Mi'kmaq
Lnu | |
|---|---|
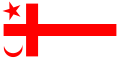 Grand Council Flag of the Mi'kmaq Nation.[1][2] Although the flag is meant to be displayed hanging vertically as shown here, it is quite commonly flown horizontally, with the star near the upper hoist. | |
 A Miꞌkmaw father and child at Tufts Cove, Nova Scotia, around 1871 | |
| Total population | |
| 66,748 registered members (2023) 168,480 claimed Mi'kmaq ancestry (2016)[3] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| (Mi'kma'ki, Dawnland) Canada, United States | |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 28,282 |
| Nova Scotia | 18,814 |
| New Brunswick | 9,025 |
| Quebec | 7,655 |
| Maine | 1,489 |
| Prince Edward Island | 1,483 |
| Languages | |
| English, Miꞌkmaq, French | |
| Religion | |
| Native American religion, Christianity, others | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Algonquian peoples Especially Abenaki, Maliseet, Passamaquoddy, Penobscot | |
| Person | Lnu |
|---|---|
| People | Lnu'k (Mi'kmaq) |
| Language | Mi'kmawi'simk |
| Country | Mi'kma'ki Wabanaki |
The Mi'kmaq (also Mi'gmaq, Lnu, Mi'kmaw or Mi'gmaw; English: /ˈmɪɡmɑː/ MIG-mah; Miꞌkmaq: [miːɡmaɣ], and formerly Micmac)[4][5][6] are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland,[7] and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as Native Americans in the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Mi'kma'ki (or Mi'gma'gi).
There are 66,748 Mi'kmaq people in the region as of 2023 (including 25,182 members in the more recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland[8][9]). According to the Canadian 2021 census, 9,245 people claim to speak Mi'kmaq, an Eastern Algonquian language.[10] Once written in Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet.
The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties with the British Crown throughout the eighteenth century; the first was signed in 1725, and the last in 1779. The Mi'kmaq maintain that they did not cede or give up their land title or other rights through these Peace and Friendship Treaties.[11] The landmark 1999 Supreme Court of Canada decision in R v Marshall upheld the 1752 Peace and Friendship Treaty "which promised Indigenous Peoples the right to hunt and fish their lands and establish trade."[12]
The Mi'kmaw Grand Council is the official authority that engages in consultation with the Canadian federal government and the provincial government of Nova Scotia, as established by the historic August 30, 2010, agreement with the Mi'kmaq Nation, resulting from the Mi'kmaq–Nova Scotia–Canada Tripartite Forum.[13] This collaborative agreement, which includes all the First Nations within the province of Nova Scotia, was the first in Canadian history.[13]
Historically, the Santé Mawiómi, or Grand Council, which was made up of chiefs of the district councils of Mi'kma'ki, was the traditional senior level of government for the Mi'kmaw people. The 1876 Indian Act disrupted that authority, by requiring First Nations to establish representative elected governments along the Canadian model, and attempting to limit the Council's role to spiritual guidance.[14][15]
Grand Council Santé Mawiómi
[edit]On August 30, 2010, the Mi'kmaw Nation and the Nova Scotia provincial government reached an historic agreement, affirming that the Mi'kmaw Grand Council was the official consultative authority that engages with the Canadian federal government and the provincial government of Nova Scotia.[13] The Mi'kmaq–Nova Scotia–Canada Tripartite Forum preceded the agreement.[13] The August 2010 agreement is the first such collaborative agreement in Canadian history; it includes representation for all the First Nations within the entire province of Nova Scotia.[13]
Historically the Santé Mawiómi, or Grand Council, which was made up of chiefs of the district councils of Mi'kma'ki, was the traditional senior level of government for the Mi'kmaw people. The 1876 Indian Act disrupted that authority, by requiring First Nations to establish representative elected governments and attempting to limit the Council's role to that of spiritual guidance.[16][15]
In addition to the district councils, the M'ikmaq have been traditionally governed by a Grand Council or Santé Mawiómi. The Grand Council was composed of Keptinaq ("captains" in English), who were the district chiefs. There were also elders, the putús (wampum belt readers and historians, who also dealt with the treaties with the non-natives and other Native tribes), the women's council, and the grand chief. The grand chief was a title given to one of the district chiefs, who was usually from the Mi'kmaw district of Unamáki or Cape Breton Island. This title was hereditary within a clan and usually passed on to the grand chief's eldest son.
On June 24, 1610, Grand Chief Membertou converted to Catholicism and was baptised. He concluded an alliance with the French Jesuits. The Mi'kmaq, as trading allies of the French, were amenable to limited French settlement in their midst.

Gabriel Sylliboy (1874–1964), a respected Mi'kmaq religious leader and traditional Grand Chief of the Council, was elected as the Council's Grand Chief in 1918. Repeatedly re-elected, he held this position for the rest of his life.[17]
In 1927, Grand Chief Sylliboy was charged by Nova Scotia with hunting muskrat pelts out of season. He was the first to use the rights defined in the Treaty of 1752 in his court defence. He lost his case. In 1985, the Supreme Court of Canada finally recognized the 1752 treaty rights for indigenous hunting and fishing in their ruling on R. v. Simon.[18] On the 50th anniversary of Sylliboy's death, the Grand Council asked the Nova Scotia government for a pardon for the late Grand Chief. Premier Stephen McNeil granted the posthumous pardon in 2017.[17] Lieutenant-Governor of Nova Scotia, John James Grant, McNeil, and the Justice Minister Diana Whalen, pardoned Sylliboy and issued a formal apology: it was the "second posthumous pardon in Nova Scotia's history".[17] His grandson, Andrew Denny, now the Grand Keptin of the Council, said that his grandfather had "commanded respect. Young people who were about to get married would go and ask for his blessing. At the Chapel Island Mission boats would stop if he was crossing."[17]
Traditionally, the Grand Council met on a small island, Mniku, on the Bras d'Or Lake in Cape Breton. In the early 21st century, this site is now within the reserve known as Chapel Island or Potlotek. The Grand Council continues to meet at Mniku to discuss current issues within the Miꞌkmaq Nation.
Taqamkuk (Newfoundland) was historically defined as part of Unama'kik territory. (Later the large island was organized as a separate district in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.)
Mi'kmaq language
[edit]According to the 2021 census, 9,245 people identified as speakers of the Mi'kmaq language. 4,910 of which said it was their mother tongue, and 2,595 reported it to be their most often spoken language at home.[10]
Hieroglyphic writing
[edit]The Mi'kmaq language was written using Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing using a hieroglyphic system created in 1677 by French Catholic missionary Chrestien Le Clerq.[19] Le Clerq noted that the Mi'kmaq children were memorizing prayers utilizing the counting of marks, but did not claim to have incorporated any of this system into the hieroglyphs he created. It is likely that this pre-Le Clerq writing system was part of a writing tradition by the Mi'kmaq similar to that observed in 1651 amongst the Eastern Abenaki of Maine.[20] Today, it is written mainly using letters of the Latin alphabet.
At the Kejimkujik National Park and National Historic Site, petroglyphs of "life-ways of the Mi'kmaq", include written hieroglyphics, human figures, Mi'kmaq houses and lodges, decorations including crosses, sailing vessels, and animals, etched into slate rocks. These are attributed to the Mi'kmaq, who have continuously inhabited the area since prehistoric times.[21]: 1 The petroglyphs date from the late prehistoric period through the nineteenth century.[21]: 32
Jerry Lonecloud (1854 – 1930, Mi'kmaq) is considered the "ethnographer of the Mi'kmaq nation". In 1912, he transcribed some of the Kejimkujik petroglyphs, and donated his works to the Nova Scotia Museum.[21]: 6 He is credited with the first Mi'kmaq memoir, which was recorded from his oral history in the 1920s.[22]
In the late 1670s, French missionary Chrestien Le Clercq, who was working in the Gaspé Peninsula, was inspired by marks made by a young Mi'kmaq using charcoal on birchbark. Leclercq created what is now known as Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing to teach Catholic prayers and hymns to the people in their own unique form of language.[19][23] After Le Clerq's returned to France in 1687, the script had to be taught to other groups of Mi'kmaq by other missionaries, indicating it was not a script that the indigenous peoples already knew.[24]

Christian Kauder was a Luxembourg missionary in Mi'kma'ki from 1856 to 1871. He included samples of Mi'kmaq hieroglyphic writing, such as the Holy Mary Rosary prayer and the Lord's Prayer, in his German Christian catechism published in Vienna in 1866.[25]
David L. Schmidt and Murdena Marshall published some of the prayers, narratives, and liturgies represented in hieroglyphs—pictographic symbols in a 1995 book. As noted, the pre-contact Mi'kmaq utilized some form of writing, but Le Clerq indicated that the hieroglyphs were "formed" by him.[19] French Jesuit missionaries adopted their use to teach Catholic prayers and religion to the Mi'kmaq.[26] Schmidt and Marshall showed that these hieroglyphics served as a fully functional writing system.[26] They assert it is the oldest writing system for an indigenous language in North America north of Mexico.[26]
Etymology of the word Mi'kmaq
[edit]By the 1980s, the spelling of the ethnonym Mi'kmaq, which is preferred by the Mi'kmaq people, was widely adopted by scholarly publications and the media. It replaced the previous spelling Micmac.[27]: 3 [Notes 1] Although this older spelling is still in use, the Mi'kmaq consider the spelling "Micmac" to be "tainted" by colonialism.[28] The "q" ending is used in the plural form of the noun, and Mi'kmaw is used as singular of Mi'kmaq. It is also used as an adjective, for example, "the Miꞌkmaw nation".[29]
The Mi'kmaq prefer to use one of the three current Miꞌkmaq orthographies when writing the language.[30][Notes 2] Spellings used by Mi'kmaq people include Mi'kmaq (singular Mi'kmaw) in Prince Edward Island (Epekw'itk), Nova Scotia (Mi'kma'ki-Unama'ki), and Newfoundland (K'taqamkuk); Miigmaq (Miigmao) in New Brunswick (Sipekni'katik); Mi'gmaq by the Listuguj Council in Quebec (Kespek); and Mìgmaq (Mìgmaw) in some native literature.[28]
Lnu (the adjectival and singular noun, previously spelled "L'nu"; the plural is Lnúk, Lnu'k, Lnu'g, or Lnùg) is the term the Mi'kmaq use for themselves, their autonym, meaning "human being" or "the people".[31] Members of the Mi'kmaq historically referred to themselves as Lnu, but used the term níkmaq (my kin) as a greeting.[32]
The French initially referred to the Mi'kmaq as Souriquois and later as Gaspesiens. Adopting a term from the English, they referred to them as Mickmakis. The British originally referred to the people as Tarrantines, which appears to have a French basis.[33]
Various explanations exist for the rise of the term Mi'kmaq. The Mi'kmaw Resource Guide says that "Mi'kmaq" means "the family".[34][Notes 3] The Anishinaabe refer to the Mi'kmaq as Miijimaa(g), meaning "The Brother(s)/Ally(ies)", with the use of the nX prefix m-, opposed to the use of n1 prefix n- (i.e. Niijimaa(g), "my brother(s)/comrade(s)") or the n3 prefix w- (i.e., Wiijimaa(g), "brother(s)/compatriot(s)/comrade(s)").[35]
Charles Aubert de La Chesnaye was documented as the first European to record the term "Mi'kmaq" for the people, using it in his 1676 memoir. Marion Robertson stated this in the book Red Earth: Tales of the Mi'kmaq (1960s), published by the Nova Scotia Museum,[36]: 5 Robertson cites Professor Ganong, who suggested that "Mi'kmaq" was derived from the Mi'kmaq word megamingo (earth). Marc Lescarbot had also suggested this.[36]: 5
The Mi'kmaq may have identified as "the Red Earth People, or the People of the Red Earth".[36] Megumaagee, the name the Mi'kmaq used to describe their land, and Megumawaach, what they called themselves, were linked to the words megwaak, which refers to the colour red, and magumegek, "on the earth".[36]: 5 Rand translated megakumegek as "red on the earth", "red ground", or "red earth".[36]: 5 Other suggestions from Robertson include its origin in nigumaach, which means "my brother" or "my friend", or a term of endearment.[36] Stansbury Hagar suggested in Mi'kmaq Magic and Medicine that the word megumawaach is from megumoowesoo, in reference to magic.[36]
Geography
[edit]
Mi'kmaw Country, known as Mi'kma'ki, is traditionally divided into seven districts. Prior to the imposition of the Indian Act, each district had its own independent government and boundaries. The independent governments had a district chief and a council. The council members were band chiefs, elders, and other worthy community leaders. The district council was charged with performing all the duties of any independent and free government by enacting laws, justice, apportioning fishing and hunting grounds, making war and suing for peace.
Districts
[edit]The eight Mi'kmaw districts (including Ktaqmkuk which is often not counted) are Epekwitk aq Piktuk (Epegwitg aq Pigtug), Eskikewa'kik (Esge'gewa'gi), Kespek (Gespe'gewa'gi), Kespukwitk (Gespugwitg), Siknikt (Signigtewa'gi), Sipekni'katik (Sugapune'gati), Ktaqmkuk (Gtaqamg), and Unama'kik (Unama'gi). The orthography between parentheses is the Listuguj orthography used in the Gespe'gewa'gi area.
Current federal and provincial relations with Mi'kmaq
[edit]Tripartite Forum
[edit]In 1997, the Mi'kmaq–Nova Scotia–Canada Tripartite Forum was established. On August 31, 2010, the governments of Canada and Nova Scotia signed a historic agreement with the Mi'kmaw Nation, establishing a process whereby the federal government must consult with the Miꞌkmaw Grand Council before engaging in any activities or projects that affect the Mi'kmaq in Nova Scotia. This covers most, if not all, actions these governments might take within that jurisdiction. This is the first such collaborative agreement in Canadian history including all the First Nations within an entire province.[13]
Marshall decision
[edit]On September 17, 1999, the Supreme Court of Canada upheld the treaty rights of Mi'kmaw Donald Marshall Jr. its landmark R v Marshall ruling, which "affirmed a treaty right to hunt, fish and gather in pursuit of a 'moderate livelihood'."[38] The Supreme Court also cited Section 35 of the 1982 Constitution Act in their 1999 ruling that resulted in Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Peskotomuhkati people the "right to hunt, fish and gather in pursuit of a 'moderate livelihood' from the resources of the land and waters."[39] The legal precedent had previously been established in the Treaty of 1752, one in a series of treaties known as the Peace and Friendship Treaties,[38] but was not being respected prior to R v Marshall.[38] This resulted in the 1993 charges laid against Marshall Jr. for "fishing eels out of season, fishing without a licence, and fishing with an illegal net".[40] In the 2018 publication, Truth and conviction: Donald Marshall Jr. and the Mi'kmaq quest for justice, Marshall was quoted as saying, "I don't need a licence. I have the 1752 Treaty."[41] The 1989 Royal Commission on the Donald Marshall Jr. Prosecution resulted in a compensation to Marshall of a lifetime pension of $1.5 million.[42][41] Marshall used the financial compensation to finance the lengthy and costly Supreme Court case.[39] When Marshall won, 34 Mi'kmaq and Maliseet First Nations bands were affected in the provinces of New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, Nova Scotia, and the Gaspé region of Quebec.[38] The West Nova Fishermen's Coalition submitted an appeal asking for the Marshall decision to be set aside.[40] In November 17, 1999, released a new ruling (Marshall 2) to clarify that the DFO had the power to regulate the fishery for conservation purposes if it "consulted with the First Nation and could justify the regulations".[43][Notes 4]
Soon after the September 17 decision, Miramichi Bay—"one of Canada's most lucrative lobster fisheries"—[44] became the site of a violent conflict between Mi'kmaq fishers and non-Mi'kmaq commercial fishers. Immediately after the ruling, Mi'kmaq fishers began to lay lobster traps out of season. Incidents such as the Burnt Church Crisis were widely covered by the media from 1999 and 2002.[39] On October 3, 1999, non-Indigenous commercial fishers in 150 boats destroyed hundreds of Mi'kmaq lobster traps, then returned to shore and vandalized fishing equipment, as well as three fish plants.[45] This was captured and documented in the 2002 National Film Board feature-length documentary Is the Crown at war with us? by Alanis Obomsawin. The documentary also described how Ocean and Fisheries department officials seemed to "wage a war" on the Mi'kmaq fishermen of Burnt Church, New Brunswick with "helicopters, patrol boats, guns, with observation by airplanes and dozens of RCMP officers".[46] The documentary asks why the fishers were being harassed for "exercising rights that had been affirmed by the highest court in the land."[46] Following lengthy negotiations with the Mi'kmaq, the DFO developed the $160 million Marshall Response Initiative, which operated until 2007, through which the DFO offered to purchase over 1,000 commercial fishing licences, including boats and gear, to support the expansion of the Mi'kmaq lobster fishery. By mid-2000, about 1,400 commercial fishermen stated their intention to retire over 5,000 licences.[45] On August 20, 2001, the DFO issued a temporary license to Burnt Church Mi'kmaq fishers while negotiations for a more permanent agreement were underway.[45] The DFO license had restrictions that some Burnt Church fishers refused: the fishers could not sell their lobsters, they could only use them for food, social, and ceremonial (FSC) purposes.[45] The "Aboriginal right to fish for food, social and ceremonial purposes (FSC)" was confirmed in the landmark 1990 R. v. Sparrow Supreme Court case which cited section 35 of the Constitution Act, 1982.[Notes 5] In May 2003, the House of Commons' Standing Committee On Fisheries And Oceans chaired by MP Tom Wappel, submitted its report on fisheries issues, which "recommended that all charges stemming from the [confrontation over the lobster fisheries]" be dropped and that the fishers should be compensated by federal government for "their lost traps and boats."[47] The report said that Mi'kmaq fishers have the "same season as non-native fishermen" and could not therefore, fish in the fall. It recommended that "native bands be issued licences, which they would distribute to native fishermen."[47]
On the tenth anniversary of the benchmark decision, CBC News reported that "Maritime waters" were "calm a decade after Marshall decision."[40]
However, by 2020, the Fish Buyers' Licensing and Enforcement Regulations, under the 1996 N.S. Fisheries and Coastal Resources Act, remains in effect—as it does in other Atlantic provinces.[48][49] These regulations do not mention the Mi'kmaq or the Marshall decision. These regulations prevent Mi'kmaq lobster fishers from selling their lobster to non-Mi'kmaq. Mi'kmaq fishers say that this does not align with the Marshall decision.[50] In 2019, the government of the Listuguj First Nation in the Bay of Chaleur developed their own self-regulated lobster fisheries management plan and opened their own lobster fishery in the fall of 2020.[50] Under the existing Fish Buyers' Licensing Regulations the self-regulated Listuguj fisheries can harvest, but can only use the lobster for "food, social and ceremonial purposes".[50]
According to Chief Terry Paul of Membertou First Nation, early in 2020, a negotiator for the DFO had offered Nova Scotia First Nations nearly $87 million for boats, gear, and training, with the condition that the First Nations would not practice their treaty right to earn a moderate livelihood fishing (ie out of the DFO season) for a period of 10 years. The proposal did not define "moderate livelihood", and was rejected.[51]
On November 9, 2020, a group of Mi'kmaq First Nations and Premium Brands Holdings Corporation announced their $1 billion purchase of Clearwater Seafoods, which was finalised on January 25, 2021. The group of First Nations includes Sipekne'katik, We'koqma'q, Potlotek, Pictou Landing, and Paqtnkek First Nations, and is led by Membertou and Miapukek First Nations.[52] The purchase represents the "largest investment in the seafood industry by a Canadian Indigenous group". The harvest of non-Indigenous fishermen in the region will now be purchased by Clearwater Seafoods' Mi'kmaq part owners.[53]
Dispute over rights-based inshore lobster fishery (2020–present)
[edit]| Dispute over rights-based inshore lobster fishery | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | September 2020 – ongoing | ||
| Location | |||
| Caused by | Miꞌkmaq exercising their treaty rights to fish | ||
| Status | ongoing | ||
| Parties | |||
| |||
| Casualties | |||
| Charged | 23 | ||
Since September 2020, there has been an ongoing lobster fishing dispute between Sipekne'katik First Nation[54] members of the Mi'kmaq and non-Indigenous lobster fishers mainly in Digby County and Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia.
Background
[edit]After Mi'kmaq chiefs declared a state of emergency in October 2020,[55] the federal government appointed Allister Surette as Federal Special Representative to investigate.[56]
In the March 2021 report's backgrounder, Surette cited Macdonald-Laurier Institute's Ken Coates who said that Mik'maq communities had benefitted from improvements resulting from the Marshall decision, as the Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) granted access to Mi'kmaq fishers to the "commercial fishery through communal licences operated by the bands". Macdonald-Laurier Institute's Ken Coates said that the commercial fishing industry had not suffered because of this.[56][57] Others disagreed, saying that Canada had never fully implemented the Marshall decision, and that, over the decades, various levels of government and authorities mishandled and neglected local concerns related to the implementation of the Marshall decision.[55]
In September 2020, the Sipekne'katik First Nation developed a fishing plan based on their right to fish in pursuit of a moderate livelihood.[56] They issued seven lobster licenses to band members; each license has 50 tags, representing a combined total of 350 tags. One commercial lobster license represents 350 tags.[58] The lobster fishery they initiated was located "outside of the regulated commercial season in Lobster Fishing Area 34[56] in St. Marys Bay, Nova Scotia—the Kespukwitk (also spelled Gespogoitnag) district of Mi'kma'ki.
The inshore fishery is the last small-scale fishery in Nova Scotia.[59] St. Marys Bay is part of Lobster Fishing Area (LFA) 34, making it the "largest lobster fishing area in Canada with more than 900 licensed commercial fishermen harvesting from the southern tip of Nova Scotia up to Digby in the Bay of Fundy."[60] It is also "one of the most lucrative fishing areas in Canada".[58] DFO reported that as of December 2019, there were 979 commercial lobster licenses in LFA 34.[58]
The Sipekneꞌkatik fishing plan "became a flash point" resulting in violent highly-charged conflict pitting non-Miꞌkmaw lobster fishers in the adjacent coastal communities and Mi'kmaw fishers those carrying out the moderate livelihood fishery.[56]
Violence
[edit]On September 11, Sipekne'katik First Nation Chief Michael Sack sent a letter to Premier Stephen McNeil, DFO Minister Bernadette Jordan and Nova Scotia RCMP Commanding Officer Lee Bergerman, calling for them "to uphold the rule of law amid ongoing violence, threats, human rights discrimination and ongoing failure to uphold the 1999 Supreme Court of Canada decision in R. v. Marshall, recognizing the Mi'kmaq right to fish and trade." By that point, vehicles and property belonging to members of the Sipekne'katik First Nation had already been damaged and stolen, including boats being burned. There were already planned protests by non-Indigenous fishers to block the Mi'kmaq fishers' access to several wharves.[61] One such protest took place on September 15 at Saulnierville and Weymouth wharves.[62]
On September 17, Sipekne'katik launched a "moderate livelihood fishery" with a ceremony at the Saulnierville wharf, the first lobster fishery regulated by Mi'kmaq in Nova Scotia. On September 18, the Assembly of Nova Scotia Mi'kmaw Chiefs declared a province-wide state of emergency in response to threats by commercial and non-indigenous fishers, including some that had cut the Mi'kmaw lobster traps.[55] On September 25, the Sipekne'katik fishery released its proposed regulations allowing the legal sale of seafood harvested under the fishery to Indigenous and non-Indigenous consumers and wholesalers. However, at the time of the announcement, Nova Scotia's Fisheries and Coastal Resources Act prohibited anyone in Nova Scotia from purchasing fish from "a person who does not hold a valid commercial fishing license issued by Fisheries and Oceans Canada," which would include the fishery.[50]
On October 1, Potlotek First Nation and Eskasoni First Nation[63] launched their own moderate livelihood fishery in a celebration at Battery Provincial Park that coincided with Mi'kmaq Treaty Day. The management plan behind this fishery had been in development for three months, prompted by the seizure of lobster traps by DFO officials. Community licenses issued through this fishery will entitle fishers to 70 tags, and boats will be allowed to carry up to 200 lobster traps each. At the time of the launch of the Potlotek fishery, Membertou was also planning on launching their own fishery, following a similar plan.[51] After the launch of this fishery, DFO officers continued to seize Mi'kmaq traps.[63]
Harassment around the Sipekne'katik fishery continued through October. On October 5, Sipekne'katik fisher Robert Syliboy, a holder of one of the moderate livelihood fishery's licenses, found his boat at the Comeauville wharf destroyed in a suspicious fire.[64] On the evening of October 13, several hundred non-Indigenous fishers and their supporters raided two storage facilities in New Edinburgh and Middle West Pubnico that were being used by Mi'kmaw fishers to store lobsters. During the raids, a van was set aflame, another vehicle was defaced and damaged, lobsters being stored in the facilities were destroyed, and the New Edinburgh facility was damaged, while a Mi'kmaw fisher was forced to barricade himself inside the facility in Middle West Pubnico. Indigenous leaders called the raids racist hate crimes and called on the RCMP to intervene, citing their slow response on the evening and lack of arrests even a day after the police claimed they "witnessed criminal activity". Social media posts from the commercial fishers and their supporters claimed that the lobsters taken in the raids were removed as they represented "bad fishing practices" on the part of the Mi'kmaq, but Sipekne'katik Chief Mike Sack and a worker at the Middle West Pubnico facility claimed the lobsters that were stored there were caught by the commercial fishers, not Mi'kmaw. Assembly of First Nations national chief Perry Bellegarde, federal Fisheries minister Bernadette Jordan, and Colin Sproul, president of the Bay of Fundy Inshore Fishermen's Association, all condemned the violence. Nova Scotia Premier Stephen McNeil maintained his position that this issue must be solved federally when asked about it at a press conference.[65] Several months later, in January 2021, the manager of the Middle West Pubnico facility, James Muise, made a public post in a Facebook group for commercial fishers, claiming that he gave the people involved in the raids permission to enter the facility and take the lobsters. Muise offered to work with people charged with offenses connected to the raids and try to get those charges dropped.[66]
Chief Mike Sack was sucker punched while trying to give a press conference on October 14.[67] Also during the violence, an elder had sage knocked out of her hand while smudging, and a woman was grabbed by the neck.[68]
On October 15, the Mi'kmaq Warrior Peacekeepers arrived at the Saulnierville wharf with the intention of providing protection to Miꞌkmaq who were continuing to fish amid the violence.[68]
On Friday, October 16, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said that his government was "extremely active" in trying to de-escalate the situation. He also stated that he expected the police to be keeping people safe, and acknowledged concerns that the police had not been doing so.[68]
Three days after the initial raids on the storage facilities, on the evening of October 16, the Middle West Pubnico facility was destroyed in a large fire, deemed "suspicious" by the RCMP. One man was taken to hospital with life-threatening injuries after the fire, but the RCMP did not provide details regarding the man's association to the lobster pound, other than that he was not an employee.[67] The destruction led to further calls from Chief Sack for increased police presence, as well as an appeal from the Maritime Fisherman's Union for the federal government to appoint an independent mediator.[69][67]
On October 16, Mi'kmaq lobster fishers from the Sipekne'katik First Nation quickly sold all their lobsters after setting up shop in front of the Province House in Halifax with potential customers lined up around the block.[70] The fishers said they were putting pressure on Premier McNeil to act.[70]
On October 17, Nova Scotia Premier Stephen McNeil, released a Twitter statement requesting that the federal government define "what constitutes legal harvesting in a "moderate livelihood" fishery.[12]
On October 21, Sipekne'katik managed to secure an interim injunction against the restriction of band members' access to the Saulnierville and Weymouth wharves, as well as the New Edinburgh lobster pound. The motion for the injunction was filed ex parte due to the urgency of the situation, as the band was struggling to sell any of their catch in the midst of the violence and protests. The injunction will remain in place until December 15, 2020.[71]
In January 2021, 23 people were charged in connection to the violence at the lobster storage facilities on October 13, 2020: 15 for break-and-enter and 8 for break-and-enter and mischief.[66] Their court date was set for March 29, 2021.[72]
Intimidation over the fishery dispute has continued into 2021. In mid-January, lobster harvester and Sipekne'katik citizen Jolene Marr, whose brother was surrounded in the West Pubnico lobster pound on October 13, was sent a seven second-long close-up video of a man's face that included what "sounds like a racial slur and six gunshots in the background."[72]
Legal action
[edit]On March 26, 2021, 43 Mi'kmaq lobster fishers from the Sipekne'katik First Nation filed a statement of claim against the attorney general of Canada, the RCMP, the DFO, and 29 non-Indigenous fishers including the Bay of Fundy Inshore Fishermen's Association (BFIFA). The claim alleges that the non-Indigenous fishers named as defendants took the law into their own hands and engaged in violence against the moderate livelihood fishery, that they were encouraged to do so by BFIFA, and that the DFO and RCMP contributed to the harm by not intervening in the foreseeable violence.[73]
Talks with DFO
[edit]On October 23, 2020, the Mi'kmaq Rights Initiative (known as the KMKNO for "Kwilmu'kw Maw-klusuaqn Negotiation Office") announced that talks with the DFO over defining "moderate livelihood" had broken down. The following Wednesday (October 28), Terry Paul, chief of Membertou First Nation, stepped down from his position with KMKNO and the Assembly of Nova Scotia Mi'kmaq Chiefs, saying "[his] confidence in the operations of the organization [sic] have weakened over time," citing issues of transparency, and preferring to pursue treaty rights negotiations outside of the Assembly.[63] Membertou's withdrawal follows Sipekne'katik's own withdrawal earlier in the month on October 6, leaving the Assembly as a representative of 10 of the 13 Mi'kmaq First Nation bands (Millbrook having also withdrawn earlier). According to Paul, when he talked with the other ANSMC Chiefs about his decision, there seemed to be a willingness to deal with the issues he had identified in the negotiation process, so that he could rejoin shortly.[74]
Fisheries Minister Bernadette Jordan sent a letter to Chief Mike Sack on March 3, 2021, outlining the terms under which a moderate livelihood fishery could be negotiated, and what the federal government would be "prepared" to allow; the letter proposed balancing "additional First Nations access through already available licences" and stated that "these fisheries will operate within established seasons." These terms were rejected by Chief Sack, who stated that "we have a management plan that is better for conservation than theirs is, so we're going to follow our own plan."[75]
Truth and Reconciliation Commission
[edit]In 2005, Nova Scotian Mi'kmaw Nora Bernard led the largest class-action lawsuit in Canadian history, representing an estimated 79,000 survivors of the Canadian Indian residential school system. The Government of Canada settled the lawsuit for upwards of CA$5 billion.[76][77]: 190
In autumn 2011, there was an Indian Residential Schools Truth and Reconciliation Commission that travelled to various communities in Atlantic Canada, who were all served by the Shubenacadie Indian Residential School, the sole residential school for the region. In his 2004 book entitled Legacies of the Shubenacadie Residential School, journalist Chris Benjamin wrote about the "raw wounds" of Mi'kmaw children who attended the Shubenacadie institution in the period spanning over three decades, from 1930 to 1967.[77]: 195
Mi'kmaq Kina' matnewey
[edit]The first Mi'kmaq-operated school in Nova Scotia—the Mi'kmaq Kina' matnewey—[77]: 208 was established in 1982 he result of a collaboration between the Mi'kmaw community and the Nova Scotia government. The school is the most successful First Nation Education Program in Canada, according to Benjamin.[77]
By 1997, all Mi'kmaq on reserves were given the responsibility for their own education.[77]: 210 By 2014, there were 11 band-run schools in Nova Scotia,[77]: 211 and the province has the highest rate of retention of aboriginal students in schools in Canada.[77]: 211 More than half the teachers are Mi'kmaq.[77]: 211 From 2011 to 2012 there was a 25% increase in Mi'kmaw students going to university. Atlantic Canada has the highest rate of aboriginal students attending university in the country.[77]: 214 [78]
History
[edit]Pre-contact period
[edit]
In southwestern Nova Scotia, there is archaeological evidence that traces traditional land use and resources to at least 4,000 years.[79]: 23 [80][81] In Kejimkujik National Park and National Historic Site, there are canoe routes that have been used for thousands of years by Indigenous people travelling from the Bay of Fundy to the Atlantic ocean.[82] Research published in 1871 showed that some Mi’kmaq believed they had emigrated from the west, and then lived alongside the Kwēdĕchk.[83] According to Mi'kmaw traditions recorded by S. T. Rand, the Kwēdĕchk were the original inhabitants of the land.[84] The two tribes engaged in a war that lasted "many years", and involved the "slaughter of men, women, and children, and torture of captives", and the eventual displacement of the Kwēdĕchk by the victorious Mi'kmaq.[83]
In his Memorial University Masters thesis, Mi'kmaq elder Roger Lewis investigated how pre-contact Mi'kmaq populations had a reciprocal relationship with the environment that was reflected in subsistence fishing, hunting and gathering, as well as in settlement locations.[79]: 10 Lewis, who has held the position of ethnology curator at the Nova Scotia Museum in Halifax, since 2007[85] focused his MA research specifically on pre-contact fish weirs in southwestern Nova Scotia.[79]
In the chapter "Late Prehistory of the East Coast" in the Smithsonian's 1978 Handbook of North American Indians, archaeologist Dean Snow says that the fairly deep linguistic split between the Mi'kmaq and the Eastern Algonquians to the southwest suggests the Mi'kmaq developed an independent prehistoric cultural sequence in their territory. It emphasized maritime orientation, as the area had relatively few major river systems.[86]: 69 In the chapter "Early Indian-European Contact" in the 1978 Handbook, ethnologist T. J. Brasser, described how pre-contact small semi-nomadic bands of a few patrilineally related families indigenous people who lived in a climate unfavorable for agriculture, had subsisted on fishing and hunting. Developed leadership did not extend beyond hunting parties.[87]: 78 In the same 1978 Handbook, anthropologist Philip Bock described the annual cycle of seasonal movement of precontact Mi'kmaq. Bock wrote that the Mi'kmaq had lived in dispersed interior winter camps and larger coastal communities during the summer. The spawning runs of March began their movement to converge on smelt spawning streams. They next harvested spawning herring, gathered waterfowl eggs, and hunted geese. By May, the seashore offered abundant cod and shellfish, and coastal breezes brought relief from the biting black flies, deer flies, midges and mosquitoes of the interior. Autumn frost killed the biting insects during the September harvest of spawning American eels. Smaller groups would disperse into the interior where they hunted moose and caribou.[88][89] The most important animal hunted by the Mi'kmaq was the moose, which was used in every part: the meat for food, the skin for clothing, tendons and sinew for cordage, and bones for carving and tools. Other animals hunted/trapped included deer, bear, rabbit, beaver and porcupine.[90]
Braser described the first contact between the Mi'kmaq and early European fishermen.[87]: 79–80 These fishermen salted their catch at sea and sailed directly home with it, but they set up camps ashore as early as 1520 for dry-curing cod. During the second half of the century, dry curing became the preferred preservation method.[87]: 79–80 Brasser said that trading furs for European trade goods had changed Miꞌkmaw social perspectives. Desire for trade goods encouraged the men to devote a larger portion of the year away from the coast, trapping in the interior. Trapping non-migratory animals, such as beaver, increased awareness of territoriality. Trader preferences for good harbors resulted in greater numbers of Miꞌkmaq gathering in fewer summer rendezvous locations. This in turn encouraged their establishing larger bands, led by the ablest trade negotiators.[87]: 83–84
According to the Nova Scotia Museum, bear teeth and claws were used as decoration in regalia. The women used porcupine quills to create decorative beadwork on clothing, moccasins, and accessories. The weapon used most for hunting was the bow and arrow. The Mi'kmaq made their bows from maple. They ate fish of all kinds, such as salmon, sturgeon, lobster, squid, shellfish, and eels, as well as seabirds and their eggs. They hunted marine mammals such as porpoises, whales, walrus, and seals.[90]
Miꞌkmaw territory was the first portion of North America that Europeans exploited at length for resource extraction. Reports by John Cabot, Jacques Cartier, and Portuguese explorers about conditions there encouraged visits by Portuguese, Spanish, Basque, French, and English fishermen and whalers, beginning in the 16th century.
European fishing camps traded with Mi'kmaw fishermen, and trading rapidly expanded to include furs, according to Thomas B. Costain, (1885–1965), a journalist who wrote historical novels. By 1578, some 350 European ships were operating around the Saint Lawrence estuary. Most were independent fishermen, but increasing numbers were exploring the fur trade.[91]
17th and 18th centuries
[edit]Colonial wars
[edit]In the wake of King Philip's War between English colonists and Native Americans in southern New England (which included the first military conflict between the Mi'kmaq and New England), the Mi'kmaq became members of the Wapnáki (Wabanaki Confederacy), an alliance with four other Algonquian-language nations: the Abenaki, Penobscot, Passamaquoddy, and Maliseet.[92] The Wabanaki Confederacy was allied with the Acadian people.
Over a period of seventy-five years, during six wars in Mi'kma'ki, the Mi'kmaq and Acadians fought to keep the British from taking over the region (See the four French and Indian Wars as well as Father Rale's War and Father Le Loutre's War). France lost military control of Acadia in 1710 and political claim (apart from Cape Breton) by the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht with England.
But the Mi'kmaq were not included in the treaty, and never conceded any land to the British. In 1715, the Mi'kmaq were told that the British now claimed their ancient territory by the Treaty of Utrecht. They formally complained to the French commander at Louisbourg about the French king transferring the sovereignty of their nation when he did not possess it. They were informed that the French had claimed legal possession of their country for a century, on account of laws decreed by kings in Europe, that no land could be legally owned by any non-Christian, and that such land was therefore freely available to any Christian prince who claimed it. Mi'kmaw historian Daniel Paul observes that, "If this warped law were ever to be accorded recognition by modern legalists they would have to take into consideration that, after Grand Chief Membertou and his family converted to Christianity in 1610, the land of the Mi'kmaq had become exempt from being seized because the people were Christians. However, it's hard to imagine that a modern government would fall back and try to use such uncivilized garbage as justification for non-recognition of aboriginal title."[30]: 74–75
Along with Acadians, the Mi'kmaq used military force to resist the founding of British (Protestant) settlements by making numerous raids on Halifax, Dartmouth, Lawrencetown, and Lunenburg. During the French and Indian War, the North American front of the Seven Years' War between France and Britain in Europe, the Mi'kmaq assisted the Acadians in resisting the British during the Expulsion. The military resistance was reduced significantly with the French defeat at the Siege of Louisbourg (1758) in Cape Breton. In 1763, Great Britain formalized its colonial possession of all of Miꞌkmaki in the Treaty of Paris.
Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties
[edit]
Between 1725 and 1779, the Mi'kmaq, Wolastoqey (Maliseet), and Peskotomuhkati (Passamaquoddy) signed numerous treaties, commonly referred to as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties, through which they entered into a "peaceful relationship with the British Crown." The Mi'kmaq assert that through these treaties—which were referenced as legal precedent by the Supreme Court of Canada in R v Marshall—the Mi'kmaq "did not cede or give up their land title and other rights."[11]
Some historians have asserted that first treaty signed in 1725, after Father Rale's War, did not cede hunting, fishing, and gathering rights.[93] The Halifax Treaties (1760–61), marked the end of warfare between the Mi'kmaq and the British.[94]
The 1752 Peace and Friendship Treaty Between His Majesty the King and Jean-Baptiste Cope,[18] on behalf of the Shubenacadie Mi'kmaq has been cited in the Supreme Court of Canada's 1985 decision in R. v. Simon.[18] In his 2002, book on the Marshall case, historian William Wicken said that there is no written documentation to support this assertion that Cope made the treaty on behalf of all the Miꞌkmaq.[95] : 184 has been cited in the Supreme Court of Canada's 1985 decision in R. v. Simon.[18] With the signing of various treaties, the 75 years of regular warfare ended in 1761 with the Halifax Treaties.[96][97]
Although the treaties of 1760–61 contain statements of Mi'kmaw submission to the British crown, later statements made by Miꞌkmaw reveal that they intended a friendly and reciprocal relationship, according to the 2009 book, Nova Scotia: a pocket history, by Saint Mary's University history professor, John G. Reid and Brenda Conroy.[98]: 23 In the early 1760s, there were approximately 300 Mi'kmaw fighters in the region and thousands of British soldiers. The goals of the Mi'kmaw treaty negotiators engaged in the 1760 Halifax treaty negotiations, were to make peace, establish secure and well-regulated trade in commodities such as furs, and begin an ongoing friendship with the British crown. In return, the Mi'kmaq offered friendship and tolerance of limited British settlement, although without any formal land surrender, according to Reid and Connor.[98]: 23 To fulfill the reciprocity intended by the Mi'kmaq, that any additional British settlement of land would have to be negotiated, and accompanied by giving presents to the Mi'kmaq. The documents summarizing the peace agreements failed to establish specific territorial limits on the expansion of British settlements, but assured the Mi'kmaq of access to the natural resources that had long sustained them along the regions' coasts and in the woods.[98] Their conceptions of land use were quite different. In his 2003 book about the British expulsion of the Acadians, University of Cincinnati history professor, Geoffrey Plank, described the relationship between the Mi'kmaq and Acadians as strong. The Mi'kmaq believed they could share their traditional lands with both the British and the Acadians—with the Mi'kmaq hunting as usual, and getting to the coast for seafood.[99]: 163
The arrival of the New England Planters and United Empire Loyalists in greater number put pressure on land use and the treaties. This migration into the region created significant economic, environmental and cultural pressures on the Mi'kmaq. The Mi'kmaq tried to enforce the treaties through threat of force. At the beginning of the American Revolution, many Mi'kmaw and Maliseet tribes supported the Americans against the British. They participated in the Maugerville Rebellion and the Battle of Fort Cumberland in 1776. Mi'kmaw delegates concluded the first international treaty, the Treaty of Watertown, with the United States soon after it declared its independence in July 1776. These delegates did not officially represent the Mi'kmaw government, although many individual Mi'kmaq did privately join the Continental Army as a result. In June 1779, Mi'kmaq in the Miramichi valley of New Brunswick attacked and plundered some of the British in the area. The following month, British Captain Augustus Harvey, in command of HMS Viper, arrived and battled with the Mi'kmaq. One Mi'kmaw was killed and 16 were taken prisoner to Quebec. The prisoners were eventually taken to Halifax. They were released on 28 July 1779 after signing the Oath of Allegiance to the British Crown.[100][101][102]
As their military power waned in the beginning of the 19th century, the Mi'kmaw people made explicit appeals to the British to honor the treaties and reminded them of their duty to give "presents" to the Mi'kmaq in order to occupy Mi'kma'ki. In response, the British offered charity or, the word most often used by government officials, "relief". The British said the Mi'kmaq must give up their way of life and begin to settle on farms. Also, they were told they had to send their children to British schools for education.[103]

Gabriel Sylliboy was the first Mi'kmaw elected as grand chief in 1919 and the first to fight for treaty recognition—specifically, the Treaty of 1752—in the Supreme Court of Nova Scotia.
In 1986, the first Treaty Day was celebrated by Nova Scotians on October 1, 1986 in recognition of the treaties signed between the British Empire and the Mi'kmaw people.
The treaties were only formally recognized by the Supreme Court of Canada once they were enshrined in Section 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982. The first Treaty Day occurred the year after the Supreme Court upheld the Peace Treaty of 1752 signed by Jean-Baptiste Cope and Governor Peregrine Hopson.
19th century
[edit]Royal Acadian School
[edit]Walter Bromley was a British officer and reformer who established the Royal Acadian School and supported the Mi'kmaq over the thirteen years he lived in Halifax (1813–1825).[104] Bromley devoted himself to the service of the Miꞌkmaw people.[105] The Mi'kmaq were among the poor of Halifax and in the rural communities. According to historian Judith Finguard, his contribution to give public exposure to the plight of the Mi'kmaq "particularly contributes to his historical significance". Finguard writes:
Bromley's attitudes towards the Indians were singularly enlightened for his day. ... Bromley totally dismissed the idea that native people were naturally inferior and set out to encourage their material improvement through settlement and agriculture, their talents through education, and their pride through his own study of their languages.[104]
Mi'kmaq Missionary Society
[edit]Silas Tertius Rand in 1849 help found the Mi'kmaq Missionary Society, a full-time Mi'kmaw mission. Basing his work in Hantsport, Nova Scotia, where he lived from 1853 until his death in 1889, he travelled widely among Mi'kmaw communities, spreading the Christian faith, learning the language, and recording examples of the Mi'kmaw oral tradition. Rand produced scriptural translations in Mi'kmaq and Maliseet, compiled a Mi'kmaq dictionary and collected numerous legends, and through his published work, was the first to introduce the stories of Glooscap to the wider world. The mission was dissolved in 1870. After a long period of disagreement with the Baptist church, he eventually returned to the church in 1885.
Mi'kmaq hockey sticks
[edit]
The Miꞌkmaq practice of playing ice hockey appeared in recorded colonial histories from as early as the 18th century. Since the nineteenth century, the Mi'kmaq were credited with inventing the ice hockey stick.[106]: 60 The oldest known hockey stick was made between 1852 and 1856. Recently, it was sold for US$2.2 million. The stick was carved by Miꞌkmaq from Nova Scotia, who made it from hornbeam, also known as ironwood.[107]
In 1863, the Starr Manufacturing Company in Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, began to sell the Mic-Mac hockey sticks nationally and internationally.[106]: 61 Hockey became a popular sport in Canada in the 1890s.[106]: 58 Throughout the first decade of the 20th century, the Mic-Mac hockey stick was the best-selling hockey stick in Canada. By 1903, apart from farming, the principal occupation of the Mi'kmaq on reserves throughout Nova Scotia, and particularly on the Shubenacadie, Indian Brook, and Millbrook Reserves, was producing the Mic-Mac hockey stick.[106]: 61 The department of Indian Affairs for Nova Scotia noted in 1927 that the Mi'kmaq remained the "experts" at making hockey sticks.[106]: 73 The Mi'kmaq continued to make hockey sticks until the 1930s, when the product was industrialized.[106]: 63
Gallery of 19th century images
[edit]- Grand Chief Jacques-Pierre Peminuit Paul (3rd from left with beard) meets Governor General of Canada, Marquess of Lorne, Red Chamber, Province House, Halifax, Nova Scotia, 1879.[108]
- Miꞌkmaq encampment, Sydney, Cape Breton Island
- Miꞌkmaq People (1873)
- Miꞌkmaq people (1865)
20th and 21st centuries
[edit]Jerry Lonecloud worked with historian and archivist Harry Piers to document the ethnography of the Mi'kmaw people in the early 20th century. Lonecloud wrote the first Mi'kmaw memoir, which his biographer entitled "Tracking Dr. Lonecloud: Showman to Legend Keeper".[109] Historian Ruth Holmes Whitehead writes, "Ethnographer of the Mi'kmaq nation could rightly have been his epitaph, his final honour."[110]
World Wars
[edit]Over 150 Mi'kmaw men signed up during World War I. During the First World War, thirty-four out of sixty-four male Mi'kmaq from Lennox Island First Nation, Prince Edward Island enlisted in the armed forces, distinguishing themselves particularly in the Battle of Amiens.[111] In 1939, over 250 Miꞌkmaq volunteered in World War II. (In 1950, over 60 Mi'kmaq enlisted to serve in the Korean War.)
Mi'kmaq of Newfoundland
[edit]When Newfoundland joined Canada in confederation in 1949, political leader (later Premier) Joey Smallwood declared that there were "no Indians in Newfoundland."[112] This ultimately led to the Mi'kmaq people of Newfoundland not receiving indian status or recognition as First Nations that other indigenous groups in Canada did in the years following.[112][113]
In 1972, activists formed the Native Association of Newfoundland and Labrador as the main organization representing the Mi'kmaq, Innu, and Inuit peoples of Newfoundland and Labrador.[114] After the Labrador Innu and Inuit left the Association in 1975, the organization was renamed as the Federation of Newfoundland Indians. The FNI included six Mi'kmaq bands (Elmastogoeg First Nations, Corner Brook Indian Band, Flat Bay Indian Band, Gander Bay Indian Band, Glenwood Mi'kmaq First Nation, and the Port au Port Indian Band). The provincial government supported the FNI.[115]
The federal government approved only the petition for recognition made by the Mi'kmaq at Conne River. In 1987, the Miawpukek Mi'kmaq First Nation was recognized under the Indian Act, and their community of Conne River was classified as reserved land for the Mi'kmaq.[116]
Recognition for the remainder of Newfoundland's Mi'kmaq was a much longer process. Minister David Crombie was willing to work with the FNI and the government of Newfoundland, but the provincial government considered it to be a federal matter.[115]
In 2003, Minister Andy Scott was presented with a report recommending a First Nations band without any reserved land to represent the Mi'kmaq of Newfoundland. An Agreement-in-principle was reached in 2006, which the FNI accepted in 2007. The federal government ratified it in 2008.[117]
In 2011, the Government of Canada announced recognition by an order-in-council to a group in Newfoundland and Labrador called the Qalipu First Nation. The new band, which is landless, had accepted 25,000 applications to become part of the band by October 2012.[118] In total over 100,000 applications were sent in to join the Qalipu, equivalent of one-fifth of the province's population. In response, parliament passed Bill C-25, authorizing it to review all applications and retroactively reject some, based on criteria similar to those used in the R v Powley case that defined rights for the Métis people.[119][120][121][122] Several Mi'kmaw institutions, including the Grand Council, had argued that the Qalipu Miꞌkmaq Band did not have legitimate aboriginal heritage and was accepting too many members.[123][124][125]
In 2017, only 18,044 people were eligible for Band membership.[122][126] In 2018, the Qalipu First Nation announced that the updated Founding Members List for the Band had been adopted by way of an Order in Council which came into effect on June 25, 2018. The 2018 Band list included 18,575 members.[127] In November 2019, after concerns about legitimacy had been addressed, the Qalipu First Nation was accepted by the Mi'kmaq Grand Council as being part of the Mi'kmaq Nation. Qalipu Chief Mitchell stated, "Our inclusion into the AFN, APC and acknowledgement by the Mi'kmaq Grand Council are important to us; it is part of our reconciliation as Mi'kmaq people. Friendships are being formed, and relationships are being established. It is a good time for the Qalipu First Nation."[128] By 2021, nearly 24,000 people were recognized as founding members, in 67 Newfoundland communities and abroad.[129]
The Friends of Qalipu Advocacy Association is currently[when?] taking Qalipu First Nation (and its precursor) to court over the enrolment process.[130]
Religion, spirituality, and tradition
[edit]
Current forms of Mi'kmaw faith
[edit]Some Mi'kmaw people practice the Catholic faith while some only practice traditional Mi'kmaw beliefs. However, many have adopted both because of the compatibility between both systems.[131]
Oral traditions in Mi'kmaw culture
[edit]The Mi'kmaw people had very little in the way of physical recording and storytelling; petroglyphs, while used, are believed to have been rare. In addition, it is not believed that pre-contact Mi'kmaq had any form of written language. As such, almost all of Mi'kmaw traditions were passed down orally, primarily via storytelling. There were traditionally three levels of oral traditions: religious myths, legends, and folklore. This includes Mi'kmaw creation stories and myths which account for the organization of the world and society; for instance, how men and women were created and why they are different from one another. The most well known Mi'kmaw myth is that of Glooscap. Good storytellers are highly prized by the Mi'kmaq,[132] as they provide important teachings that shape who a person grows to be, and are sources of great entertainment.
One myth explains that the Mi'kmaq once believed that evil and wickedness among men is what causes them to kill each other. This causes great sorrow to the creator-sun-god, who weeps tears that become rains sufficient to trigger a deluge. The people attempt to survive the flood by traveling in bark canoes, but only a single old man and woman survive to populate the earth.[133]
Spiritual sites
[edit]One spiritual capital of the Mi'kmaq Nation is Mniku, the gathering place of the Mi'kmaw Grand Council or Santé Mawiómi, Chapel Island in Bras d'Or Lake of Nova Scotia. The island is also the site of the St. Anne Mission, an important pilgrimage site for the Mi'kmaq.[131] The island has been declared a historic site.[134]
Ethnobotany
[edit]Abies balsamea (balsam fir) is traditionally used for a variety of purposes by the Mi'kmaq. They use the buds, cones and inner bark for diarrhea; the gum for burns, colds, fractures, sores and wounds; the cones for colic; the buds as a laxative; and the bark for gonorrhea.[135] They use the boughs to make beds, the bark to make a beverage, and the wood for kindling and fuel.[136]
First Nation subdivisions
[edit]Mi'kmaw names in the following table are spelled according to several orthographies. The Mi'kmaw orthographies in use are Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing, the orthography of Silas Tertius Rand, the Pacifique orthography, and the most recent Smith-Francis orthography. The latter has been adopted throughout Nova Scotia and in most Mi'kmaw communities.
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Population | Verification |
|---|---|---|
| 1500 | 4,500 | Estimation |
| 1600 | 3,000 | Estimation |
| 1700 | 2,000 | Estimation |
| 1750 | 3,000[168] | Estimation |
| 1800 | 3,100 | Estimation |
| 1900 | 4,000 | Census |
| 1940 | 5,000 | Census |
| 1960 | 6,000 | Census |
| 1972 | 10,000 | Census |
| 1998 | 15,000 | SIL |
| 2006 | 20,000 | Census |
| 2021 | 66,748 | Census |
The pre-contact population is estimated at 3,000–30,000.[169] In 1616, Father Biard believed the Mi'kmaw population to be in excess of 3,000, but he remarked that, because of European diseases, there had been large population losses during the 16th century. Smallpox and other endemic European infectious diseases, to which the Mi'kmaq had no immunity, wars and alcoholism led to a further decline of the native population. It reached its lowest point in the middle of the 17th century. Then the numbers grew slightly again, before becoming apparently stable during the 19th century. During the 20th century, the population was on the rise again. The average growth from 1965 to 1970 was about 2.5%.
Commemorations
[edit]The Mi'kmaw people have been commemorated in numerous ways, including HMCS Mi'kmaq (R10), and place names such as Lake Mi'kmaq, and the Mic Mac Mall.[170]
Notable Mi'kmaq
[edit]Academics
[edit]- Pamela Palmater, professor at Toronto Metropolitan University
- Marie Battiste, professor at the University of Saskatchewan
Activists
[edit]- Anna Mae Aquash, activist (1946–1976)
- J. Kevin Barlow, health campaigner
- Nora Bernard, Canadian Indian residential school system activist
- Donald Marshall, Jr., wrongly convicted of murder; later, fought for Mi'kmaq fishing rights
- Daniel N. Paul, elder, author, tribal historian, columnist, and human rights activist
- Gabriel Sylliboy, Grand Chief of the Mi'kmaq Nation, 1918 to 1964
Artists
[edit]- Rita Joe, poet
- Ursula Johnson, visual artist
- Nikki Gould, actress, Degrassi: Next Class
- Bretten Hannam, screenwriter and film director
- Amanda Peters, writer
- Morgan Toney, folk singer-songwriter and fiddler
- Jeff Barnaby, film director and screenwriter
- Cody Bowles, drummer, lead singer-Crown Lands
Athletes
[edit]- Patti Catalano, marathon runner
- Jahkeele Marshall-Rutty, soccer player
- Sandy McCarthy, played for the Calgary Flames ice hockey team
- Everett Sanipass, played for the Quebec Nordiques ice hockey team and the Chicago Blackhawks NHL team.
Military
[edit]- Étienne Bâtard (18th century)
- Chief Jean-Baptiste Cope
- Sam Gloade
- Paul Laurent[171]
Other
[edit]- Peter Paul Toney Babey, a Mi'kmaw chief and medical practitioner in the 1850s
- Elsie Charles Basque, first Mi'kmaw to earn a teaching certificate and recipient of the Order of Canada
- Brian Francis, Senator of Canada
- Judge Timothy Gabriel, first Mi'kmaw judge in Nova Scotia[172]
- Indian Joe, a scout around the time of the American Revolutionary War
- Noel Jeddore, Saqmaw forced into exile (1865–1944)[173]: 5 [174]: 33 [175]: 163
- Henri Membertou, grand chief and spiritual leader (c. 1525–1611)
- Lawrence Paul, a chief of Millbrook First Nation
Maps
[edit]Maps showing the approximate locations of areas occupied by members of the Wabanaki Confederacy (from north to south):
- Eastern Abenaki (Penobscot, Kennebec, Arosaguntacook, Pigwacket/Pequawket
- Western Abenaki (Arsigantegok, Missisquoi, Cowasuck, Sokoki, Pennacook
See also
[edit]- Algonquian peoples
- List of grand chiefs (Mi'kmaq)
- Military history of the Mi'kmaq
- Mi'kmaq History Month
- Mi'kmaq language
- Silas Tertius Rand
- Tarrantine
- Qalipu Miꞌkmaq First Nation Band
Notes
[edit]- ^ Anne-Christine Hornbord is a Lund University professor of history of religions; she conducted fieldwork on reservations of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, and Canada in 1992–1993, 1996 and 2000.
- ^ "It is now the preferred choice of our People." See Paul:2000.
- ^ "The definite article "the" suggests that "Mi'kmaq" is the undeclined form indicated by the initial letter "m". When declined in the singular, it reduces to the following forms: nikmaq – my family; kikmaq – your family; wikma – his/her family. The variant form Mi'kmaw plays two grammatical roles: 1) It is the singular of Mi'kmaq and 2) it is an adjective in circumstances where it precedes a noun (e.g., mi'kmaw people, mi'kmaw treaties, miꞌkmaw person, etc.)" see Mi'kmaw Resource Guide, Eastern Woodlands Publishing (1997).
- ^ CBC News reported that, "In 'Marshall 2,' the supreme court ruled that governments must justify restrictions or regulations on treaty rights based on previous, legally-tested criteria including "a valid legislative objective" such as conservation, "whether there has been as little infringement as possible" on rights, and "whether the aboriginal group in question has been consulted" on the government's proposed restrictions."
- ^ In Ahousaht Indian Band and Nation v. Canada, a Supreme Court case that spanned over a decade, the Ahousaht Indian Band and Nation in British Columbia confirmed their right to "fish in their court-defined territories and sell that fish into the commercial marketplace."
References
[edit]- ^ "Mi'kmaq Grand Council Flag".
- ^ "Various Mi'kmaq flags and their meanings".
- ^ "Aboriginal Ancestry Responses (73)". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Government of Canada. October 25, 2017. Retrieved November 23, 2017.
- ^ "Native Languages of the Americas: Mi'kmaq Language (Mi'kmaw, Micmac, Mikmaq, Mikmak)". Native-Languages.org. Retrieved October 31, 2018.
- ^ Lockerby, Earle (2004). "Ancient Miꞌkmaq Customs: A Shaman's Revelations" (PDF). The Canadian Journal of Native Studies. 24 (2): 403–423. see page 418, note 2
- ^ Sock, S., & Paul-Gould, S. (2011). Best Practices and Challenges in Miꞌkmaq and Maliseet/Wolastoqi Language Immersion Programs.
- ^ Gallant, David Joseph (2008). "Mi'kmaq". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Retrieved July 23, 2023.
- ^ "Programs and Services". Qalipu.ca.
- ^ "Thousands of Qalipu Mi'kmaq applicants rejected again", CBC, Dec 08, 2017.
- ^ a b Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (February 9, 2022). "Profile table, Census Profile, 2021 Census of Population – Canada [Country]". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved June 14, 2023.
- ^ a b Bernard, Tim; Rosenmeier, Leah Morine; Farrell, Sharon L., eds. (2015). Mi'kmawe'l Tan Teli-kina'muemk Teaching About the Mi'kmaq (PDF). The Mi'kmawey Debert Cultural Centre. p. 106.
- ^ a b Bundale, Brett (October 18, 2020). "N.S. calls on Ottawa to define a 'moderate livelihood,' as fishing dispute boils over". Atlantic. Retrieved October 18, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f "Miꞌkmaq of Nova Scotia, Province of Nova Scotia and Canada Sign Landmark Agreement" (Press release). Indian and Northern Affairs Canada and Government of Nova Scotia – Aboriginal Affairs. Retrieved August 31, 2021.
- ^ Julien, Donald M. (October 2007). Kekina'muek (learning)Learning about the Mi'kmaq of Nova Scotia (PDF). Eastern Woodland Print Communication. p. 11. Retrieved February 21, 2020.
- ^ a b "Mi'kmaq Historical Overview". Cape Breton University. Retrieved February 21, 2020.
- ^ Julien, Donald M. (October 2007). Kekina'muek (learning)Learning about the Mi'kmaq of Nova Scotia (PDF). Eastern Woodland Print Communication. p. 11. Retrieved February 21, 2020.
- ^ a b c d Weeks, Joan (February 16, 2017). "9 decades after hunting conviction, Mi'kmaq leader gets posthumous pardon". CBC. Nova Scotia. Retrieved October 21, 2020.
- ^ a b c d "1752 Peace and Friendship Treaty", Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada, Government of Canada, Treaty Texts, November 3, 2008, retrieved October 18, 2020
- ^ a b c Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Mi'kmaq Hieroglyphic Prayers: Readings in North America's First Indigenous Script. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus. pp. 6–7. ISBN 1-55109-069-4.
- ^ Thwaites, Ruben G. (1959). The Jesuit Relations and Allied Documents: Travel and Explorations of the Jesuit Missions in New France, 1610–1791 (Vol. 38 ed.). Cleveland: Burrows Bros. p. 27.
- ^ a b c Cave, Beverley (September 2005). The Petroglyphs of Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia: A Fresh Perspective on their Physical and Cultural Contexts (PDF). Memorial University (Thesis). Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Whitehead, Ruth Holmes; Dennis, Clara; Lonecloud, Jerry (2002). Tracking Doctor Lonecloud: showman to legend keeper. Fredericton, N.B. : Halifax, N.S: Goose Lane Editions via Nova Scotia Museum. ISBN 978-0-86492-356-1.
- ^ Dubé, Alexandre (2003). "Tradition, Change and Survival: Mi'kmaq Tourist Art". McCord Museum. Archived from the original on October 21, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Mi'kmaq Hieroglyphic Prayers: Readings in North America's First Indigenous Script. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus. pp. 8–9. ISBN 1-55109-069-4.
- ^ Kauder, Christian (1866). Buch das Gut, enthaltened den Katechismus. Wien [Vienna: Die Kaiserliche wie auch Königliche Buchdruckerei hat es gedruckt. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ a b c Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Mi'kmaq hieroglyphic prayers: readings in North America's first indigenous script. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus Pub. ISBN 978-1-55109-069-6.
- ^ Hornborg, Anne-Christine (2008). Mi'kmaq landscapes: from animism to sacred ecology. Vitality of indigenous religions series. Aldershot, England ; Burlington, VT: Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-6371-3.
- ^ a b Metallic, Emmanuel N; Cyr, Danielle E; Sévigny, Alexandre (2005). The Metallic Mìgmaq-English reference dictionary. Sainte-Foy, Québec: Presses de l'Université Laval/IQRC. ISBN 978-2-7637-8015-3.
- ^ "The use of the terms Mi'kmaq and Mi'kmaw" (PDF). Office of L’nu Affairs. Government of Nova Scotia.
- ^ a b Paul, Daniel N. (2000). We Were Not the Savages: A Miꞌkmaq Perspective on the Collision Between European and Native American Civilizations (2nd ed.). Fernwood. ISBN 978-1-55266-039-3.
- ^ "Mi'kmaq Portraits Collection". Nova Scotia Museum. Retrieved January 12, 2024.
- ^ Johnston, A. J. B. (2013). Niꞌn na L'nu: The Miꞌkmaq of Prince Edward Island. Acorn Press. p. 96.
- ^ Lydia Affleck; Simon White. "Our Language". Native Traditions. Archived from the original on December 16, 2006. Retrieved November 8, 2006.
- ^ Mi'kmaw Resource Guide, Eastern Woodlands Publishing (1997)
- ^ Weshki-ayaad, Lippert, Gambill (2009). Freelang Ojibwe Dictionary
- ^ a b c d e f g Robertson, Marion (2006). Red earth: tales of the Micmac with an introduction to the customs and beliefs of the Micmac (2 ed.). Halifax: Nimbus Publisher. p. 98. ISBN 978-1-55109-575-2.
- ^ Jeddore, John Nick (August 25, 2011). "There were no Indians here ..." TheIndependent.ca.
- ^ a b c d "Factsheet: The 1999 Supreme Court of Canada Marshall Decision", Fisheries and Oceans Canada, November 20, 2019, retrieved October 18, 2020
- ^ a b c Pannozzo, Linda; Baxter, Joan (October 5, 2020). "Lobster fishery at a crossroads". Halifax Examiner. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ a b c "Maritime waters calm a decade after Marshall decision". CBC. September 17, 2009. Retrieved October 18, 2020.
- ^ a b McMillan, L. Jane (2018). Truth and conviction: Donald Marshall Jr. and the Mi'kmaw quest for justice. Law and society series. Vancouver ; Toronto: UBC Press. ISBN 978-0-7748-3748-4.
- ^ Digest of Findings and Recommendations (PDF). Royal Commission on the Donald Marshall, Jr. Prosecution (Report). 1989. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Meloney, Nic (September 19, 2020). "Mi'kmaq tackle decades-old standstill on fishing rights with historic, self-regulated lobster fishery". CBC. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ CBC News (October 4, 1999). "Fishermen square off as tempers flare". CBC News. Retrieved April 9, 2024.
- ^ a b c d "CBC News In-depth: Fishing". May 9, 2004. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ a b Obomsawin, Alanis (Director) (2002). Is the Crown at war with us?. Event occurs at 1:36:35. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ a b Wappel, Tom (November 2003). Report Of The Standing Committee On Fisheries And Oceans, May 2003, Atlantic Fisheries Issues (Report). Ottawa, Ontario: Report Of The Standing Committee On Fisheries And Oceans, House Of Commons.
- ^ "Listuguj impatient with failure to define 'moderate livelihood' in fishery". CBC. September 24, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ "Fish Buyers' Licensing and Enforcement Regulations via Fisheries and Coastal Resources Act (Nova Scotia)". 2001. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ a b c d Meloney, Nic (September 25, 2020). "Mi'kmaq push for legal lobster sales for non-Indigenous buyers". CBC News. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ a b Googoo, Maureen (October 5, 2020). "Nova Scotia chiefs rejected $87-million offer from DFO, want moderate livelihood defined". Ku'ku'kwes News. Retrieved October 21, 2020.
- ^ Moore, Angel (January 26, 2021). "The deal is sealed, Mi'kmaq coalition partner with B.C company to buy seafood giant Clearwater". APTN National News. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ Morin, Brandi (December 31, 2020). "Twenty Indigenous stories that shaped 2020 — a year of racism and fear, of fighting and hope". The Star. Retrieved December 31, 2020.
- ^ Slaughter, Graham (October 20, 2020). "Mi'kmaq lobster dispute: A conflict brewing since the 1700s". CTVNews. Toronto.
- ^ a b c Roache, Trina; Moore, Angel (October 18, 2020). "Fisheries conflict: Mi'kmaw Chiefs declare state of emergency". APTN News. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Implementing the right to fish in pursuit of a moderate livelihood: Rebuilding trust and establishing a constructive path forward. Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Government of Canada (Report). Final report by the Federal Special Representative. April 29, 2021. Retrieved September 21, 2023.
- ^ Coates, Ken (October 2019). The Marshall Decision at 20: Two Decades of Commercial Re-Empowerment of the Mi'kmaq and Maliseet, Munk (PDF) (Report). Macdonald-Laurier Institute. p. 52.
- ^ a b c Smith, Emma Smith (September 22, 2020). "Scale of Sipekne'katik fishery won't harm lobster stocks, says prof". CBC. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Tress, Robin (October 15, 2020). "Trapped in Conflict: How the corporate megafishery Clearwater has set the stage for violent conflict in Mi'kma'ki". The Council of Canadians. Retrieved April 9, 2024.
- ^ Withers, Paul (October 6, 2020). "The lobster catch in St. Marys Bay is down, but there's little consensus on why". CBC. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Googoo, Maureen (September 15, 2020). "Sipekne'katik Chief calls on NS Premier, DFO, RCMP to protect Mi'kmaw harvesters' treaty rights". Ku'ku'kwes News. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ Googoo, Maureen (September 15, 2020). "Mi'kmaw harvesters confront protesters at wharf in southwestern Nova Scotia". Ku'ku'kwes News. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ a b c Moore, Angel (October 28, 2020). "Respected chief leaves two Mi'kmaw political organizations because of 'distrust' over moderate livelihood plans". APTN National News. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ Ryan, Hailey (October 5, 2020). "Mi'kmaw fishing vessel destroyed in suspicious fire at N.S. wharf". CBC News. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ Grant, Taryn (October 14, 2020). "Vehicle torched, lobster pounds storing Mi'kmaw catches trashed during night of unrest in N.S." CBC News. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ a b Moore, Angel (January 20, 2021). "Manager of Nova Scotia pound claims in online post that he 'opened the doors' for non-Indigenous fishers to take Mi'kmaw catch". APTN National News. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ a b c Young, Brandon; April, Allan (October 17, 2020). "Southwest N.S. lobster pound destroyed by fire, man in hospital with life-threatening injuries". CTV News. Retrieved October 17, 2020.
- ^ a b c Moore, Angel (October 16, 2020). "After a week of violence, Mi'kmaq Warrior Peacekeepers arrive at wharf in Nova Scotia". APTN National News. Retrieved October 17, 2020.
- ^ Boynton, Sean (October 17, 2020). "Massive fire destroys lobster pound in southern Nova Scotia". Global News. Retrieved October 17, 2020.
- ^ a b Woodford, Zane (October 20, 2020). "Lobsters quickly sell out in front of Nova Scotia legislature: 'They have a treaty right to buy from the Mi'kmaq". Halifax Examiner. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Forester, Brett; Moore, Angel; Pashagumskum, Jamie (October 21, 2020). "Mi'kmaq secure injunction against interference with treaty fishery". APTN National News. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ a b Moore, Angel (January 19, 2021). "Mi'kmaw lobster harvester fears for her safety after receiving online video". APTN National News. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ Moore, Angel (March 31, 2021). "Sipekne'katik First Nation lobster harvesters sue feds, non-Indigenous fishers". APTN National News. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ Googoo, Maureen (October 28, 2020). "Membertou latest First Nation to leave Assembly of NS Mi'kmaw Chiefs, KMKNO". Ku'ku'kwes News. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ Moore, Angel (March 3, 2021). "'We're going to establish our own fishery': Sipekne'katik First Nation rejects DFO moderate livelihood plan". APTN National News. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ "Police investigate death at Bernard's home". Halifax Daily News. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved November 10, 2018 – via Arnold Pizzo McKiggan.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Benjamin, Chris (2014). Indian school road: legacies of the Shubenacadie Residential School. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus Publishing. ISBN 978-1-77108-213-6.
- ^ "Number of Mi'kmaq graduates continues to rise | the Chronicle Herald". Archived from the original on October 26, 2014. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ^ a b c Lewis, Roger J (February 20, 2006). Pre-contact fish weirs: a case study from southwestern Nova Scotia (PDF) (Thesis). Ottawa: Library and Archives Canada. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Christianson, D. J. 1979. The Use of Subsistence Strategy Descriptions in Determining Wabanaki Residence Location. Journal of Anthropology at McMaster 5( 1 ).
- ^ Ferguson, R. 1986. Archaeological Sites of Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia. Unpublished Ms., Parks Canada , Halifax.
- ^ "Kejimkujik National Park and National Historic Site". Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ a b Elder, William (1871). The North American Review. Vol. 112, No. 230. p. 3.
- ^ Rand, Silas Tertius (1894). Legends of the Micmacs. New York and London: Longman, Green, and Co. p. 206.
- ^ "Roger Lewis". Nova Scotia Museum. April 8, 2013. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Snow, Dean R. (1978). "Late Prehistory of the East Coast: Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and Eastern New Brunswick Drainages". In Trigger, Bruce G. (ed.). Handbook of North American Indians. Northeast. Vol. 15. Smithsonian Institution Press.
- ^ a b c d Brasser, T.J. (1978). "Early Indian-European Contacts". In Trigger, Bruce G. (ed.). Handbook of North American Indians. Northeast. Vol. 15. Smithsonian Institution Press. pp. 78–88.
- ^ Bock, Philip K. (1978). "Micmac". In Trigger, Bruce G. (ed.). Handbook of North American Indians. Northeast. Vol. 15. Smithsonian Institution Press. pp. 109–122.
- ^ : 109–110
- ^ a b "The Nova Scotia Museum – Heritage Attractions across Nova Scotia". Archived from the original on January 25, 2007. Retrieved January 17, 2007.
- ^ Costain, Thomas B. (1954). The White and The Gold. Garden City, New York: Doubleday & Company. p. 54. ISBN 0385045263.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ The allied tribes occupied the territory which the French named Acadia. The tribes ranged from present-day northern and eastern New England in the United States to the Maritime Provinces of Canada. At the time of contact with the French (late 16th century), they were expanding from their maritime base westward along the Gaspé Peninsula /St. Lawrence River at the expense of Iroquoian-speaking tribes. The Mi'kmaq name for this peninsula was Kespek (meaning "last-acquired").
- ^ Nicholas, Andrea Bear. "Mascarene's treaty of 1725". University of New Brunswick Library Journals.
- ^ Patterson, Stephen (2009). "Eighteenth-Century Treaties:The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Passamaquoddy Experience" (PDF). Native Studies Review. 18 (1).
- ^ Wicken, William C. (2002). Miꞌkmaq Treaties on Trial: History, Land and Donald Marshall Junior. University of Toronto Press. ISBN 978-0-8020-7665-6.
- ^ According to historian Stephen Patterson, the British imposed the treaties on the Miꞌkmaq to confirm the British conquest of Miꞌkmaꞌki.
- ^ Patterson, Stephen (2009). "Eighteenth-Century Treaties:The Miꞌkmaq, Maliseet, and Passamaquoddy Experience" (PDF). Native Studies Review. 18 (1).
- ^ a b c Reid, John G.; Conroy, Brenda (2009). Nova Scotia: a pocket history. Halifax: Fernwood Pub. ISBN 978-1-55266-325-7.
- ^ Plank, Geoffrey Gilbert (2003). An unsettled conquest: the British campaign against the peoples of Acadia. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 256. ISBN 978-0-8122-0710-1.
- ^ Upton, L. F. S. (1983). "Julien, John". In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. V (1801–1820) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- ^ Sessional papers, Volume 5 By Canada. Parliament July 2 – September 22, 1779; Wilfred Brenton Kerr. The Maritime Provinces of British North America and the American Revolution], p. 96
- ^ Among the annual festivals of the old times, now lost, was the celebration of St. Aspinquid's Day; he was known as the Indian Saint. St. Aspinquid appeared in the Nova Scotia almanacks from 1774 to 1786. The festival was celebrated on or immediately after the last quarter of the moon in the month of May, when the tide was low. The townspeople assembled on the shore of the North West Arm and shared a dish of clam soup, the clams being collected on the spot at low water. There is a tradition that in 1786, soon after the American Revolutionary War, when there were threats of American invasion of Canada, agents of the US were trying to recruit supporters in Halifax. As people were celebrating St. Aspinquid with wine, they suddenly hauled down the Union Jack and replaced it with the Stars and Stripes [US flag]. This was soon reversed, but public officials quickly left, and St. Aspinquid was never after celebrated at Halifax. (See Akins. History of Halifax, p. 218, note 94)
- ^ Reid. p. 26
- ^ a b Fingard, Judith (1988). "Bromley, Walter". In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. VII (1836–1850) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- ^ Nova Scotia Historical Society; Nova Scotia Historical Society. Report and collections (1878). Collections of the Nova Scotia Historical Society. Halifax – via Internet Archive.
- ^ a b c d e f Cutherbertson, Brian (2005). "The Starr Manufacturing Company: Skate Exporter to the World". Journal of the Royal Nova Scotia Historical Society. 8.
- ^ "The Slingshot: Improving the Modern Hockey Stick". www.odec.ca. Archived from the original on June 10, 2015. Retrieved September 5, 2013.
- ^ "Explore the Royal Collection Online". www.rct.uk.
- ^ "New Book Features First Known Memoir of a Mi'kmaq" (Press release). Nova Scotia Museum. October 11, 2002.
- ^ Whitehead, Ruth Holmes (2005). "Lonecloud, Jerry". In Cook, Ramsay; Bélanger, Réal (eds.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. XV (1921–1930) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- ^ Sark, John Joe (December 2013). "In our words, stories of Veterans". Miꞌkmaq Maliseet Nations News.
- ^ a b Jeddore, John Nick (October 21, 2011). "Getting recognized". The Independent. Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ^ Contenta, Sandro (May 5, 2013). "In Newfoundland, too many want recognition as Mi'kmaq Indians, federal government says". The Toronto Star. Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ^ "The Mi'kmaq (Micmac)". Archived from the original on May 18, 2022. Retrieved March 28, 2022.
- ^ a b "Enrolment – Qalipu".
- ^ "About Miawpukek". Miawpukek Mi'kamawey Mawi'omi. Archived from the original on April 14, 2021. Retrieved October 16, 2020.
- ^ "Statement by the Honourable Chuck Strahl on the Ratification Vote by the Mi'kmaq of the Federation of Newfoundland Indians". Government of Canada. April 2008. Retrieved March 29, 2022.
- ^ "More than 60,000 applying for Mi'kmaq status". CBC News. October 4, 2012. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ Howells, Laura (March 27, 2016). "6,500 rejected Qalipu Mi'kmaq band applications to be reconsidered". CBC News. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ Newell, David (December 22, 2016). "Scrap Qalipu membership requirements, says Mi'kmaq association chair". CBC News. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ Hillier, Bernice (February 4, 2017). "Decision week for thousands of applicants to the Qalipu band". CBC News. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ a b Thomson, Aly (February 7, 2017). "About 80,000 denied eligibility for Newfoundland first nation band". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ^ Battiste, Jaimie. "Nova Scotia Chiefs Raise Concerns over Qalipu Miꞌkmaq Band" (PDF). mikmaqrights.com. Miꞌkmaq Rights Initiative. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 5, 2019. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ "Statement to United Nations Special Rapporteur Anaya" (PDF). Grand Council of Micmacs. October 4, 2013. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ Battiste, Jaime. "Defining Aboriginal Identity: What the Courts Have Stated" (PDF). Mikmaqrights.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 4, 2019. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ Connors, Colleen (December 8, 2017). "Thousands of Qalipu Mi'kmaq applicants rejected again". CBC News. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ "Updated Founding Members List for the Qalipu First Nation Adopted Through Order in Council – Qalipu". June 28, 2018.
- ^ "Qalipu First Nation to welcome special guests from Mi'kmaq Grand Council". Qalipu First Nation. November 7, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ^ Connors, Colleen (September 23, 2021). "Qalipu First Nation marks a milestone, celebrating 10 years as recognized Indigenous band". CBC News. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ Meloney, Nic (April 25, 2018). "Canada signed private agreement with Qalipu Mi'kmaq days before contentious changes to application process". Retrieved November 9, 2021.
- ^ a b Robinson, Angela (2005). Tán Teli-Ktlamsitasit (Ways of Believing): Míkmaw Religion in Eskasoni, Nova Scotia. Pearson Education. ISBN 0-13-177067-5.
- ^ "Mi'kmaq Spirit Home Page". www.muiniskw.org.
- ^ Canada's First Nations – Native Creation Myths Archived 2014-01-14 at the Wayback Machine, University of Calgary
- ^ CBCnews. Cape Breton Míkmaq site recognized
- ^ Chandler, R. Frank, Lois Freeman and Shirley N. Hooper, 1979, Herbal Remedies of the Maritime Indians, Journal of Ethnopharmacology 1:49–68, page 53
- ^ Speck, Frank G. and R.W. Dexter, 1951, Utilization of Animals and Plants by the Micmac Indians of New Brunswick, Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 41:250–259, page 258
- ^ "Registered Population: Abegweit". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Acadia". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Annapolis Valley". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Bear River". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Buctouche". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Eel River Bar". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Elsipogtog". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Esgenoopetitj". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Eskasoni". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Fort Folly". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Glooscap". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Indian Island". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: La Nation Micmac de Gespeg". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Lennox Island". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Listuguj Mi'gmaq Government". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Membertou". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Metepenagiag". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Aroostook Band of Micmacs". Mi'kmaq Nation. Presque Isle, ME. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Miawpukek". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Micmacs of Gesgapegiag". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Millbrook". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Natoaganeg". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Pabineau". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Paq'tnkek". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Pictou Landing". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Potlotek". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Qalipu". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^
- "Government of Canada Announces the Creation of the Qalipu First Nation Band". Marketwire. Retrieved July 31, 2020.
- "Press Release September 26, 2011". Reuters (Press release). Archived from the original on July 26, 2012. Retrieved July 31, 2020.
- ^ "Who We Are Today". Sipekne'katik. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: Wagmatcook". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. November 14, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ "Registered Population: We'koqma'q L'nue'kati". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. First Nation Profiles. Government of Canada. 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ^ Massachusetts Historical Society; John Davis Batchelder Collection (Library of Congress) (June 8, 1792). Collections of the Massachusetts Historical Society. Boston : The Society – via Internet Archive.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: publisher location (link) - ^ "Micmac". www.dickshovel.com.
- ^ Bates, George T. (1961). Megumaage: the home of the Micmacs or the True Men. A map of Nova Scotia.
- ^ Johnson, Micheline D. (1974). "Laurent, Paul". In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. III (1741–1770) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- ^ Sawler, Sarah (July 30, 2013). "50 Things You Don't Know About Halifax – Halifax Magazine". Halifax Magazine.
- ^ Tulk, Jamie Esther (July 2008), "Our Strength is Ourselves: Identity, Status, and Cultural Revitalization among the Miꞌkmaq in Newfoundland" (PDF), Memorial University via Collections Canada Theses, Newfoundland, retrieved August 5, 2008
- ^ Jeddore, Roderick Joachim (March 2000), "Investigating the restoration of the Miꞌkmaq language and culture on the First Nations reserve of Miawpukek" (PDF), University of Saskatchewan (Master's), Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, retrieved August 5, 2016
- ^ Jackson, Doug (1993). On the country: The Micmac of Newfoundland. St. John's, Newfoundland: Harry Cuff Publishing. ISBN 0921191804.
Further reading
[edit]- Davis, Stephen A. (1998). Míkmaq: Peoples of the Maritimes. Nimbus Publishing.
- Joe, Rita; Choyce, Lesley (2005). The Míkmaq Anthology. Nimbus Publishing. ISBN 1-895900-04-2.
- Johnston, A.J.B.; Francis, Jesse (2013). Niꞌn na L'nu: The Miꞌkmaq of Prince Edward Island. Charlottetown: Acorn Press. ISBN 978-1-894838-93-1.
- Magocsi, Paul Robert, ed. (1999). Encyclopedia of Canada's Peoples. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
- Prins, Harald E. L. (1996). The Míkmaq: Resistance, Accommodation, and Cultural Survival. Case Studies in Cultural Anthropology. Wadsworth.
- Speck, Frank (1922). Beothuk and Micmac.
- Whitehead, Ruth Holmes (2004). The Old Man Told Us: Excerpts from Míkmaq History 1500–1950. Nimbus Publishing. ISBN 0-921054-83-1.
Archival primary references
[edit]In chronological order
- 1749 A Geographic History of Nova Scotia. 1749
- 1758 Malliard, Antoine Simon (1758). An account of the customs and manners of the MicMakis and Marichetts Savage Nations.
- 1760 Thomas Picheon
- 1797 Miꞌkmaq Language, 1797
- 1814 Bromley, Walter (1814). Mr. Bromley's second address, on the deplorable state of the Indians delivered in the "Royal Acadian School," at Halifax, in Nova Scotia, March 8, 1814. [Halifax, N.S.?] : Printed at the Recorder Office. ISBN 9780665209987.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - 1822 Bromley, Walter (1822). An account of the aborigines of Nova Scotia called the Micmac Indians. London? : s.n. ISBN 9780665573224.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - 1819 Rand, Silas Tertius (1850). A short statement of facts relating to the history, manners, customs, language, and literature of the Micmac tribe of Indians, in Nova-Scotia and P.E. Island: being the substance of two lectures delivered in Halifax, in November, 1819, at public meetings held for the purpose of instituting a mission to that tribe. Halifax, N.S.? : s.n. ISBN 9780665395062.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - 1866 Vetromile, Eugene (1866). The Abnakis and their history: Historical notices on the aborigines of Acadia. New York : J.B. Kirker. ISBN 9780665339240.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - 1873 An account of the present state of Nova Scotia Hollingsworth. 1873
- Thomas Pichon on Miꞌkmaq
- 1896 Piers, Harry (1896). Relics of the stone age in Nova Scotia. S.l. : s.n. ISBN 9780665353376.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - Rand and the Mi'kmaqs
- 1922 Speck, Frank (1922). Beothuk and Micmac.
Documentary film
[edit]- Our Lives in Our Hands (1986) — Míkmaq basketmakers and potato diggers in northern Maine
External links
[edit]- Qalipu First Nation
- Benoit First Nation
- Bras D'Or First Nation
- Bras d'Or – Pitawpo'q, Indian name; Little Bras d'Or – Panu'skek, Indian name
- Mi'kmaq History
- Míkmaq Portraits Collection
- Mi'kmaq Language. Mass Historical Society
- Míkmaq Dictionary Online
- The Mi'kmaq of Megumaagee
- Míkmaq Learning Resource
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- Unama'ki Institute of Natural Resources
- Mi'kmaw Native Friendship Centre


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch![Grand Chief Jacques-Pierre Peminuit Paul (3rd from left with beard) meets Governor General of Canada, Marquess of Lorne, Red Chamber, Province House, Halifax, Nova Scotia, 1879.[108]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f0/Mik%27maq_at_Province_House%2C_Halifax%2CNS_1879.png/250px-Mik%27maq_at_Province_House%2C_Halifax%2CNS_1879.png)





