsequent colonization by Europeans. At various times it had French, British, Spanish and Argentine settlements. The United Kingdom reasserted its control over the archipelago in 1833, although Argentina maintains its claim to the islands. In April 1982, Argentine forces temporarily occupied the territory. British administration was restored two months later, at the end of the Falklands War. The Paraguayan war lasted from 1864 to 1870. As of 2024[update], it was last South American conflict involving Argentina. The archipelago of Tierra del Fogo is claimed by both Chile and the Argentine Republic | ||
| Asia/Europe | 28 May 1918 | 23 Sep 1991[62] | 1991–present: 1920–1991: | Armenia has the region of Nagorno-Karabakh as autonomous, seeking its independence from Armenia A maior parte de Nagorno-Karabakh foi governada por armênios étnicos sob a dissidente República de Artsakh - também conhecida como República de Nagorno-Karabakh (NKR) - desde o fim da primeira Guerra de Nagorno-Karabakh entre a Armênia e o Azerbaijão em 1994 até o anúncio do dissolução da república em setembro de 2023. Representantes de ambos os lados mantiveram inúmeras conversações de paz inconclusivas mediadas pelo Grupo de Minsk da OSCE sobre o status disputado da região, com sua população de maioria armênia ao longo do tempo defendendo de diversas maneiras a independência de Artsakh de ambos os estados ou sua integração na Arménia. | ||
| Australia | 9 Oct 1942 [note 21] | 9 Oct 1942 | 1942–present: 1901–1942: | the last important event in australia was the Eureka Rebellion was a series of events involving gold miners who revolted against the British administration of the colony of Victoria, Australia, during the Victorian Gold Rush. It culminated in the Battle of Eureka Stockade, which took place on 3 December 1854 in Ballarat between rebels and colonial forces from Australia. The fighting left at least 27 dead and many injured, with the majority of victims being rebels. There was an earlier period, beginning in 1851, of peaceful demonstrations and civil disobedience on the Victorian goldfields. Miners had several complaints, mainly the cost of mining licenses and the unofficial way in which the system was applied. | ||
| Europe | 1156 | 27 Apr 1945[note 22] | World War II Allies | 1955–present: Republic of Austria, a Federal state (via Austrian State Treaty) 1945–55: Allied-occupied Austria 1938–45: Annexed by Nazi Germany 1934–38: Federal State of Austria (client state of Italy) 1919–34: First Republic of Austria (via Treaty of Saint Germain) 1918–19: Republic of German-Austria (via Proclamation of Charles I) 1867–1918: Austro-Hungarian Monarchy, a dual monarchy with Hungary (via Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867) 1866: Austrian Empire 1815–1866: Austrian Empire (In union with other 38 states in the German Confederation) 1806–1815: Austrian Empire 1804–1806: Austrian Empire (State of the Holy Roman Empire) 1457–1804: Archduchy of Austria (State of the Holy Roman Empire) 1156–1457: Duchy of Austria (state of the Holy Roman Empire) | Austria is a Parliamentary federal republic with a president and a chanceler. At the end of the Second World War, Austria was occupied by the United Kingdom, France, the USA and the USSR. | |
| Asia/Europe | 28 May 1918 | 30 Aug 1991 | 1991–present: Republic of Azerbaijan (independence from Soviet Union declared 1991 1920–1991: Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, federated state of the | Azerbaijan contains an autonomous region, Nakhchivan. | ||
| The Americas | 10 July 1973[64] | 10 July 1973 | 1973–present: Commonwealth of the Bahamas, a monarchy in personal union with the United Kingdom (Self-government gained from the United Kingdom in 1964; independence gained on 10 July 1973) 1718–1973: Part of the British Empire as its West Indies 1492–1718: Part of the Spanish Empire 500 to 800–1492: Inhabited by the Lucayans (a Taino people) | |||
| Asia | 16 Dec 1971 | 16 Dec 1971 | 1971–present: Kingdom of Bahrain 1861–1971: Protectorate of the British Empire by way of the Perpetual Truce of Peace and Friendship | |||
| Asia | 16 Dec 1971 | 16 Dec 1971 | 1972–present: 1971–1972: | |||
| The Americas | 30 Nov 1966 | 30 Nov 1966 | 1966–present: Barbados 1625–1966: Part of the British Empire as its West Indies | |||
| Europe | 25 Aug 1991[note 23] | 25 Aug 1991 | 1990–present: Republic of Belarus 1943–1990: Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, a federated state of the Soviet Union (USSR) | |||
| Europe | 4 Oct 1830 | 1945 | 1830–present: Kingdom of Belgium (a Federal state, consisted of three regions and three communities) 1813–1830: Part of the Netherlands 1795–1813: Ruled by France 1713–1795: Austrian Netherlands (collective name of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, held by the Habsburg monarchy) 1581–1714: Spanish Netherlands (collective name of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, held in personal union by the Spanish Crown) | |||
| The Americas | 21 Sep 1981[66] | 21 Sep 1981 | 1981–present: Belize 1716–1973: Part of the British Empire | |||
| Africa | 1 Aug 1960 | 1 Aug 1960 | 1990–present: Republic of Benin 1975–1990: People's Republic of Benin 1958–1975: Republic of Dahomey (French self-governing colony) | |||
| Asia | 1634 | 1634 | (none) | 1910–1947: protectorate of the Autonomous since at least the 10th century.[67] Unified 1634, after the Battle of Five Lamas. Early history is sketchy, but may have been part of Kamarupa kingdom, and may have been occupied by Tibetan-Mongol forces ca. 10th century.[68] | ||
| The Americas | 6 Aug 1825 | 6 Aug 1825 | 2009–present: Plurinational State of Bolivia 1839–2009: Republic of Bolivia | |||
| Europe | 3 Mar 1992 | 3 Mar 1992 | 1997–present: Bosnia and Herzegovina (a Federal state) 1992–1997: Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina | |||
| Africa | 30 Sep 1966[69] | 30 Sep 1966 | 1966–present : Republic of Botswana 1885–1966: Part of the British Empire as Bechuanaland Protectorate | |||
| The Americas | 7 Sep 1822[70] | 29 Aug 1825 (Treaty of Rio de Janeiro) | 1985–Present: 1964–1985: | |||
| Asia | 1 Jan 1984 | 1 Jan 1984 | 1984–present: Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace 1945–1984: Part of the British Empire | |||
| Europe | 5 Oct 1908[71] | 5 Oct 1908 | 1990–present: 1946–1990: | |||


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch